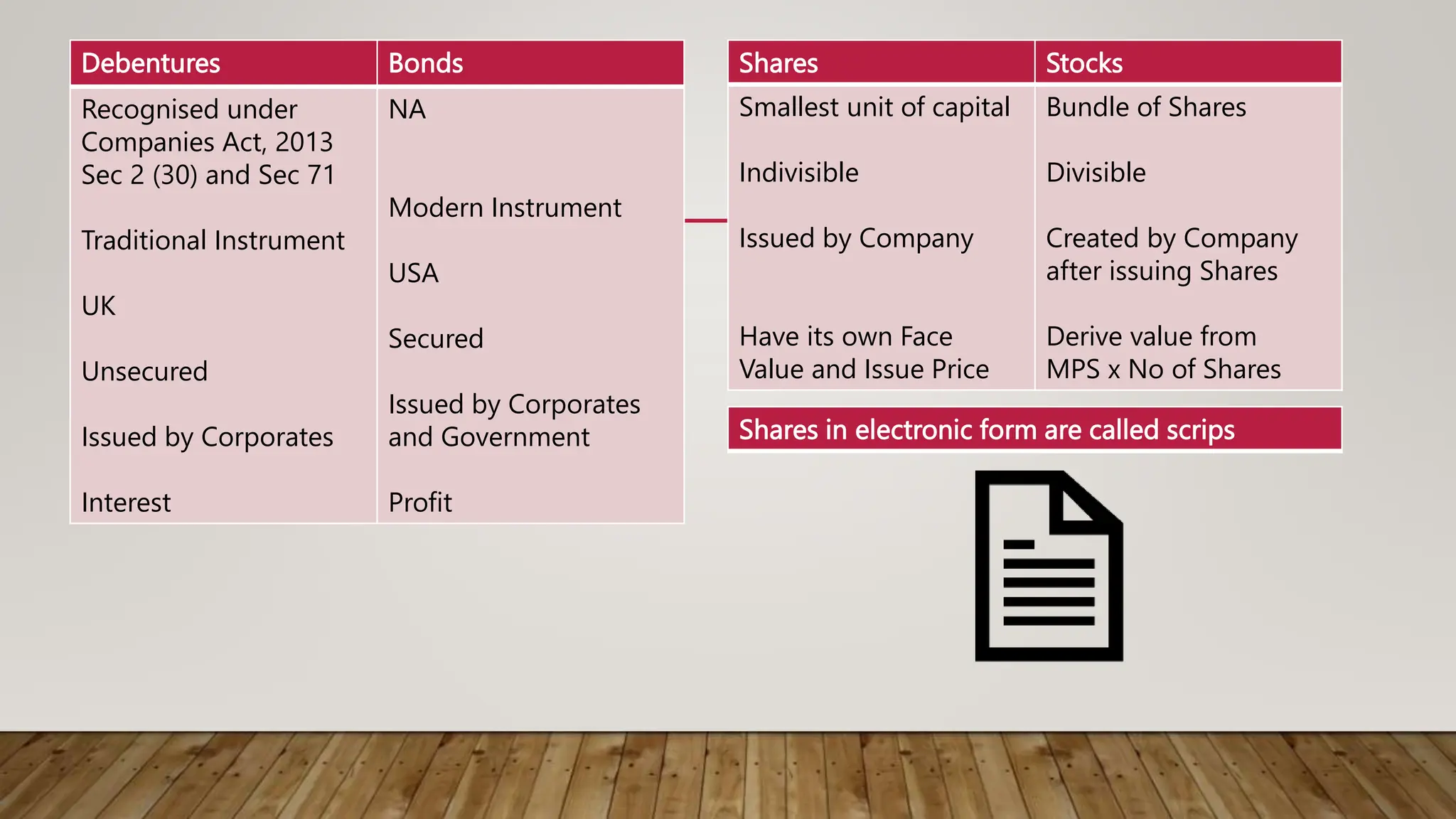
The document discusses the Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act of 1956, which provides the framework for regulation of stock exchanges and transactions in securities in India. Some key points:
- The Act was passed to provide recognition of stock exchanges by the Central Government and regulate their activities to ensure safety and protect investors.
- It defines terms related to securities and sets procedures for stock exchange recognition, company security listings, and broker operations regarding share purchases and sales.
- The objectives of the Act are to regulate stock exchanges and transactions, prevent undesirable speculation, and regulate off-exchange security transactions.
- It also discusses requirements for stock exchange recognition by the Central Government and conditions that may be imposed, such as membership














![PROCEDURE AND POWERS OF SECURITIES APPELLATE TRIBUNAL
• Section 228 stipulates that the Securities Appellate Tribunal shall not be bound by the procedure laid down by the
Code of Civil Procedure, 1908, but shall be guided by the principles of natural justice and, subject to the other
provisions of this Act and of any rules, the Securities Appellate Tribunal shall have powers to regulate their own
procedure including the places at which they shall have their sittings. The Securities Appellate Tribunal shall have,
for the purpose of discharging their functions under this Act, the same powers as are vested in a civil court under
the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908 while trying a suit, in respect of the following matters, namely:-
• (a) summoning and enforcing the attendance of any person and examining him on oath;
• (b) requiring the discovery and production of documents;
• [c] receiving evidence on affidavits
• (d) issuing commissions for the examination of witnesses or documents;
• [e] reviewing its decisions
• (1) dismissing an application for default or deciding it ex parte
• (e) setting aside any order of dismissal of any application for default or any order passed by it ex parte and
• (f) any other matter which may be prescribed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-240303111647-04fa3971/75/1-Securities-Contracts-Regulation-Act-1956-pptx-16-2048.jpg)


