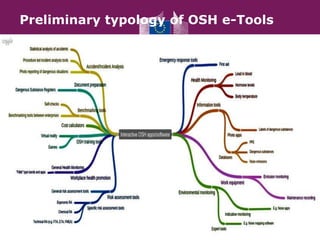
This document discusses innovative IT solutions to support occupational safety and health (OSH) in Europe. It outlines the EU's strategic objective to facilitate compliance with OSH legislation, especially for micro and small enterprises. The document then defines and provides examples of OSH e-tools, which are electronic tools that support OSH through interactive risk assessment, hazard identification, training, and other functions. It highlights several existing e-tools, such as OiRA, STOFFENMANAGER, and SUBSPORT. Finally, it discusses EU-OSHA's role in facilitating the development and sharing of OSH e-tools.