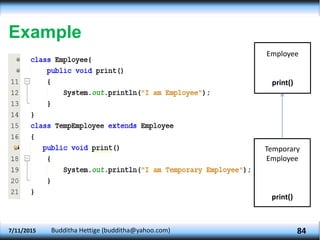
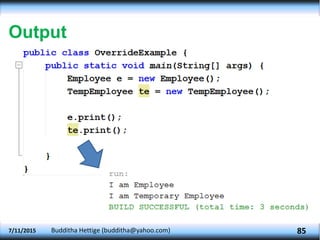
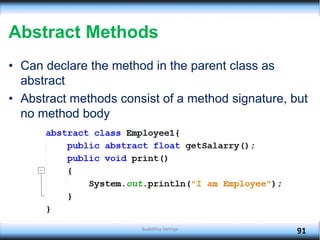
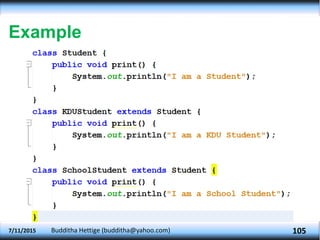
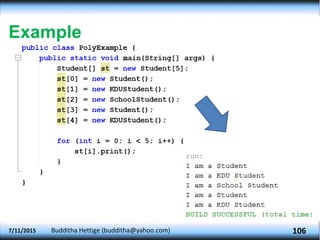
The document explains key concepts in object-oriented programming (OOP) including method overriding, abstraction, packages, and polymorphism. It details how subclasses can override methods from superclasses, the declaration and usage of abstract classes and methods, as well as how to create and utilize packages in Java. Additionally, it discusses polymorphism types such as overloading and overriding, illustrating these concepts with examples related to animals and shapes.