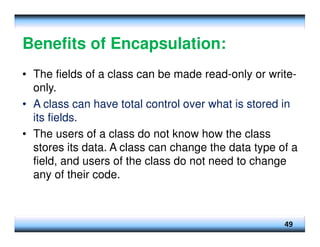
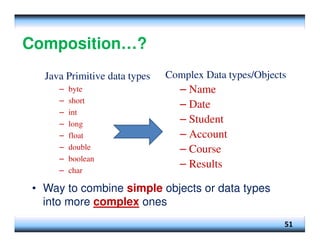
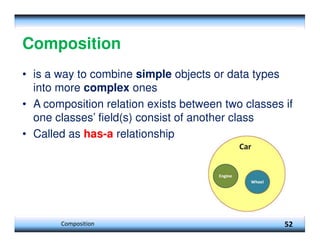
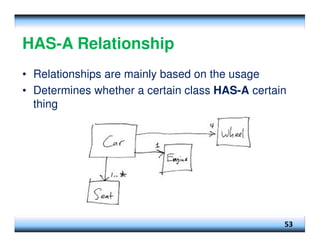
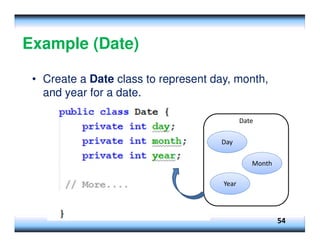
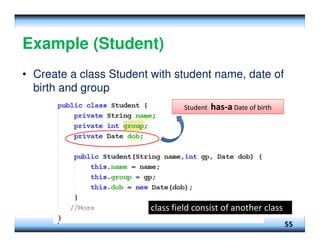
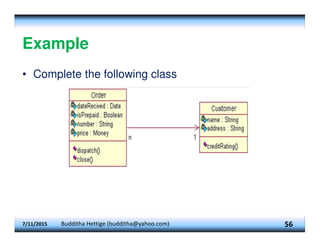
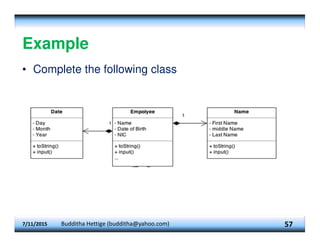
This document provides an overview of constructors and encapsulation in Java programming, explaining their roles in object-oriented programming. It details how constructors are special subroutines for creating objects, and the benefits of encapsulation for data management and protection. Additionally, the document covers the concept of composition, illustrating how simple data types can be combined into more complex objects.


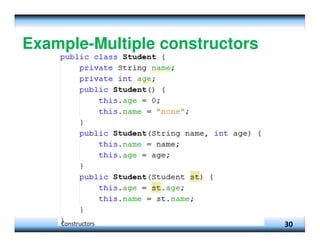
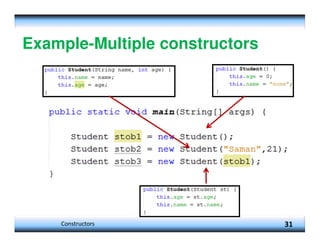
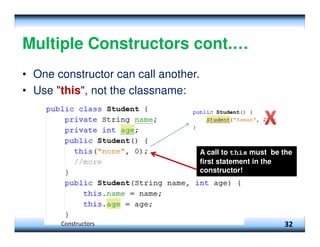


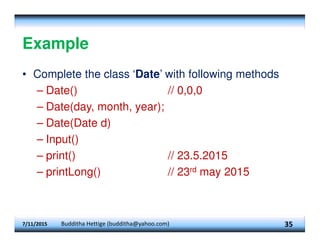






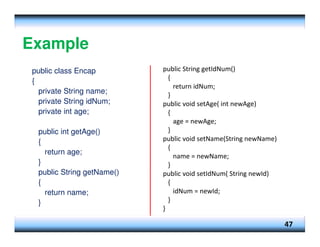
![Example
public class RunEncap
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
EncapTest encap = new EncapTest();
encap.setName("James");
encap.setAge(20);
encap.setIdNum("12343ms");
System.out.println("Name : " + encap.getName()+ " Age : "+ encap.getAge());
}
}
48](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02-advance-methods-on-class-241219105727-787e7cdf/85/02-advance-methods-on-class-jdpgs-code-pdf-24-320.jpg)