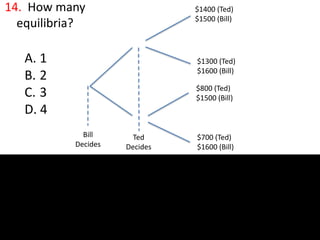
The document provides information about an economics class, including announcements about practice questions for an upcoming midterm exam, exam specifics, a teaching review request, and summaries of prior and upcoming class topics. It then provides 16 multiple choice practice questions related to the class content, including questions about efficiency, price discrimination, monopolies, game theory, externalities, and natural monopolies.