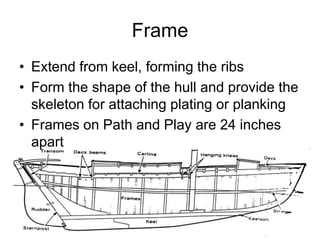
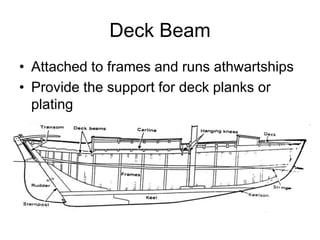
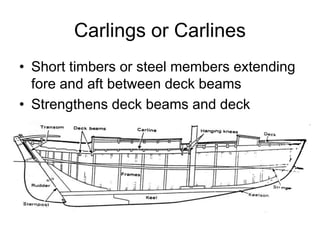
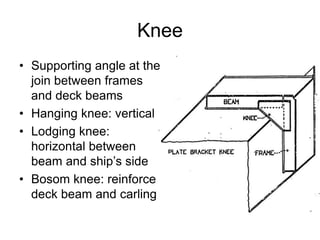
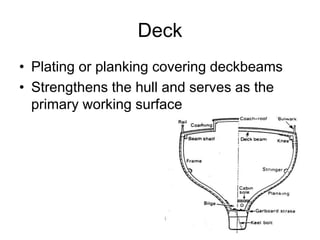
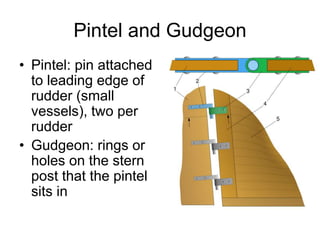
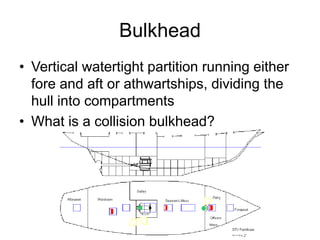
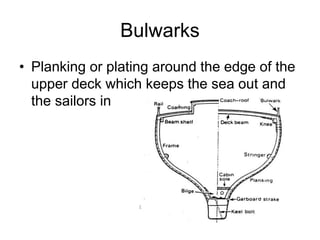
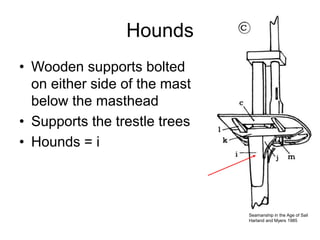
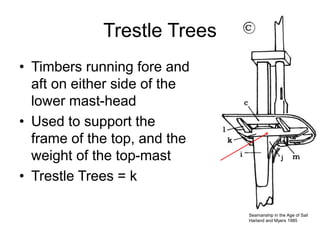
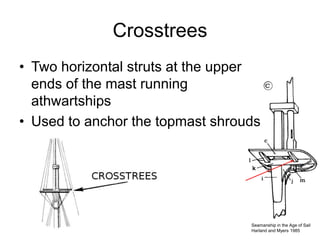
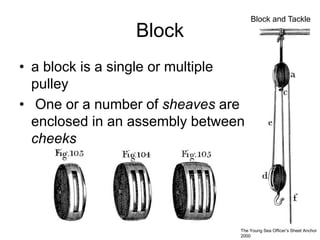
The document defines and describes various parts of a ship, including its hull, masts, rigging, and deck components. It explains key structural elements like the keel, frames, deck beams, knees, and bulkheads. It also outlines components related to steering like the rudder, pintel, and gudgeon. Additional parts described are stanchions, washboards, mast steps, trestle trees, crosstrees, and blocks. The document provides definitions to build an understanding of the basic anatomy and systems of sailing vessels.