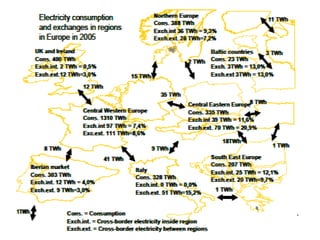
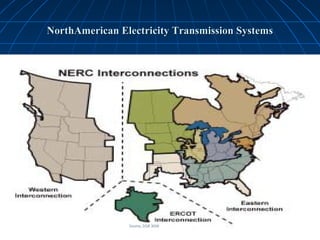
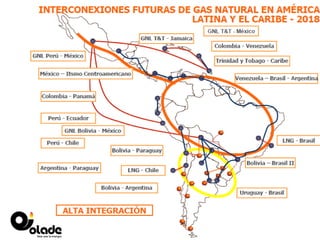
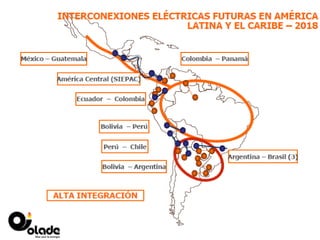
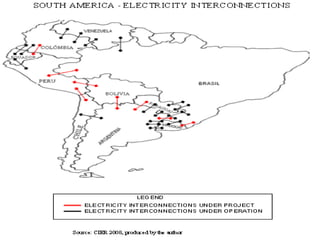
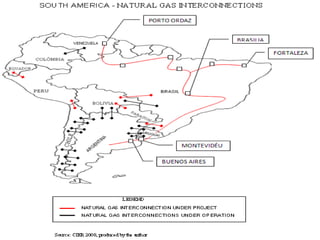
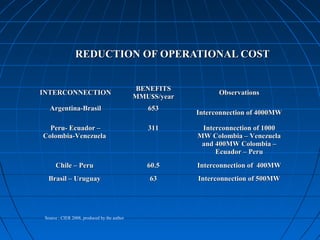
This document discusses energy integration in Latin America, including past experiences, the current status quo, and future perspectives. It analyzes the benefits of energy integration such as cost reductions, improved reliability, and increased energy trade. However, challenges remain such as developing harmonized long-term planning, legal frameworks, infrastructure, and new financing. If these challenges can be addressed, energy integration has the potential to stimulate regional cooperation, support sustainable development, and help meet growing energy demand in Latin America.