1) The document introduces web programming and the fundamentals of static versus dynamic content on the web.
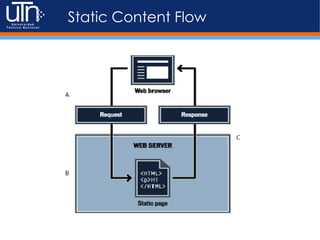
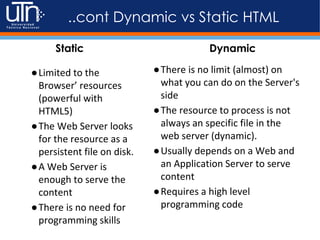
2) Static content comes from plain HTML files on a server, while dynamic content is generated programmatically using server-side languages and can pull from databases.
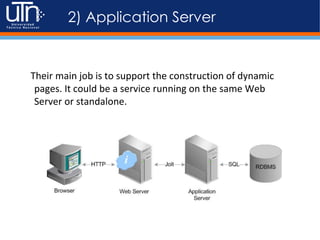
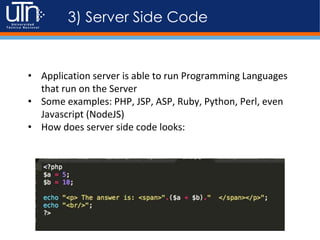
3) Key components involved in serving dynamic content include a web server, application server, server-side programming languages, databases, and other services like caching and logging. These components work together to dynamically generate responses.