The document is an overview of information technology, covering key concepts such as information processing, computer systems, networks, and software engineering. It discusses the evolution and classification of computers, the role of informatics, and the importance of data management technologies in organizations. Additionally, it highlights the historical context of information technology development and its pervasive impact on society.


![1.3. INFORMATIONTECHNOLOGY
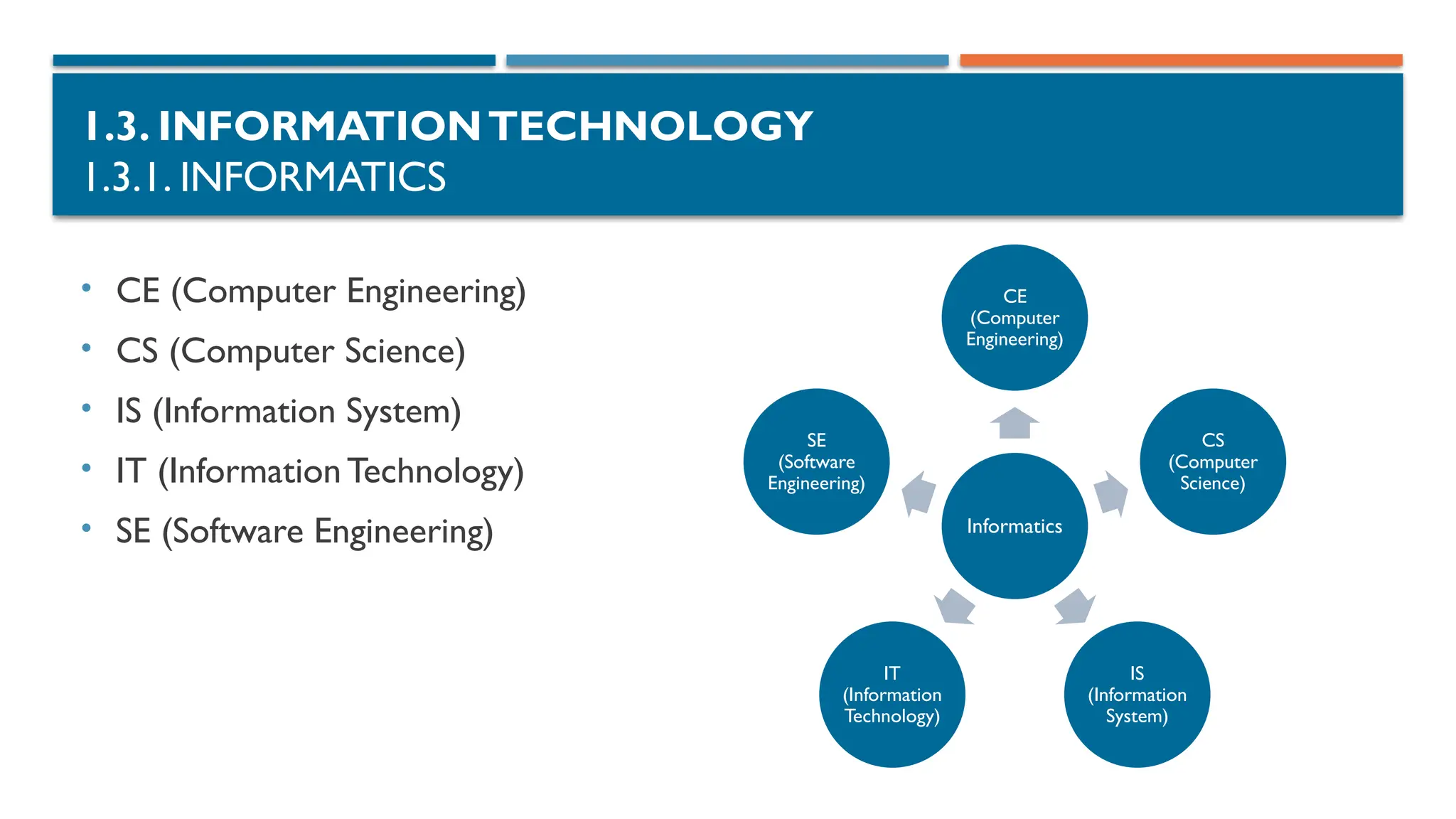
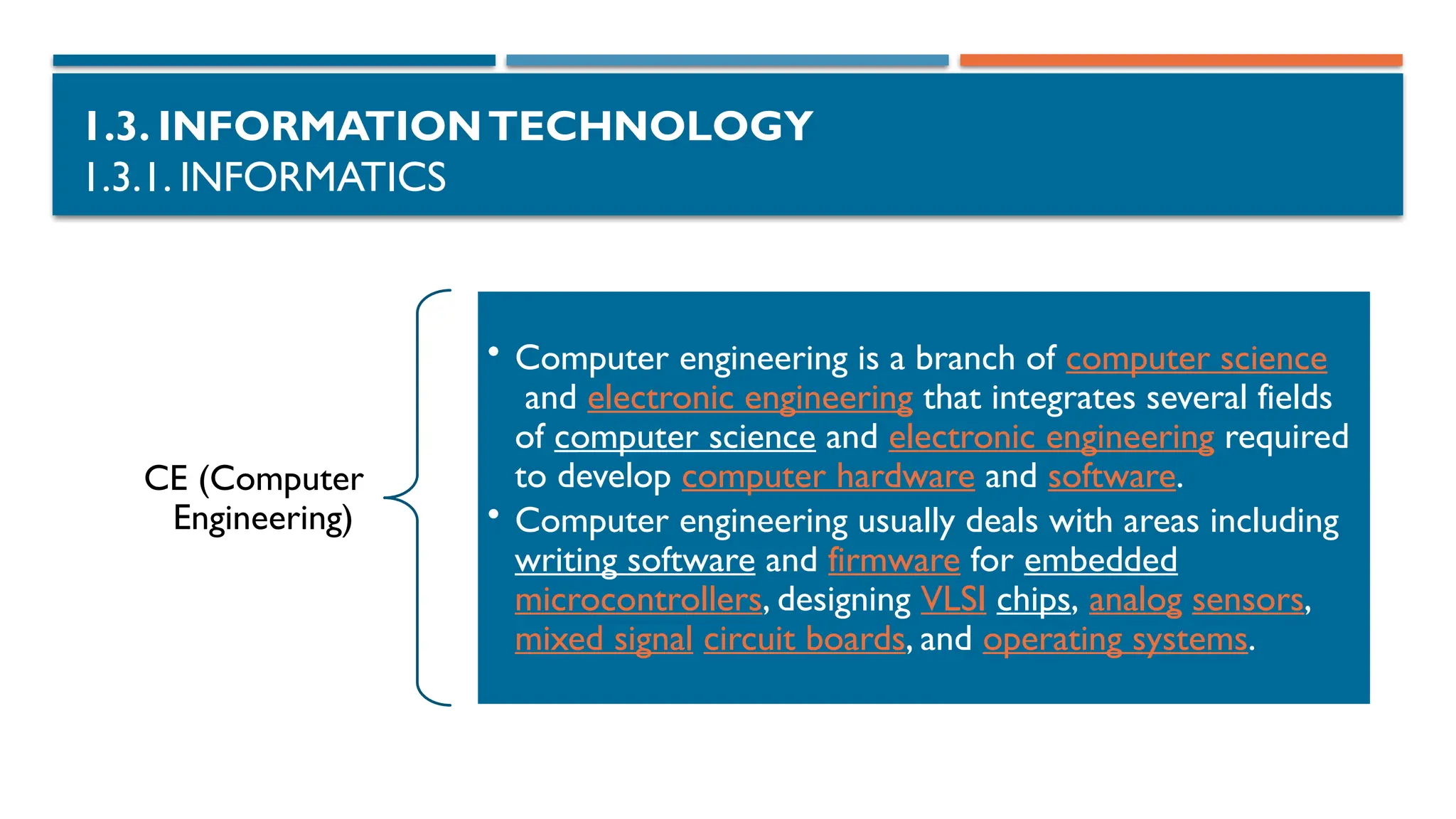
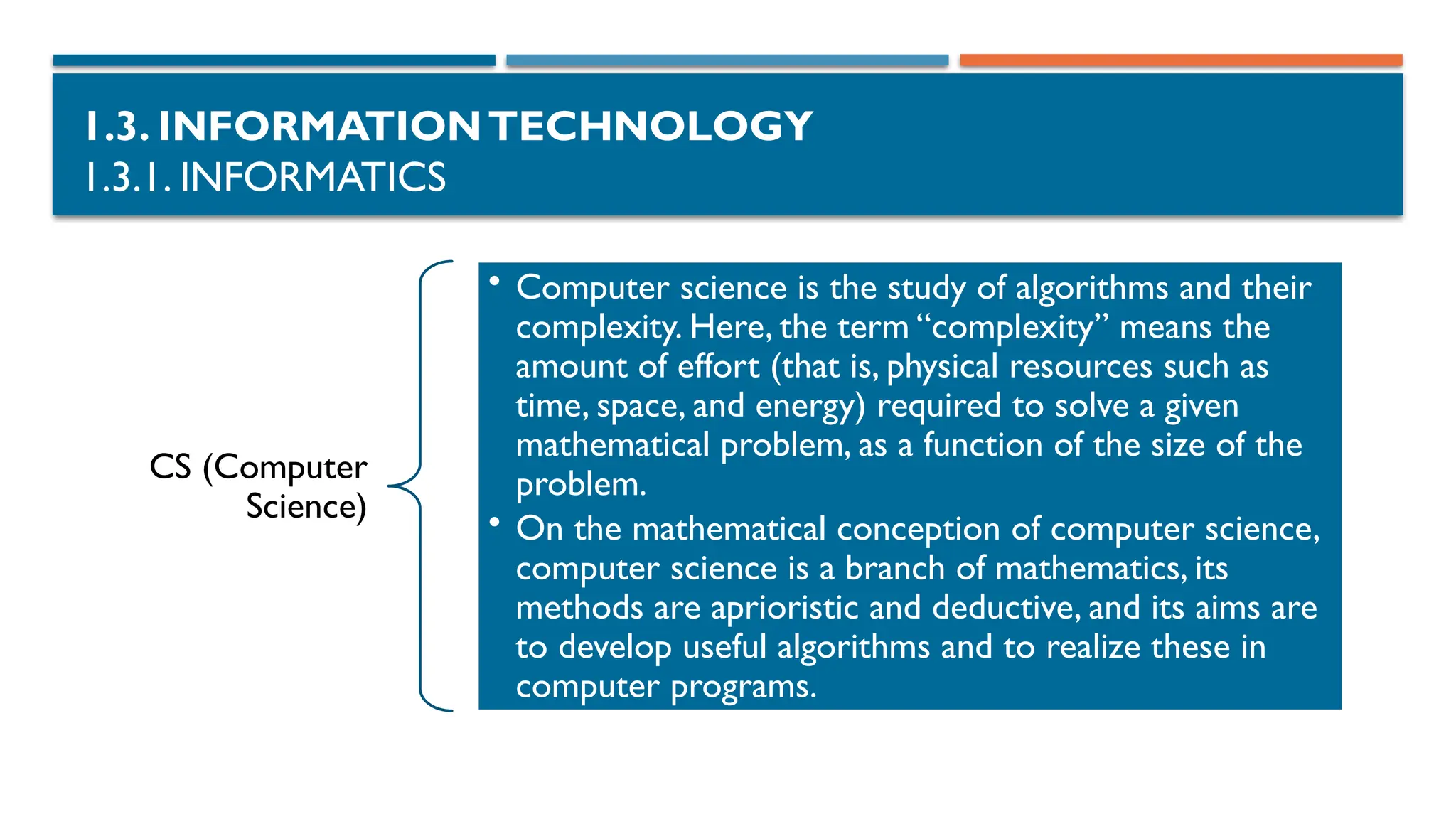
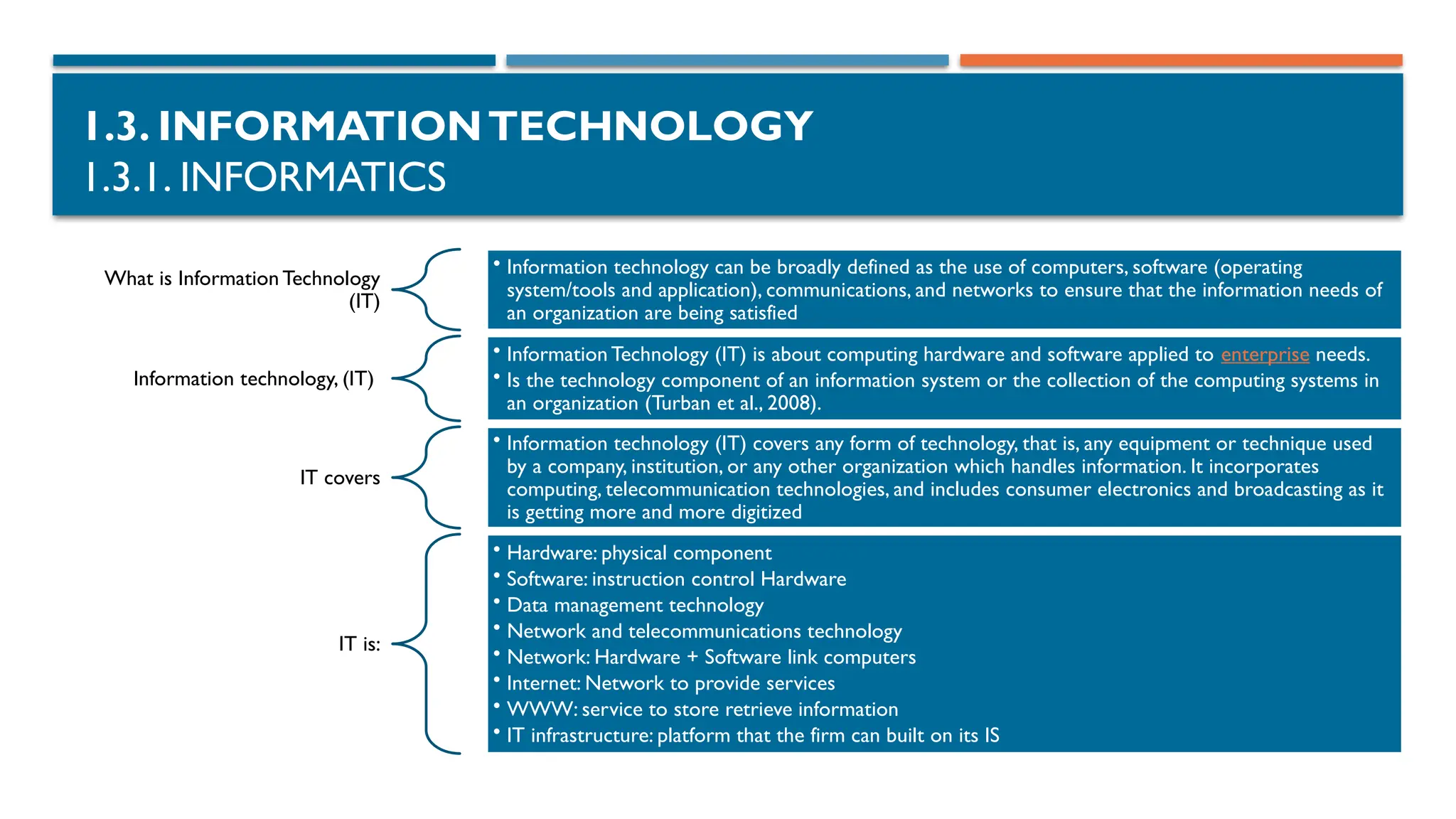
1.3.1. INFORMATICS
SE (Software Engineering)
• According to the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM), software engineering is concerned with
developing and maintaining software systems that behave reliably and efficiently, are affordable to develop and
maintain, and satisfy all the requirements that customers have defined for them [ACM 2006]. IEEE dsystematic,
disciplined, quantifiable approach to the development, operation, and maintenance of softwareefines software
engineering more succinctly as “a.”
• Software engineering (SE) emerged as a discipline in the late 70s and early 80s
• Software Engineering is a multidisciplinary discipline involving different social and technological features.
• To understand how software engineers maintain complex software systems, it is necessary to investigate not
only the tools and processes they use but also the cognitive and social processes surrounding them.
• It requires the study of human activities.We need to understand how software engineers individually develop
software as well as how teams and organizations coordinate their efforts
• Software engineering is an evolving engineering discipline. It deals with systematic approaches to building large
software systems by teams of programmers.We have given a brief review of the essential elements of
software engineering including product-related issues such as requirements, design, and validation, and
process-related issues including process models and their assessment.
Mehdi Jazayeri, in Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology (Third Editio
2003
Paulo Sérgio Medeiros dos Santos, Guilherme Horta Travassos, in
Advances in Computers, 2011](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01chapter1-introductiontoinformationtechnology-part3-241222052455-a598112b/75/01-Chapter-1-Introduction-to-information-technology-Part-3-pptx-9-2048.jpg)


![1.3. INFORMATIONTECHNOLOGY
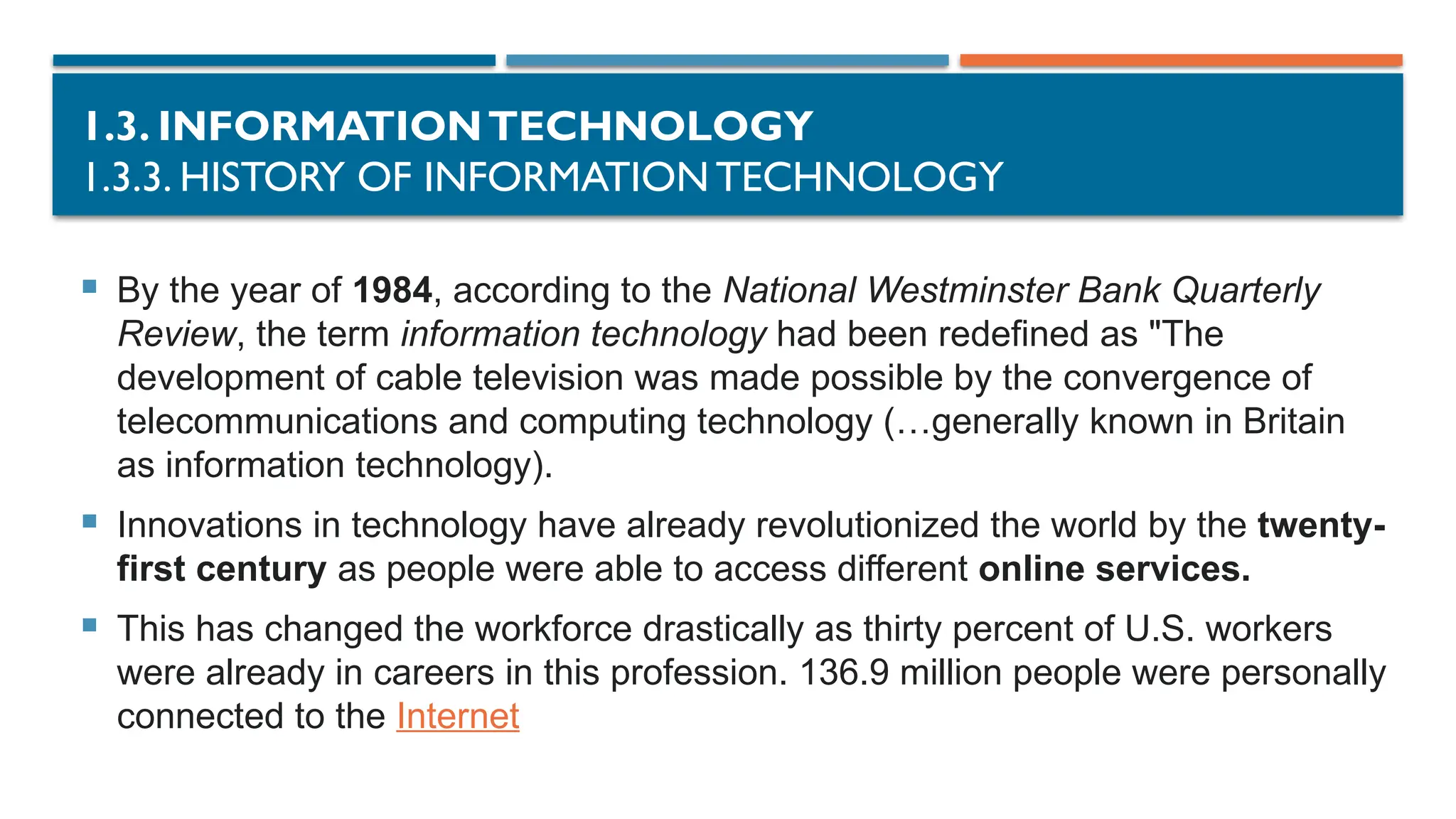
1.3.3. HISTORY OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
Information technology (IT) is a set of related fields that encompass computer
systems, software, programming languages, and data and information processing,
and storage.[1]
IT forms part of information and communications technology (ICT)
Ideas of computer science were first mentioned before the 1950s under the
Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and Harvard University, where they
had discussed and began thinking of computer circuits and numerical calculations.
As time went on, the field of information technology and computer science
became more complex and was able to handle the processing of more data.
The development of the personal computer (PC) in the 1970s, and the emergence
of information and communications technology (ICT)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01chapter1-introductiontoinformationtechnology-part3-241222052455-a598112b/75/01-Chapter-1-Introduction-to-information-technology-Part-3-pptx-16-2048.jpg)