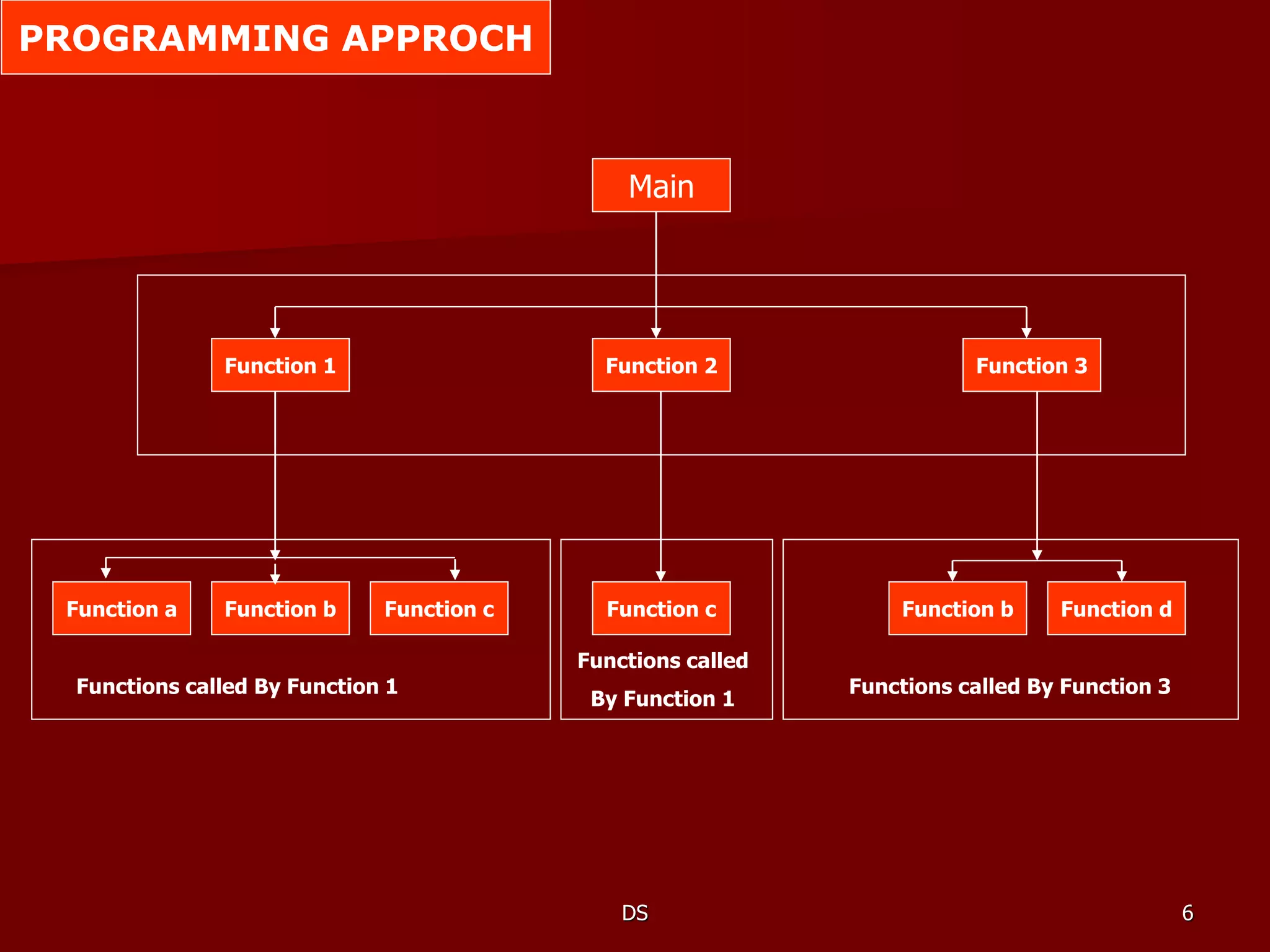
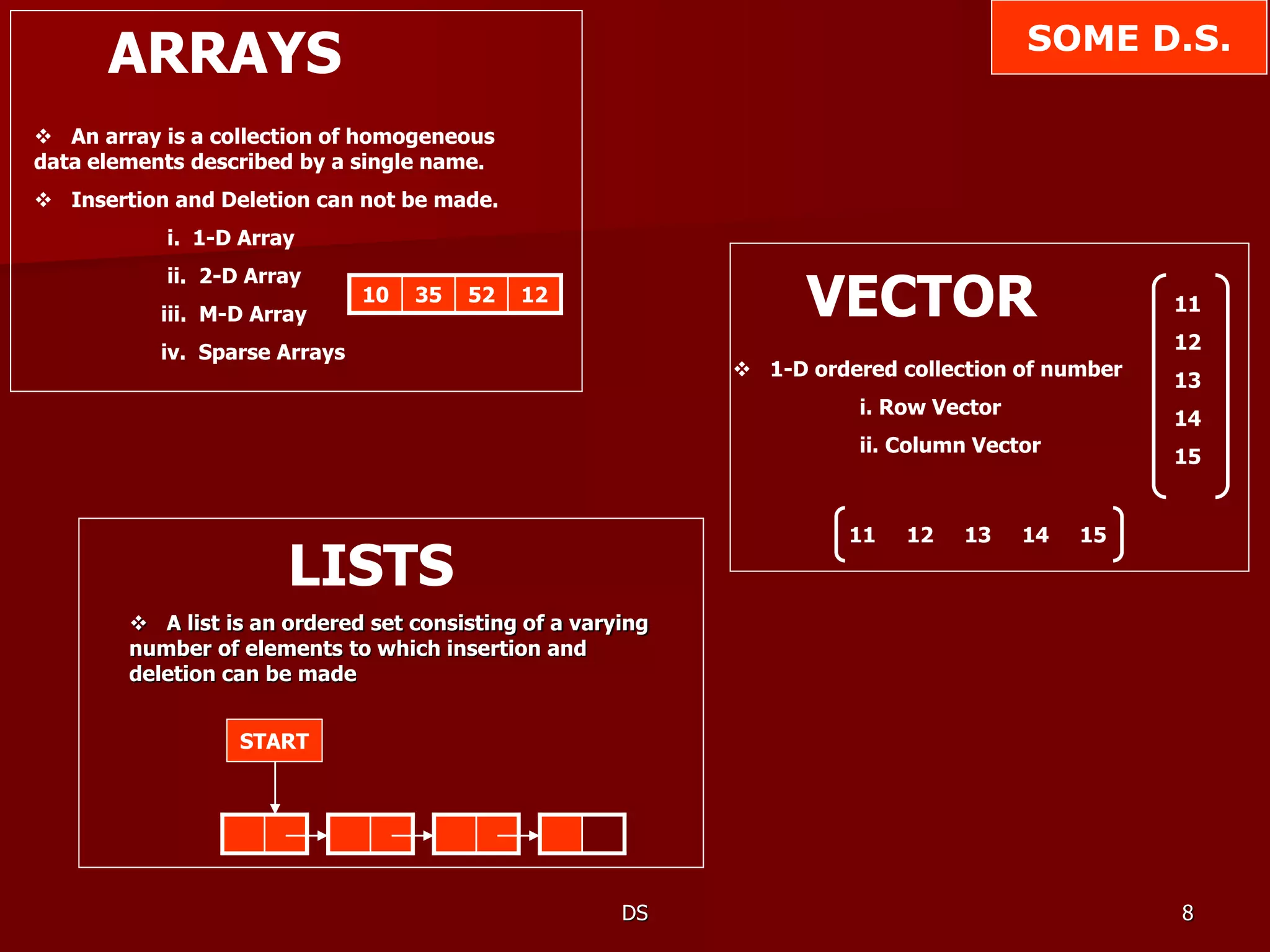
The document discusses basics of data structures and programming methodology. It defines data structures as representations of logical relationships between data elements that are used to maximize memory efficiency. An algorithm plus data structure equals a program. Data structures can be represented in memory or stored in files. Modular programming involves writing programs as independent functions with high cohesion and low coupling. Common data structures include arrays, vectors, lists, files, records, strings, linear and non-linear lists, stacks, queues, trees, and graphs. Dynamic memory allocation uses functions like malloc(), calloc(), realloc(), and free() while static allocation uses arrays. Memory management involves techniques such as free storage lists and garbage collection.








![DS 11
malloc ()
Allocates 1 block of memory
ptr=(Data_Type *)malloc(n * sizeof(Data_Type));
callloc ()
Allocates n block of memory
ptr=(Data_Type *)calloc(n , sizeof(Data_Type));
realloc ()
Resize the original block of memory
ptr=realloc(ptr, NewSize);
free ()
Free up the memory block
free (ptr);
Dynamic or Run Time memory
allocation (Linked list)
Static or Compile Time
memory allocation (Array)
int a, array[10];
char str[80];
Dynamic memory
allocation in C++
int *var1 = new int;
float *var2 = new float;
delete var1;
delete var2;
MEMORY MANAGEMENT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/00-230117061022-e4089d6b/75/00-Basics-of-Data-Structures-ppt-11-2048.jpg)

