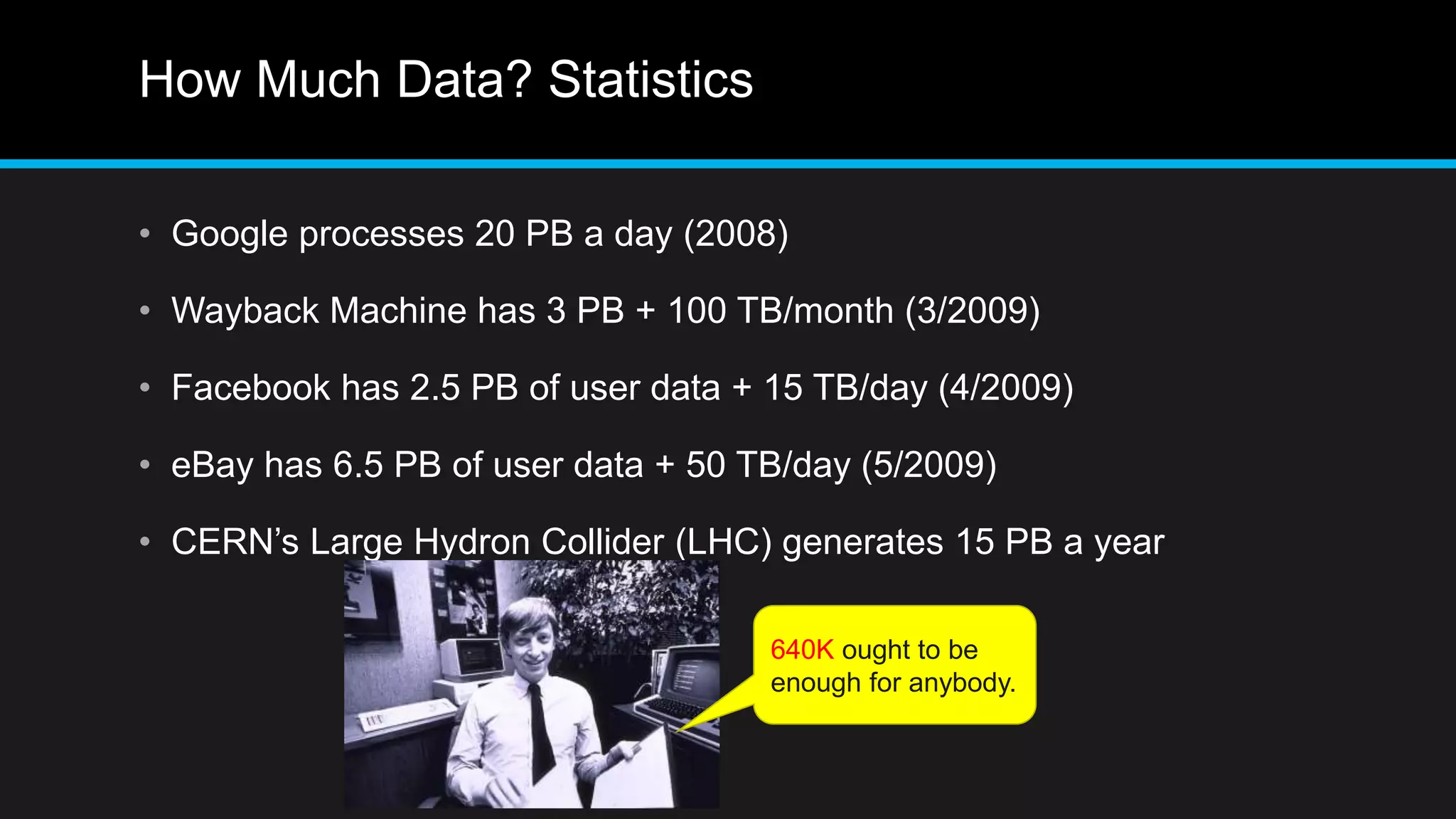
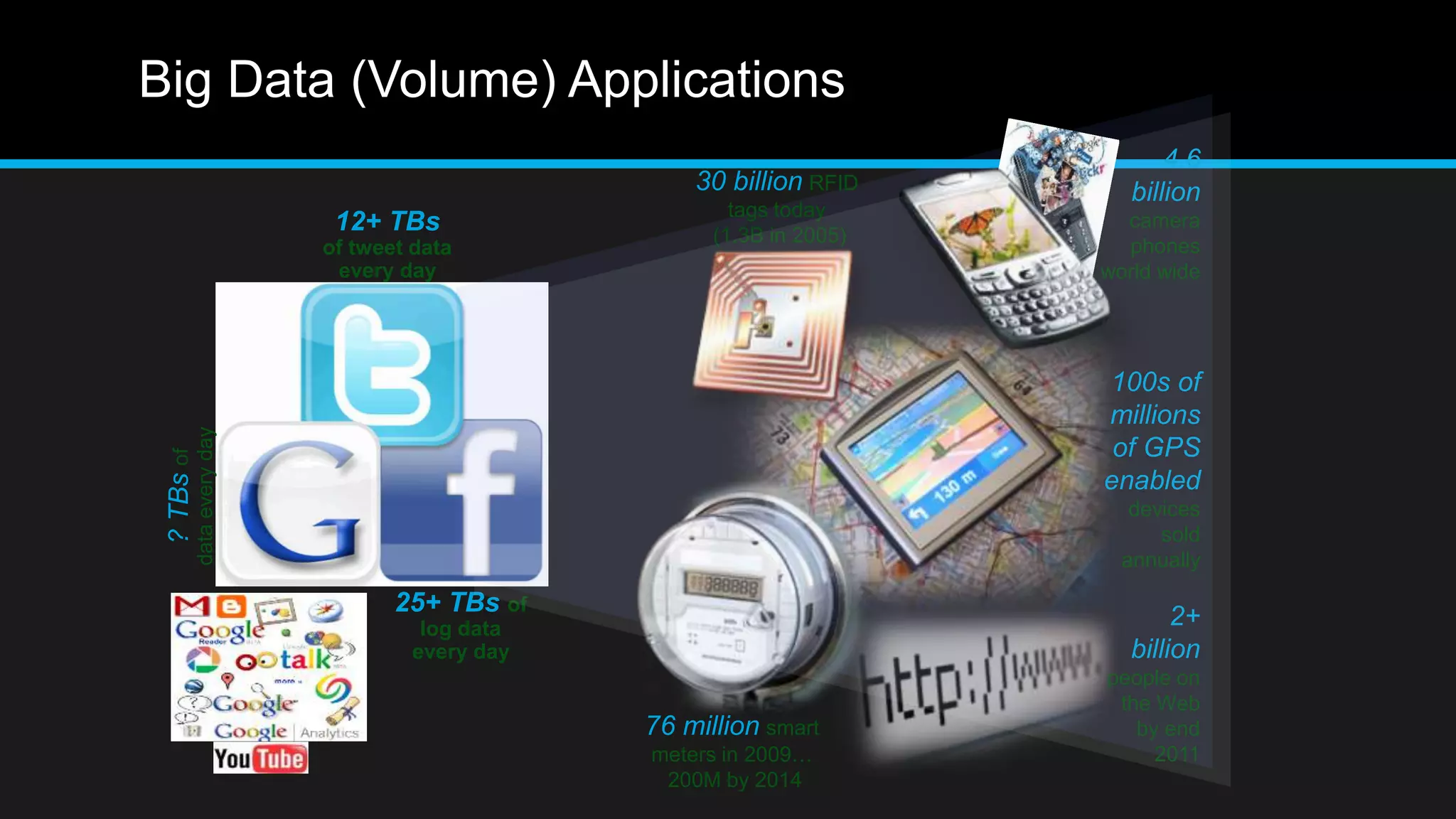
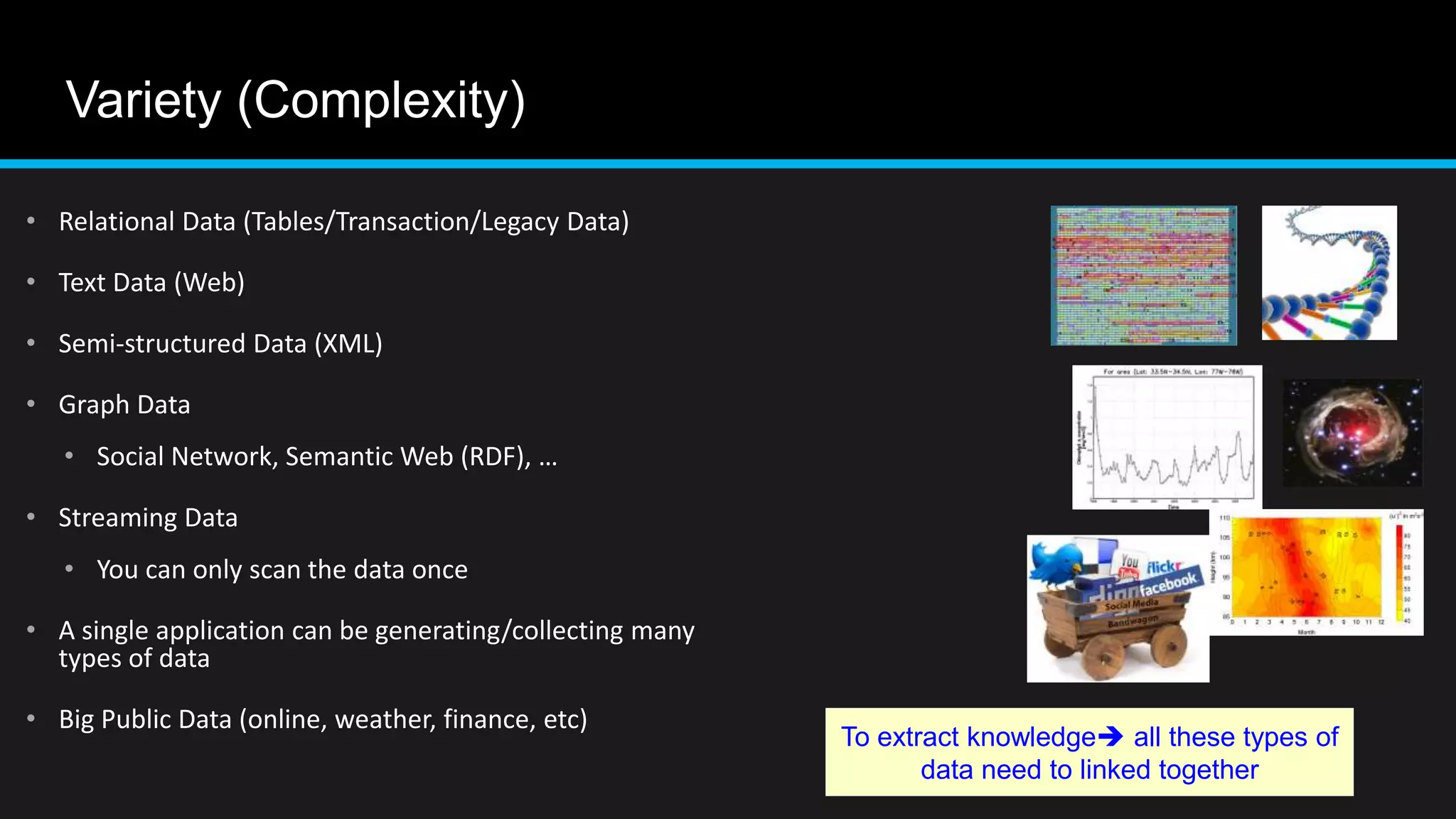
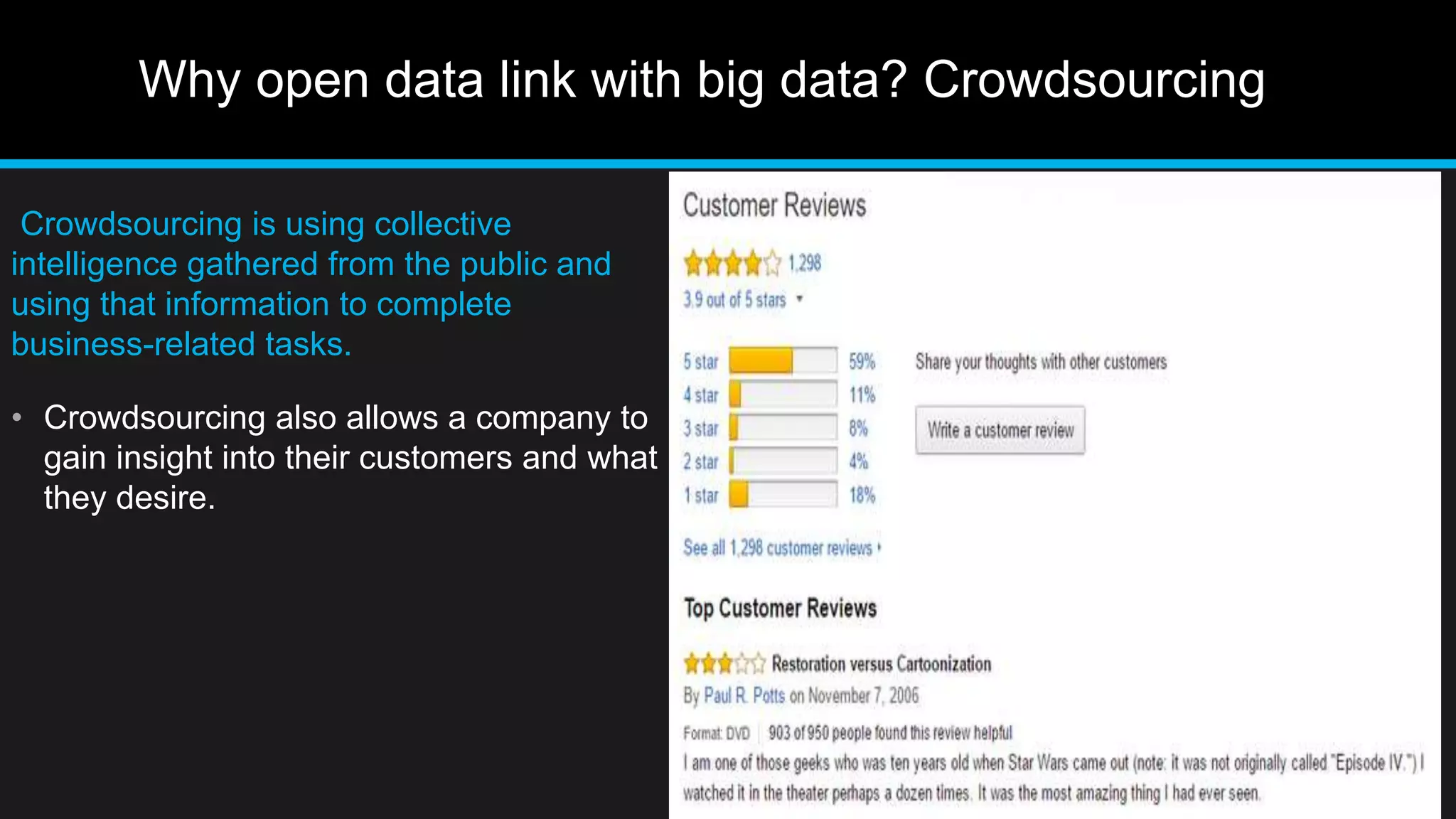
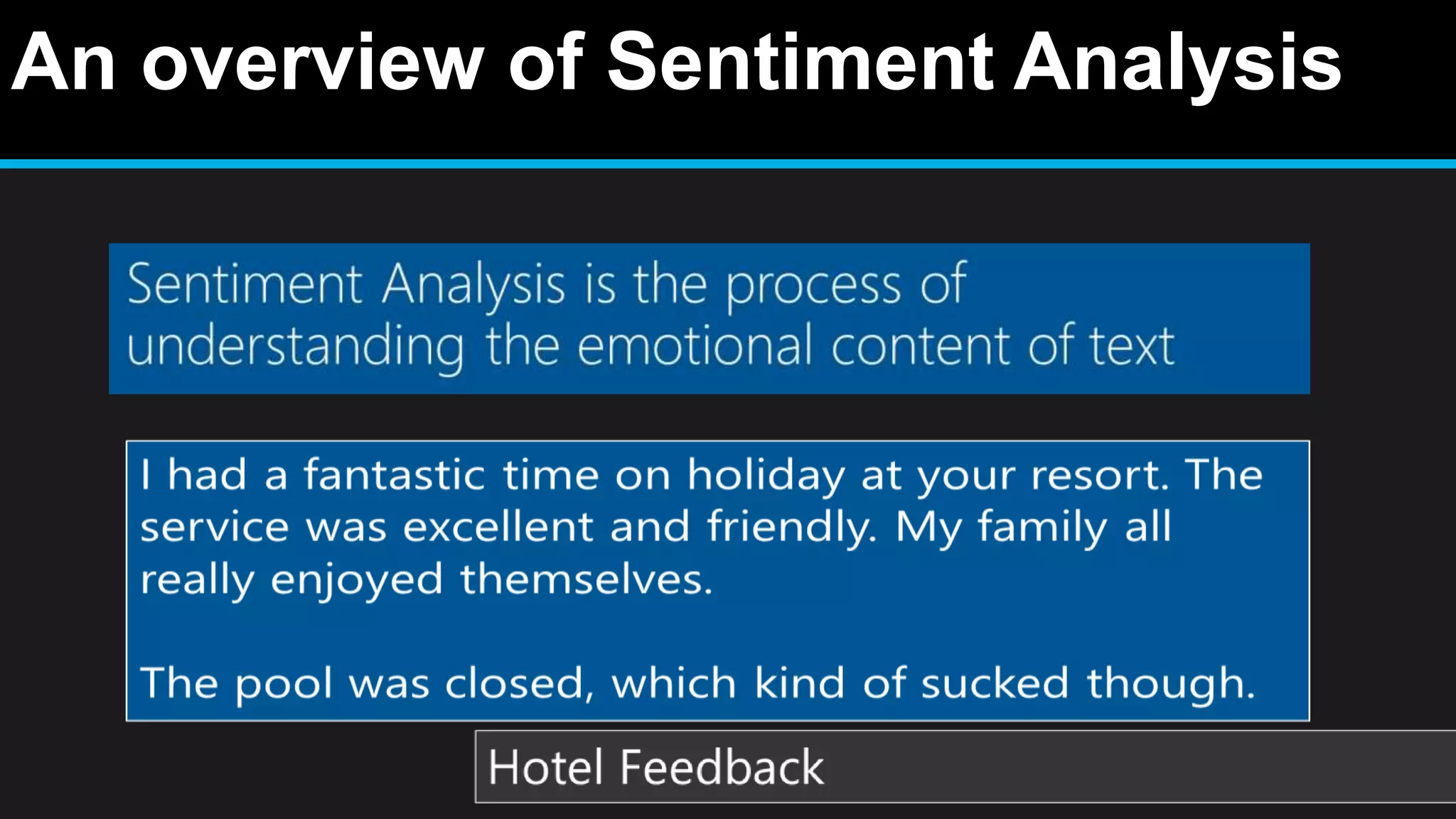
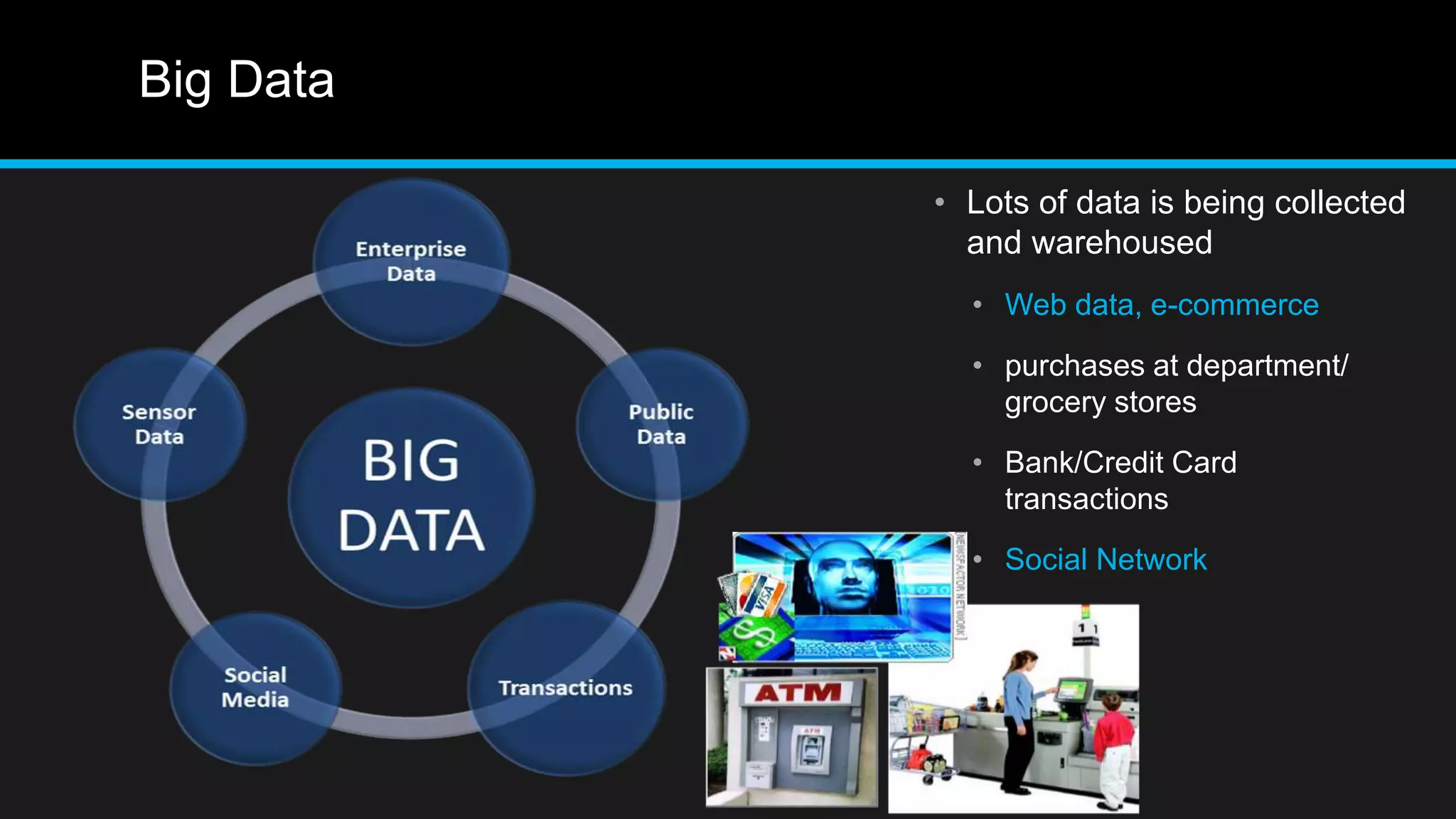
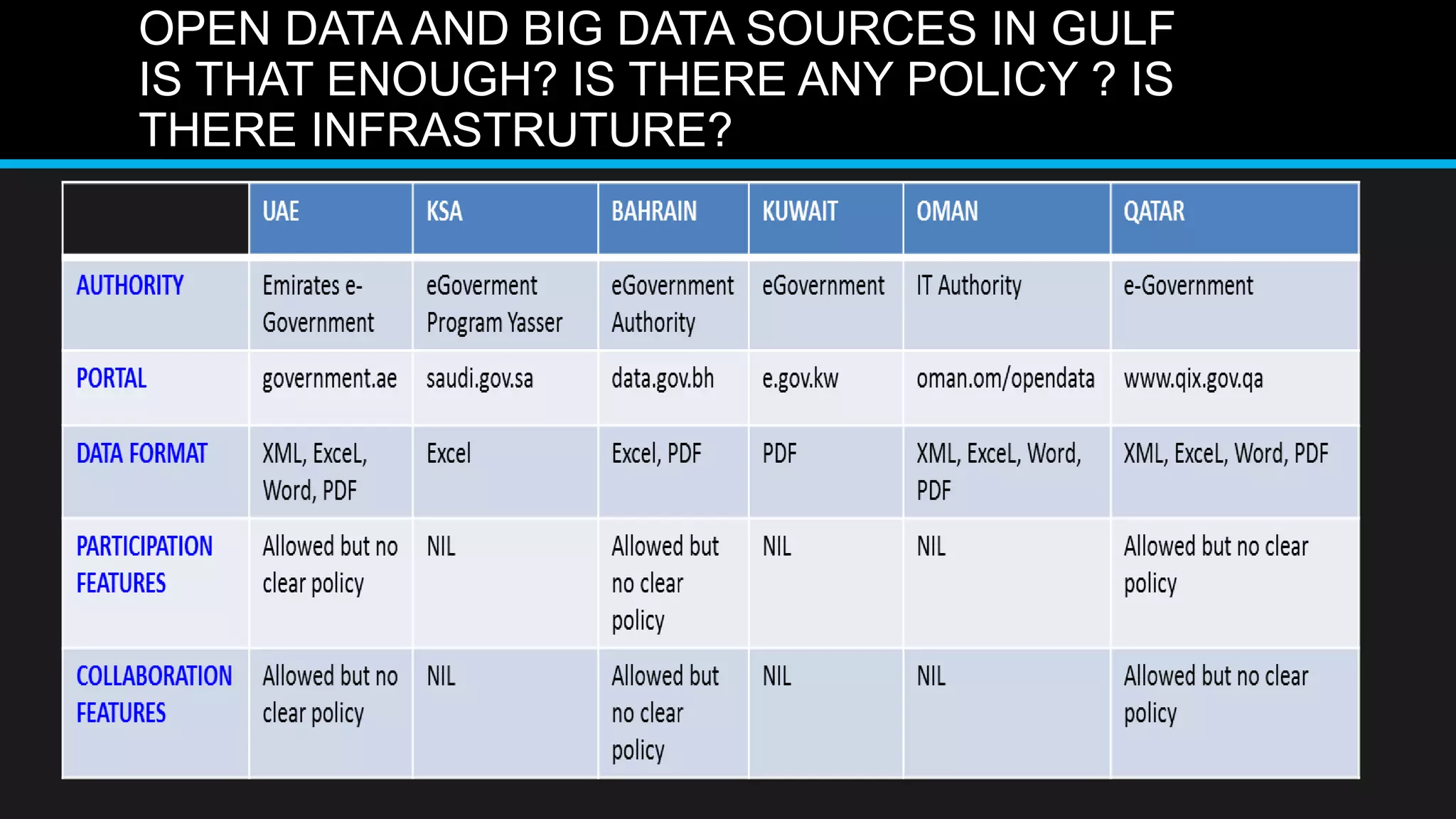
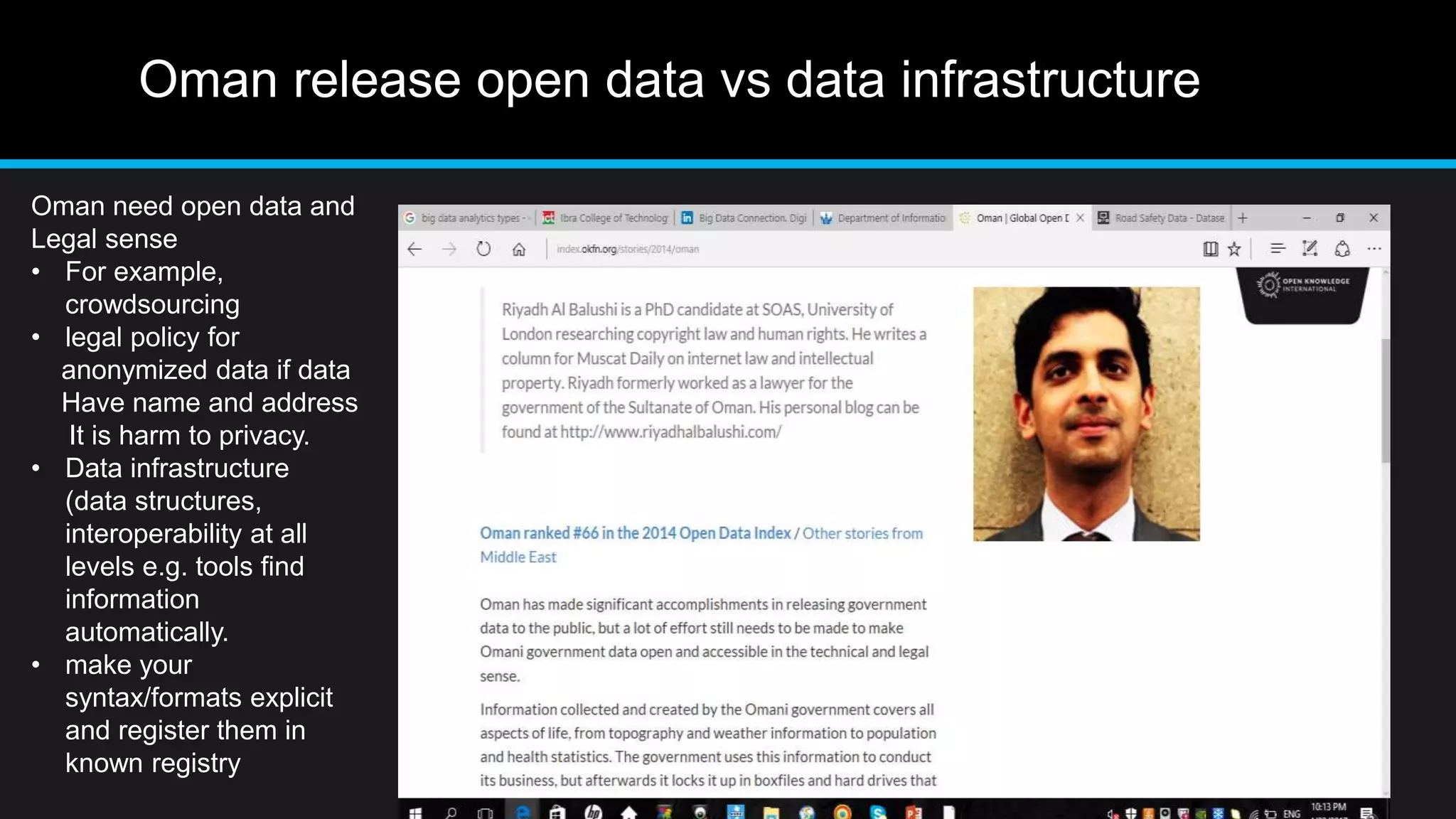
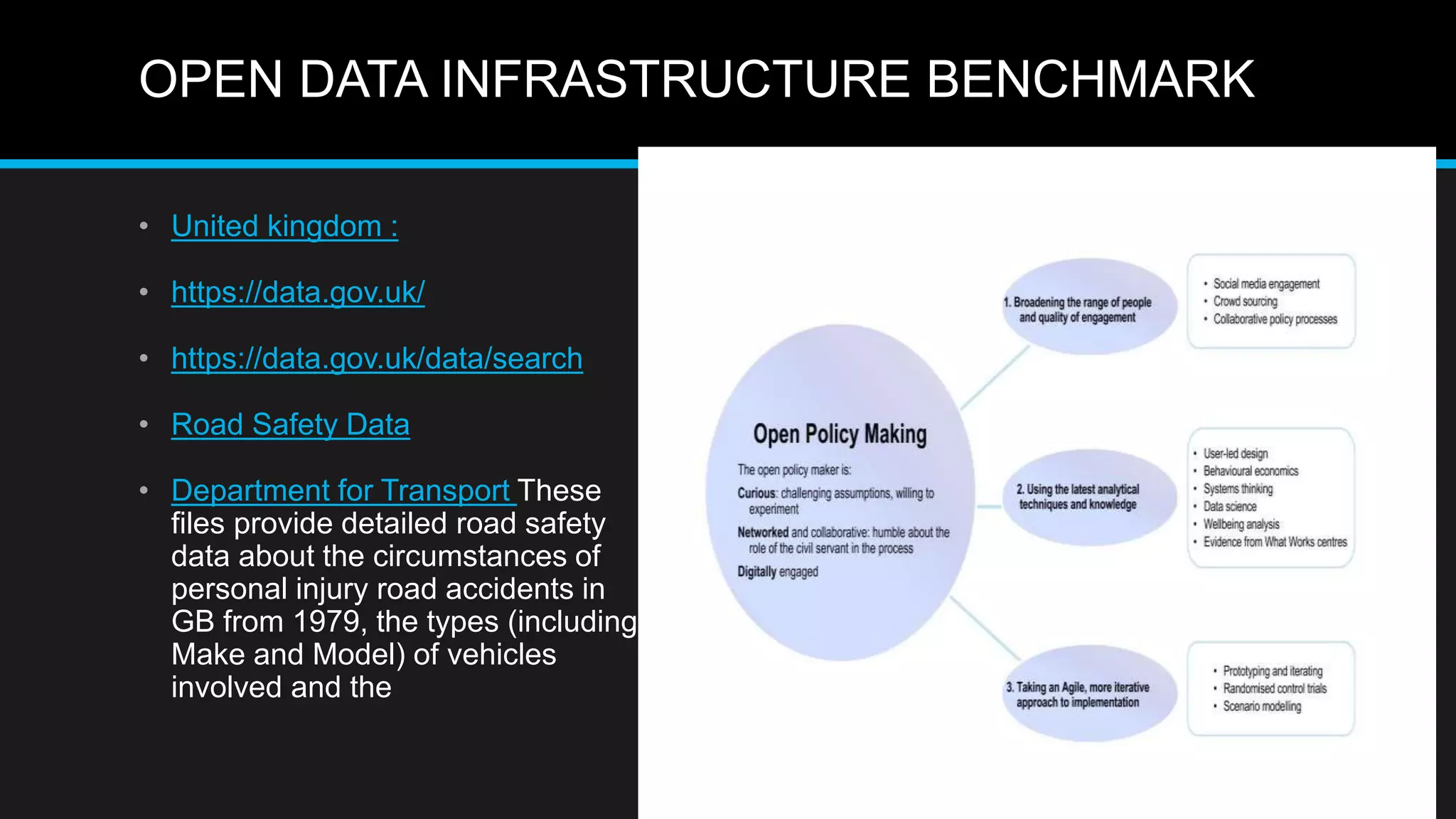
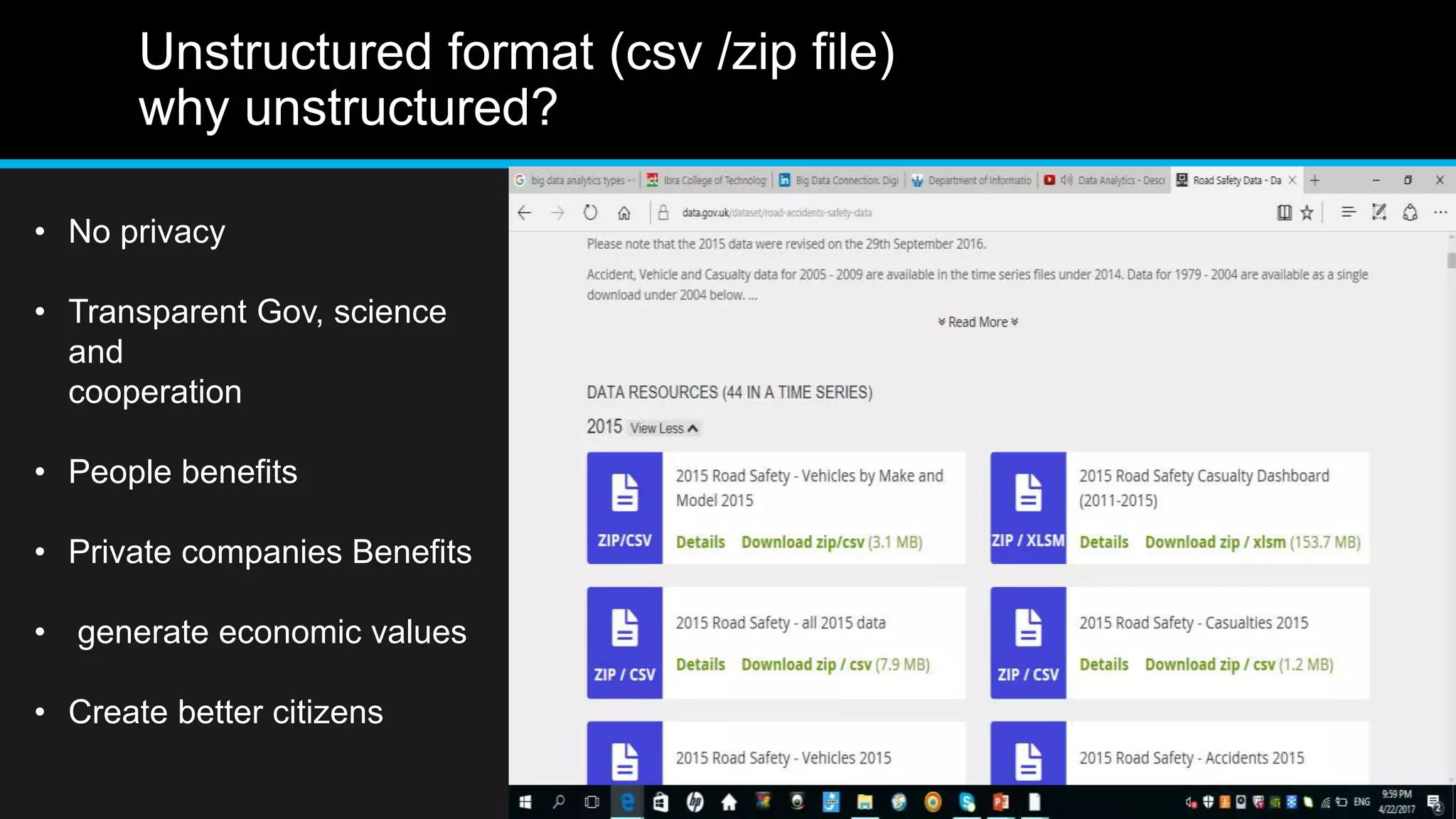
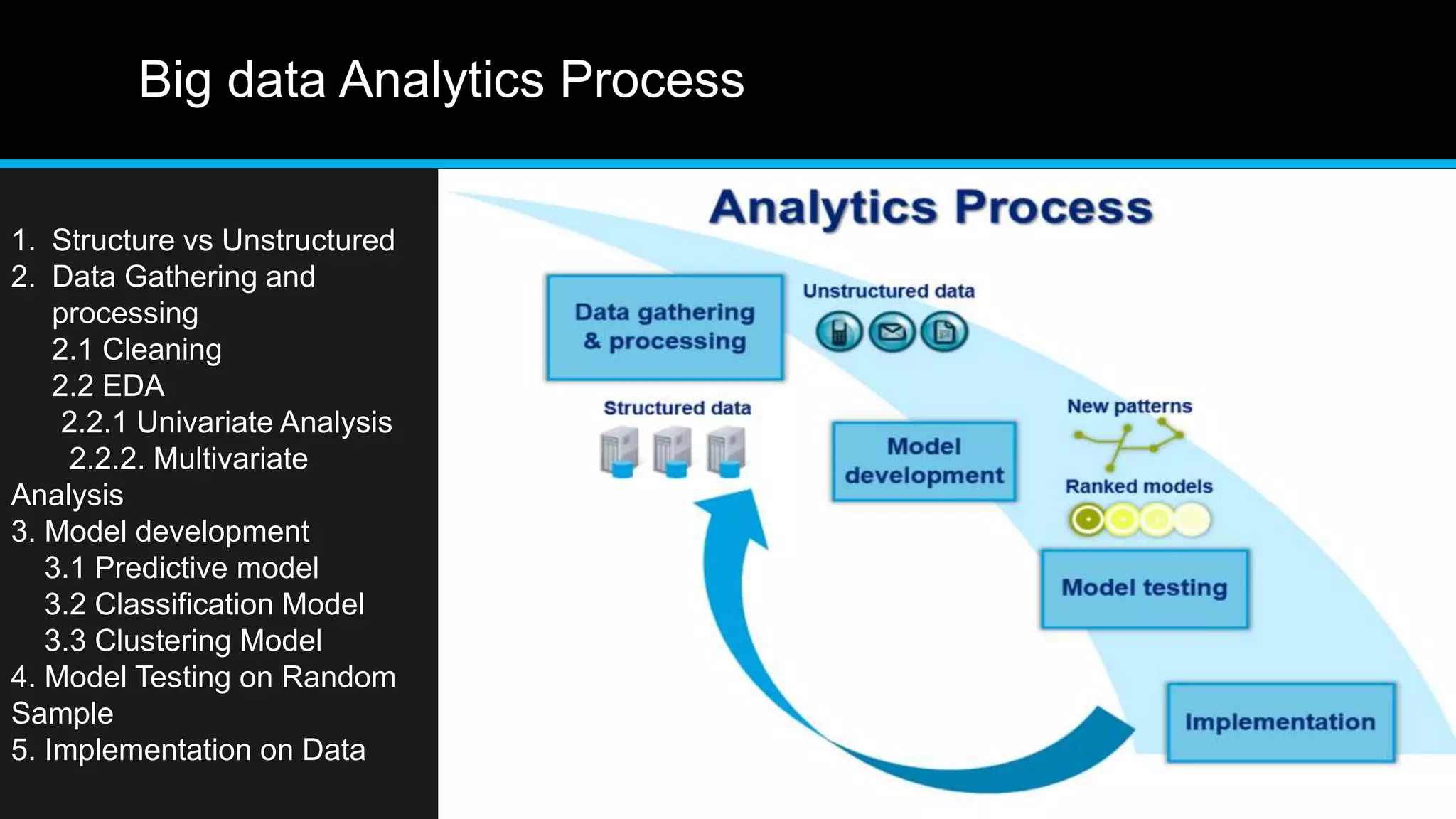
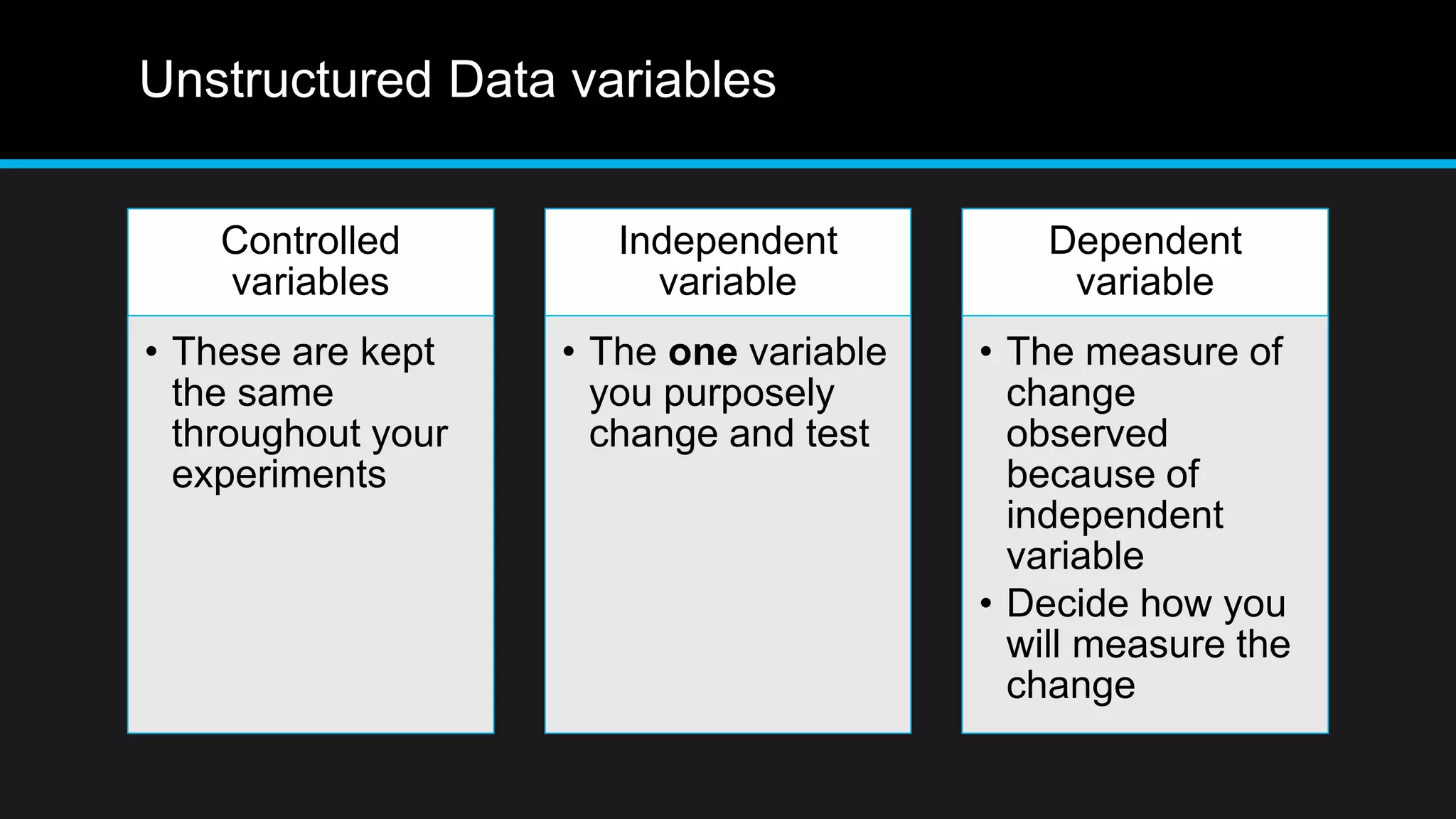
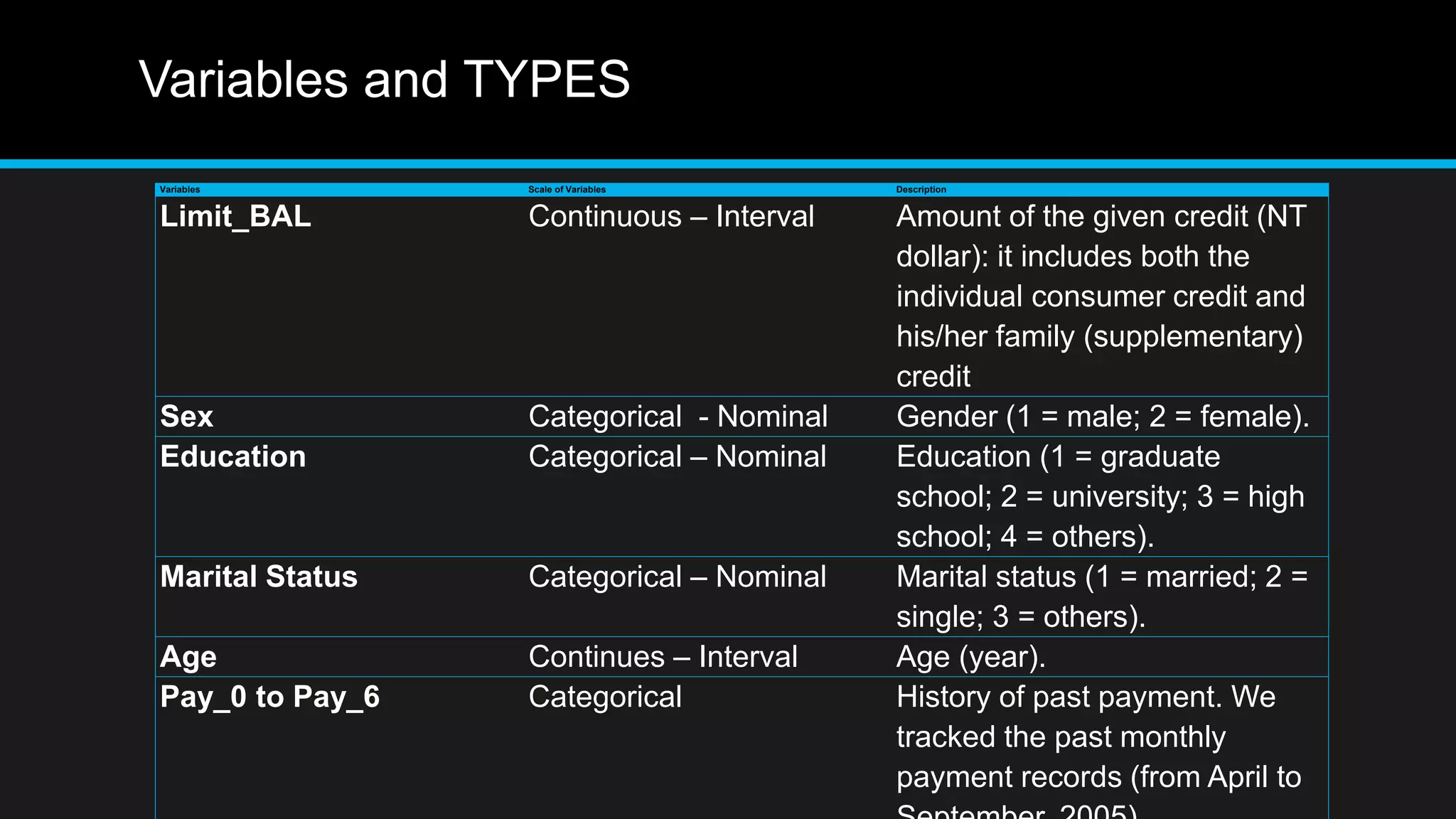
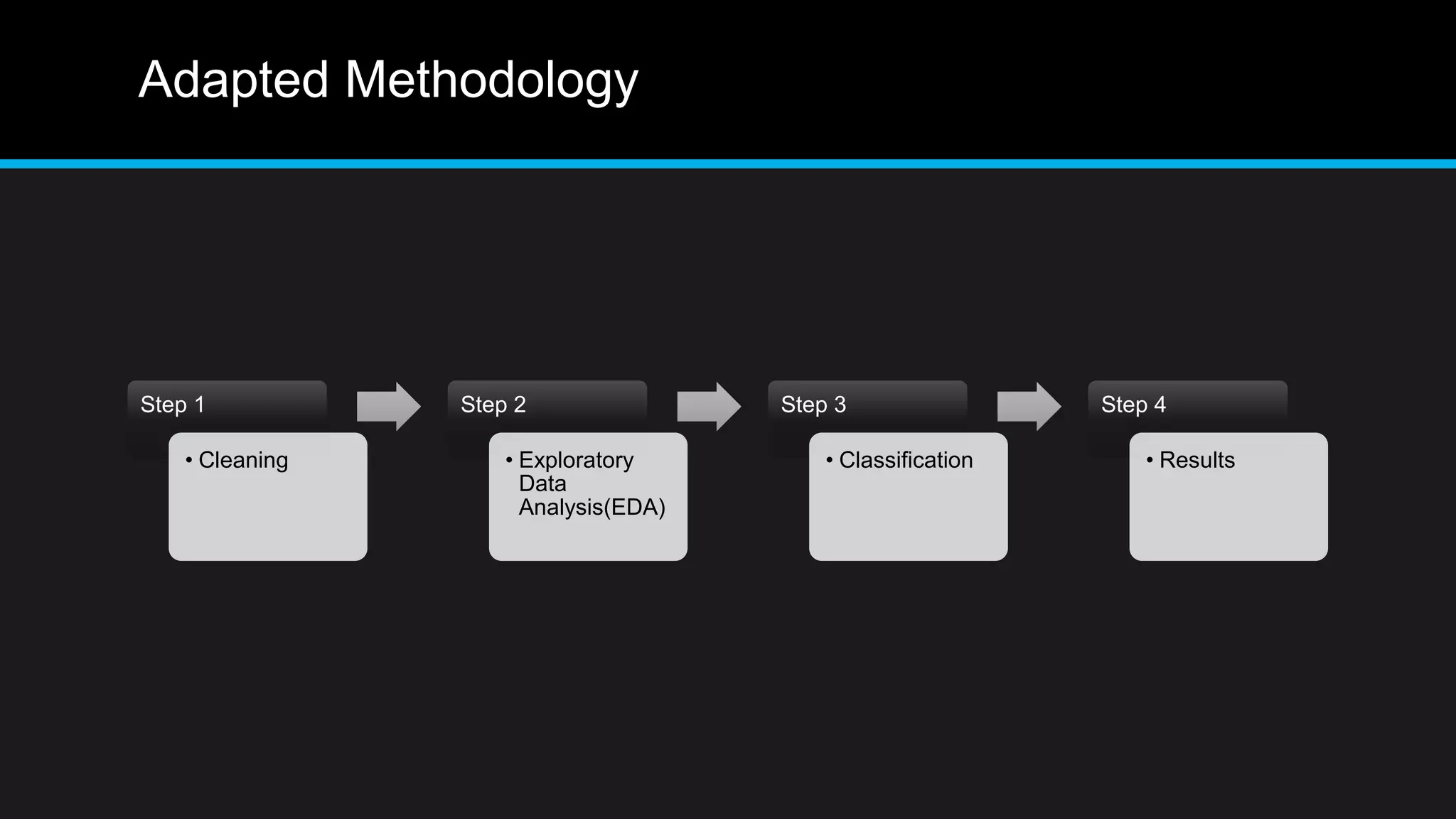
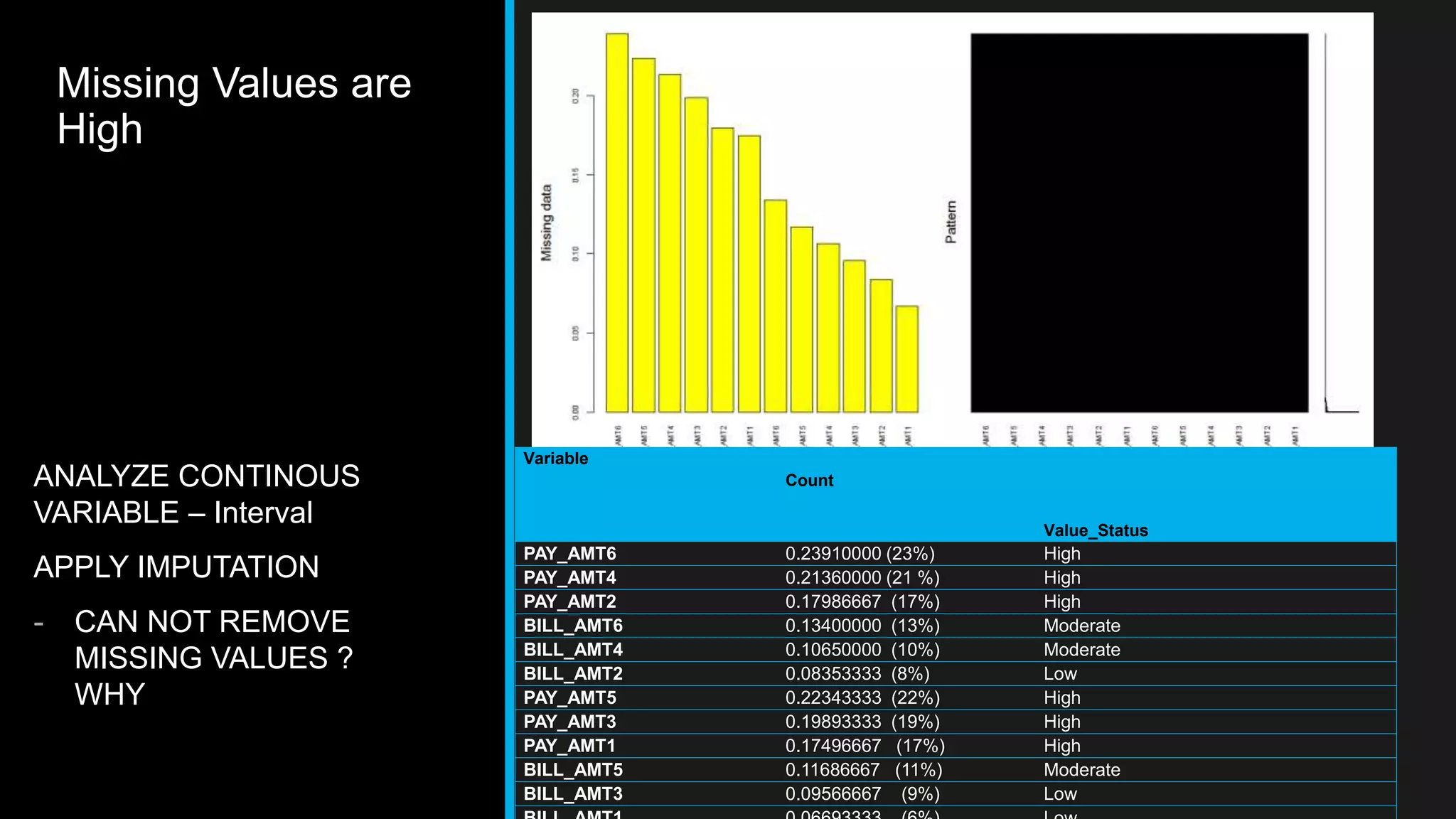
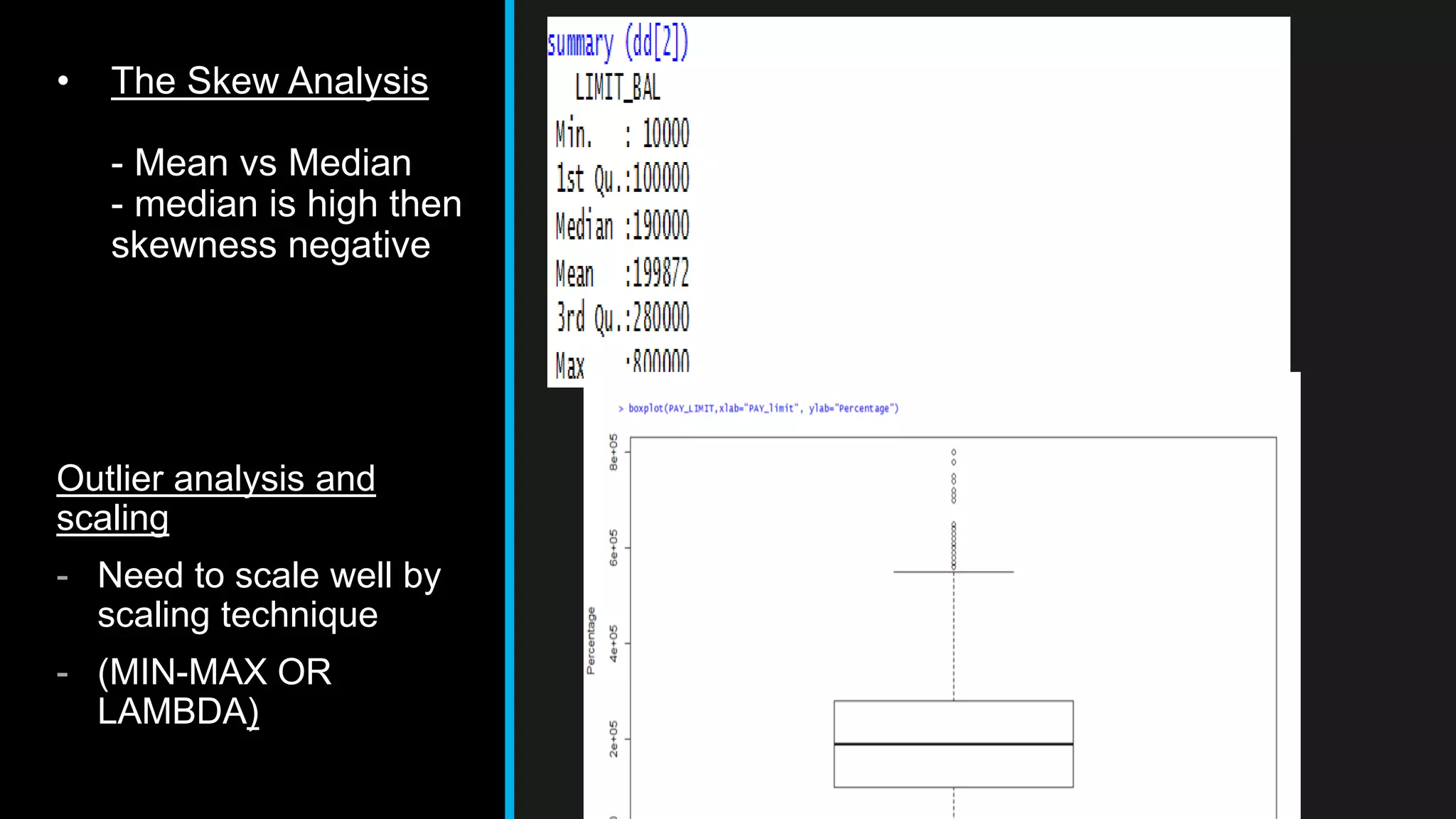
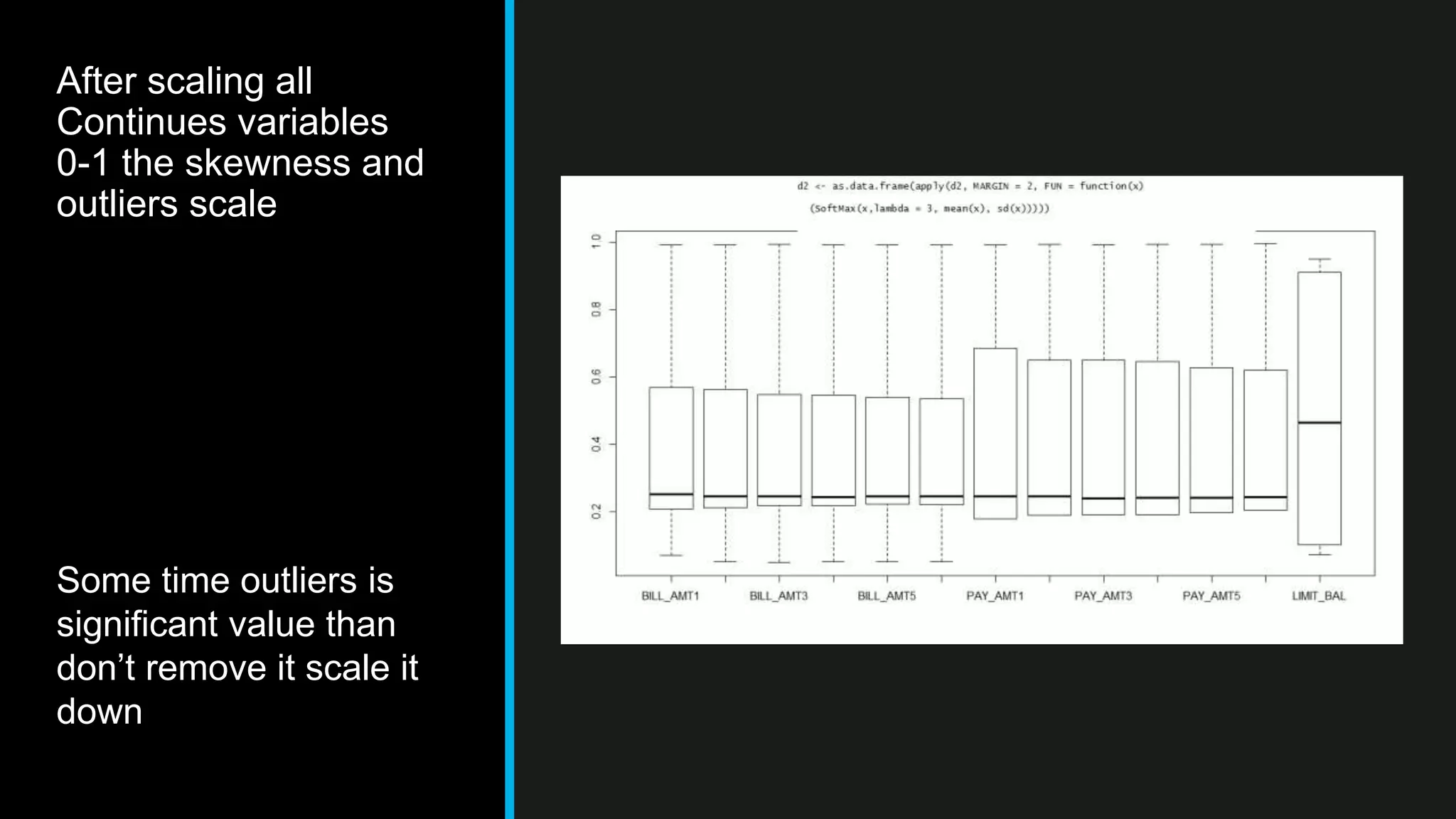
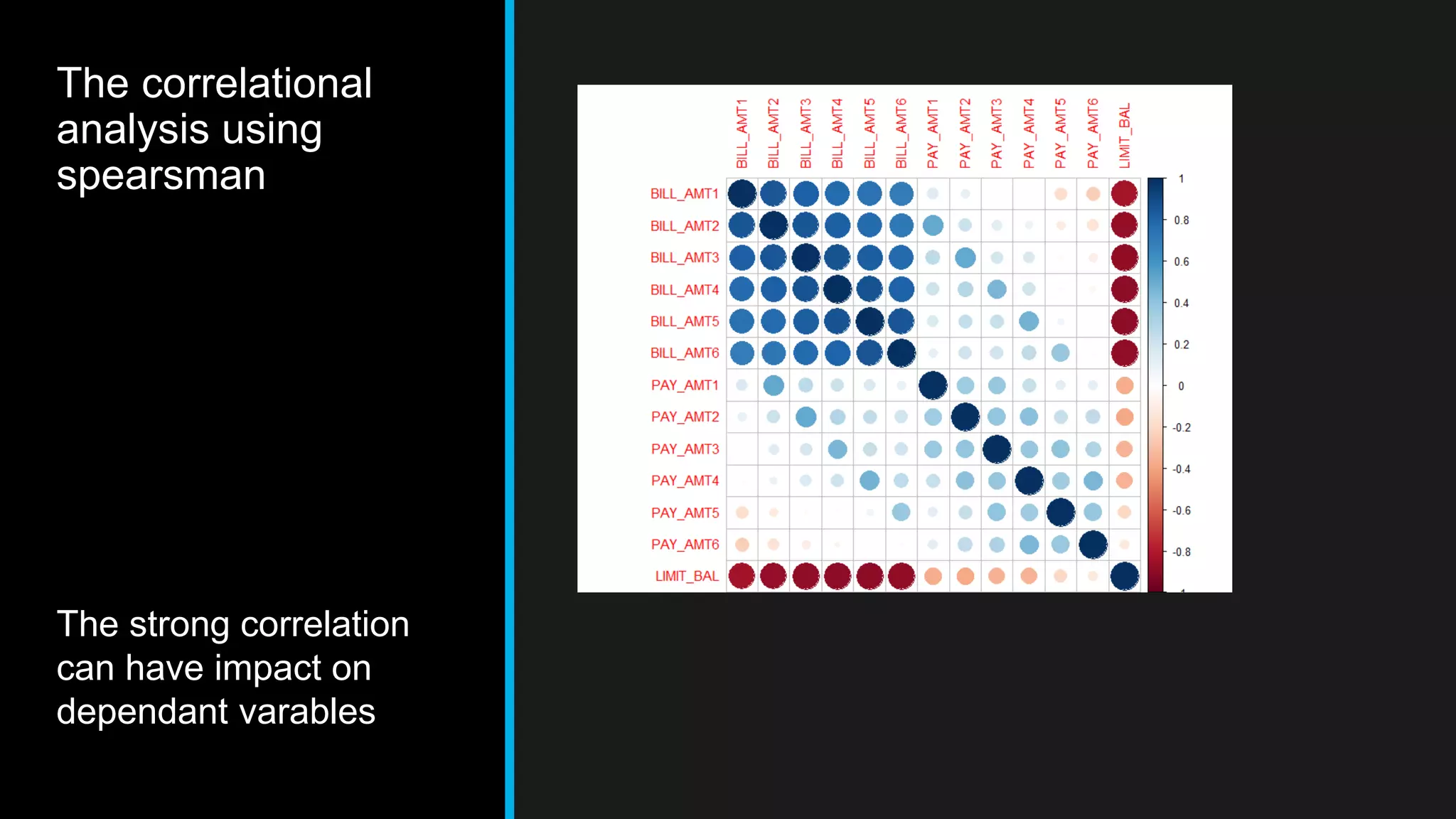
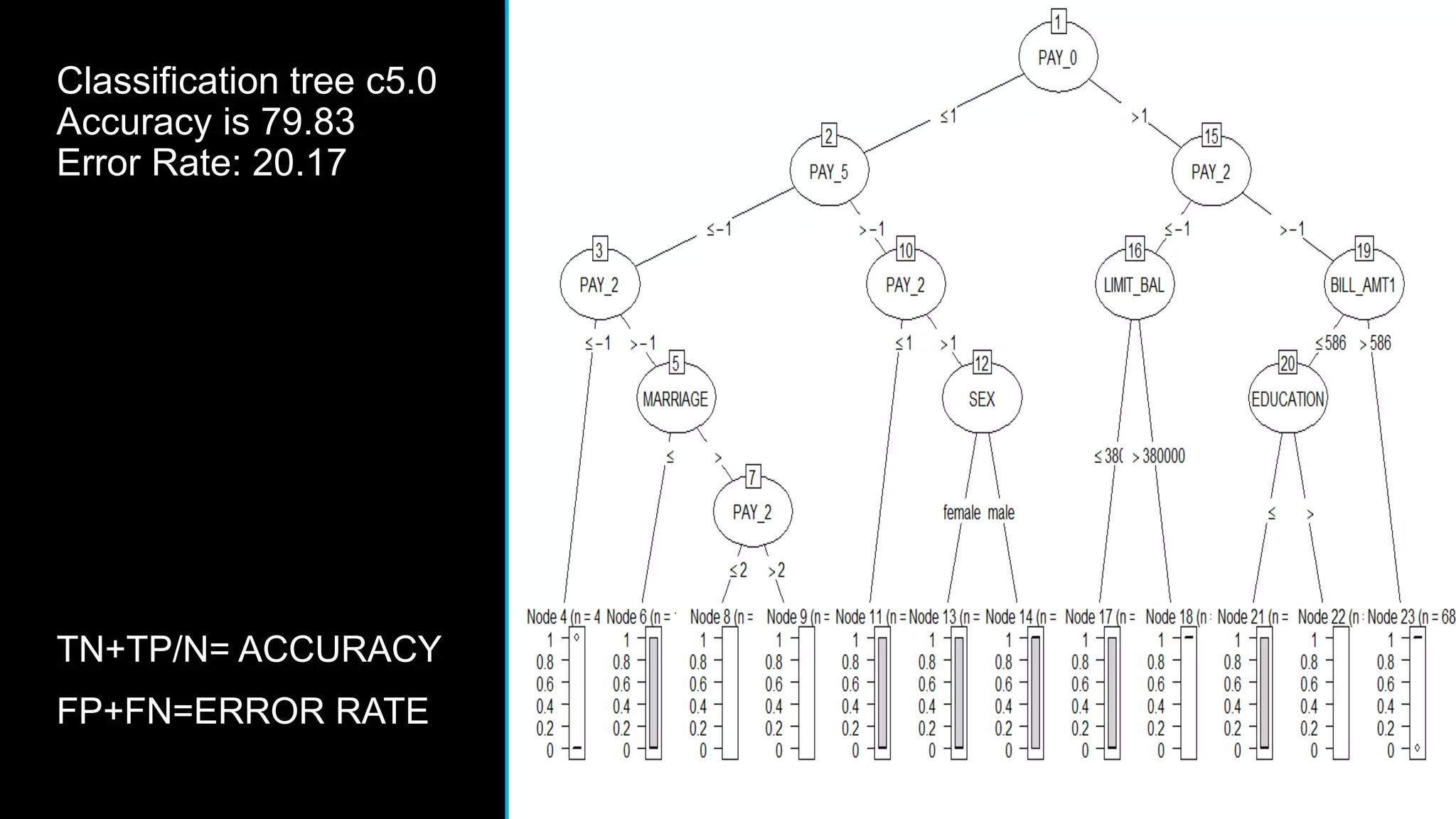
This document discusses big data analytics, including its definition, challenges, and applications, particularly in the context of Oman and open data. It emphasizes the importance of crowdsourcing for understanding customer insights and highlights case studies, such as sentiment analysis related to IKEA and Amazon. Additionally, it outlines the processes for big data analytics, including data gathering and modeling, while stressing the need for data infrastructure and legal policies for effective big data utilization.