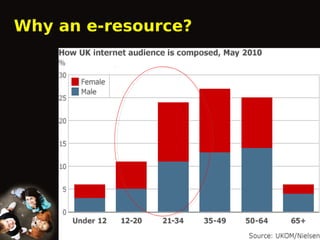
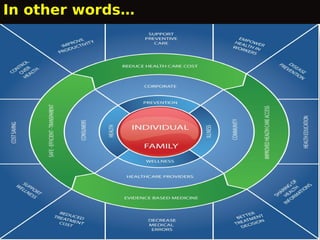
This document outlines the Proactive Intervention to Empower and Reach (P.I.E.R.) project, which aims to create an online health resource for patients, carers, and staff. The project was launched in 2010 to address issues like staff shortages and low patient satisfaction at a mental health service. P.I.E.R. will develop an interactive, multilingual e-resource allowing convenient access to illness and treatment information. By taking a collaborative approach and involving service users and carers, the e-resource aims to improve access, informed choice, empowerment, outcomes, and efficiency for patients, carers, staff, and the NHS. Several milestones are outlined, such as forming a