Shelf enviroment; By Salah ud din Shabab
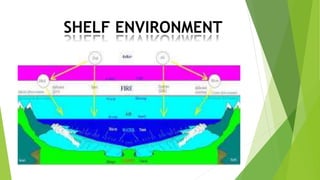
- 3. Definition Carbonate Shelf Environment. Inner shelf -nearshore, shallow water to subaerial. Middle shelf - , subtidal zone out to shelf break. Outer shelf - narrow zone including shelf break.
- 4. Diagnostic Features of Inner Shelf. Tectonic setting. Restricted to clear, shallow, tropical to subtropical. Geometry. Thin, laterally continuous beds over 1000’s sq km of shelf. Sequence. Shallowing upword – lagoonal mud to beach sand. Sedimentology. Algal lamination, stromatolite, mudcrack, tidal channel, dolomitization, evaporates.
- 5. Introduction Inner shelf environments can be well defined geographically in modern settings. In the geologic record, the term is used for low energy, shallow-water carbonates.
- 6. What is a restricted shelf? Defined as any part of a continental or island shelf with slow water circulation resulting in: Abnormal salinity Oxygen depletion Nutrient depletion Temperature extremes
- 7. Reduction of normal wave activity or current energy results from physical barriers (reefs, island, skeletal or oolitic sand shoals). In ancient settings, it may be inferred from stratigraphic evidence similar to those in modern settings.
- 8. With less stratigraphic resolution, restriction may be inferred from impoverishment of fauna or lithofacies. Presence of muddy sediment containing: Organic matter Pyrite Evaporites
- 9. Diagnostic Criteria (SBM) No single criterion is diagnostic for such environment. The most reliable guides of diagnosis are sequences and transitions. Lateral transitions. Vertical sequences
- 11. Vertical sequences are used to infer lateral relations
- 12. Biota is an important clue to restricted settings. Typically low faunal diversity. Dwarf fauna. Aberrant growth forms are clues of adverse conditions.
- 13. Abundance of burrows is characteristic, but not diagnostic.
- 14. Non-skeletal grain composition is not very diagnostic, but fecal pellets and peloids are characteristic sedimentary particles. They may comprise the entire sediment.
- 15. Grapestone aggregates and small intraclasts are also common.
- 16. Minerology is not indicative of depositional environment. Evaporites. Dolomites.
- 17. Diagnostic Criteria (scoffin) Bioturbated sand and silt substrates supporting epifauna and infauna Mollusks, benthic forams and echinoids Contribute coarse and fine grains to a poorly sorted, mixed terrigenous and calcareous sediments Carbonates are 40 to 60% of sediments Sand and gravel size with no mud Dominant mineralogy: calcite (50%), aragonite and Mg calcite (25% each)
- 18. Setting Lateral Facies Relationships Most reliable clue in restricted shelf recognition Seaward or windward deposits may produce restrictions Landward or leeward deposits may record the restricted conditions more dramatically
- 20. Islands formed by depositional or erosional topography of contemporary or earlier depositional episodes may also contribute to restriction
- 21. Restricted settings may also originate without significant physiographic barriers Broad expanses of shallow water (epeiric seas) may damp out tidal and wave energy Evaporation leading to hypersalinity Rainfall and runoff causing dilution Strong seasonal climate fluctuation influencing salinity
- 22. Restricted settings may also originate without significant physiographic barriers Broad expanses of shallow water (epeiric seas) may damp out tidal and wave energy Evaporation leading to hypersalinity Rainfall and runoff causing dilution Strong seasonal climate fluctuation influencing salinity
- 23. Shallow water, restricted environments develop further leeward or landward Covering vast expanses Little facies differentiation Lateral transitions are very gradual and fluctuate in position with time
- 24. Microfacies Characterized by a limited number of grain types: Carbonate or terrigenous mud Fecal pellets Peloids Grapestones Limited range of skeletal components Benthic forams, ostracods, gastropods, oysters, algal oncoids, serpulid worms and brachiopods
- 25. Indicators of slow accumulation rates are extensive: Micritization Boring Metal-oxide staining Encrustation
- 26. Typical standard microfacies (SMF) types: Grapestone-peloid-intraclast grainstone Laminated to bioturbated pellet mudstone Oncoid wackestone or floatstone Foraminiferal or dasyclad algal grainstone with peloids
- 27. Sequences Shallowing upward sequences common Series of cycles Supratidal – unfossiliferous, laminated, mudcracked, dolomitic, pelletal carbonated mudstone Intertidal – sparsely fossiliferous, pelletal carbonate mudstone interbedded with skeletal calcarenite Subtidal – fossiliferous, pelletal carbonate mudstones interbedded with stromatoporoids