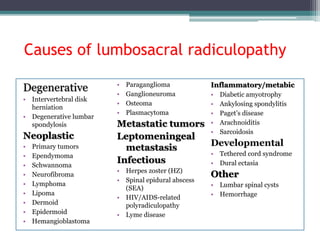
Lumbosacral radiculopathy, a prevalent condition primarily caused by degenerative spondyloarthropathies, affects approximately 3-5% of the population, with symptoms varying between genders and ages. It is diagnosed through a comprehensive history and physical examination, focusing on segmental abnormalities and pain characteristics, with differential diagnoses including neoplastic, infectious, and inflammatory disorders. Management may involve conservative therapies or surgical intervention depending on the severity and underlying cause of the radiculopathy.