This document provides an overview of sets and set theory concepts including:
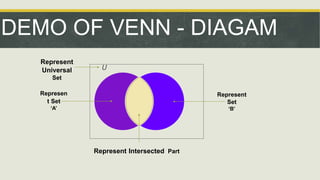
- German mathematician George Cantor developed the ideas of set as a mathematical theory in the 19th century and John Venn developed Venn diagrams to represent sets.
- Common set operations are defined including union, intersection, difference, complement, and examples are provided to demonstrate each operation.
- A Venn diagram uses overlapping circles to visually represent sets and the relationships between elements in different sets.