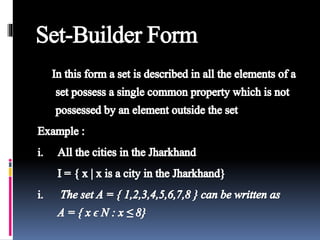
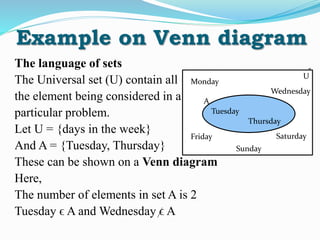
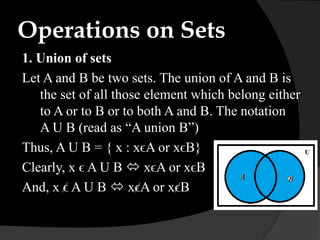
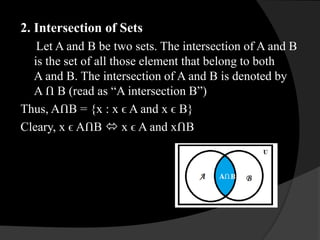
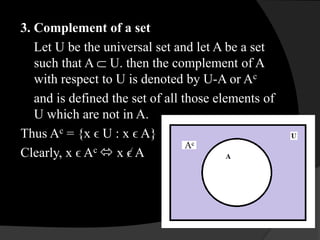
This document provides an introduction to sets and Venn diagrams. It defines what a set is, different ways to represent sets, and different types of sets. It then introduces Venn diagrams as a way to visually represent logical relationships between sets using circles and rectangles. An example Venn diagram is provided showing the relationship between days of the week. Finally, the document defines and provides examples of the set operations of union, intersection, and complement.