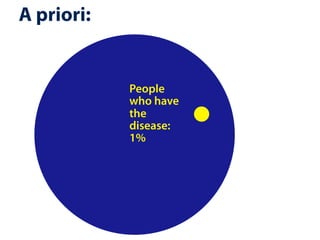
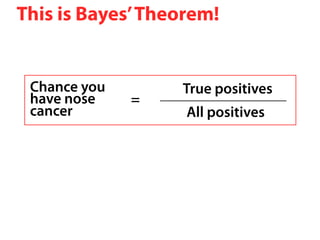
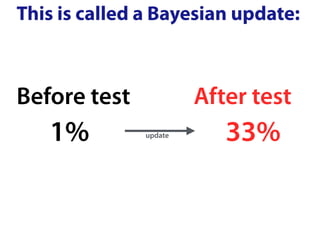
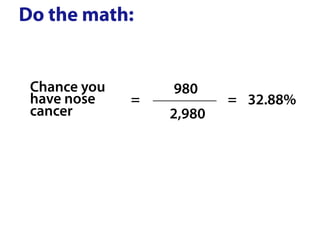The document explains Bayes' theorem by using a hypothetical example of a test for nose cancer. It states that 1 out of 100 people have nose cancer and the test is 98% accurate. For someone who tests positive, it calculates through Bayes' theorem that the likelihood they have nose cancer is approximately 33%, compared to their original 1% risk before taking the test. This Bayesian update demonstrates how additional information received from a test result can change the probability assessment.