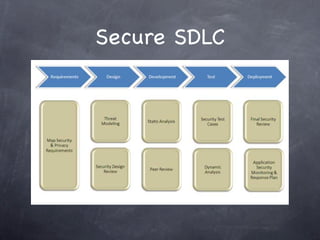
This document provides an overview of security topics that developers need to be aware of, including encryption, authentication, authorization, availability, and other technical security concepts. It discusses security at different levels, from physical security to application security to network security. It also covers security threats, designing security in from the start, balancing convenience and security, and best practices for secure coding and the software development lifecycle. The overall message is that security is holistic and requires consideration across technical, procedural, and human factors.