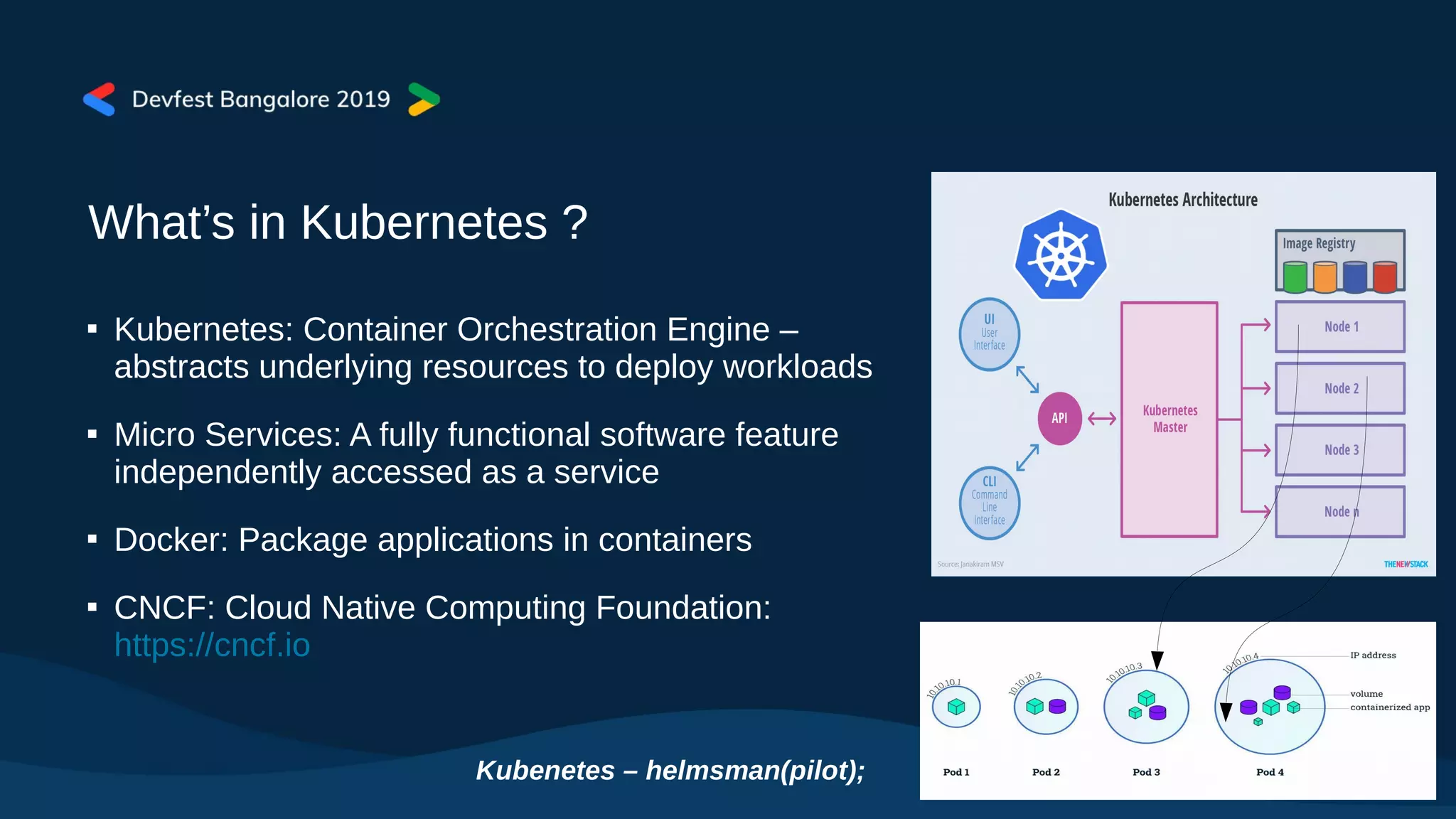
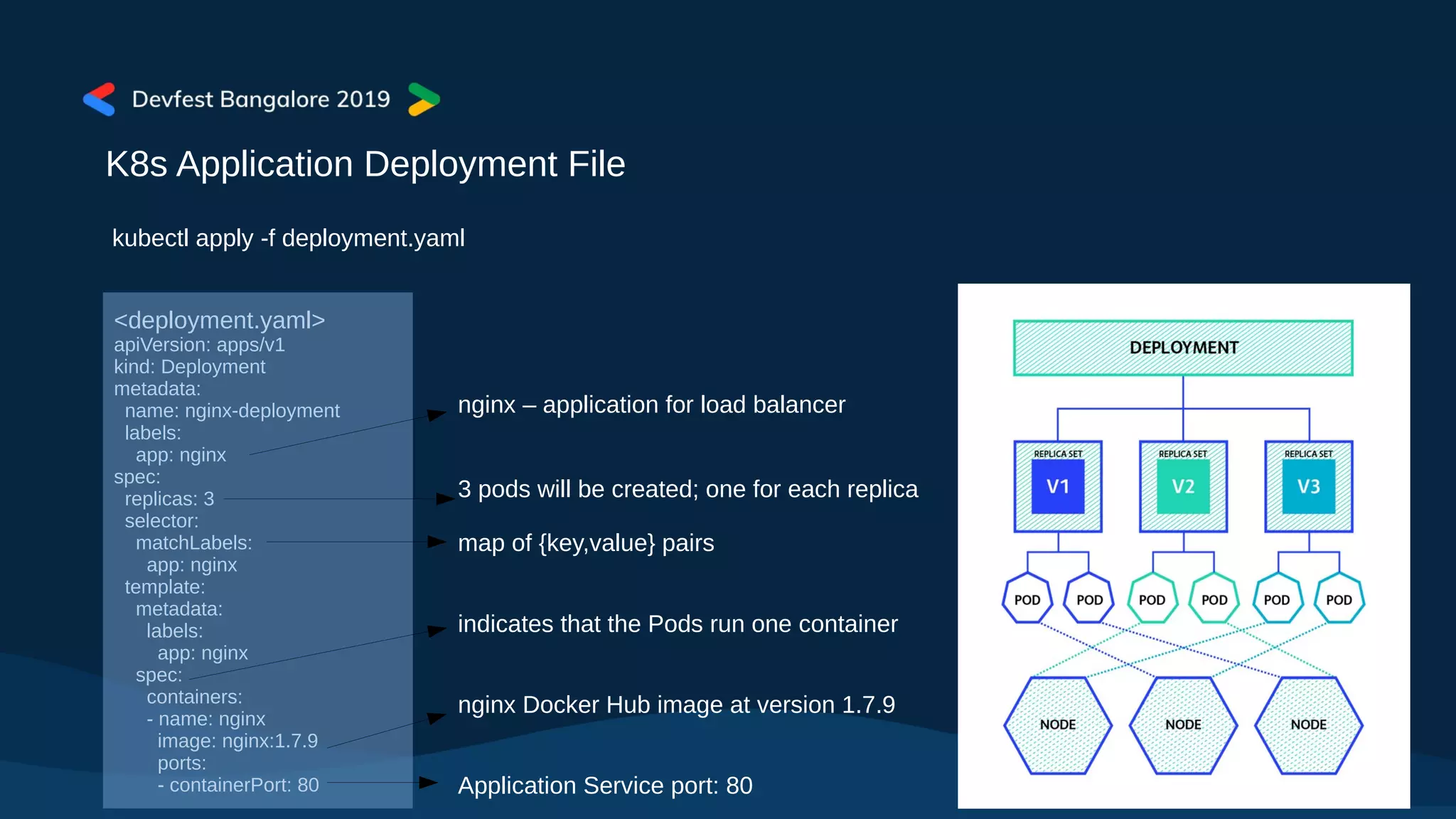
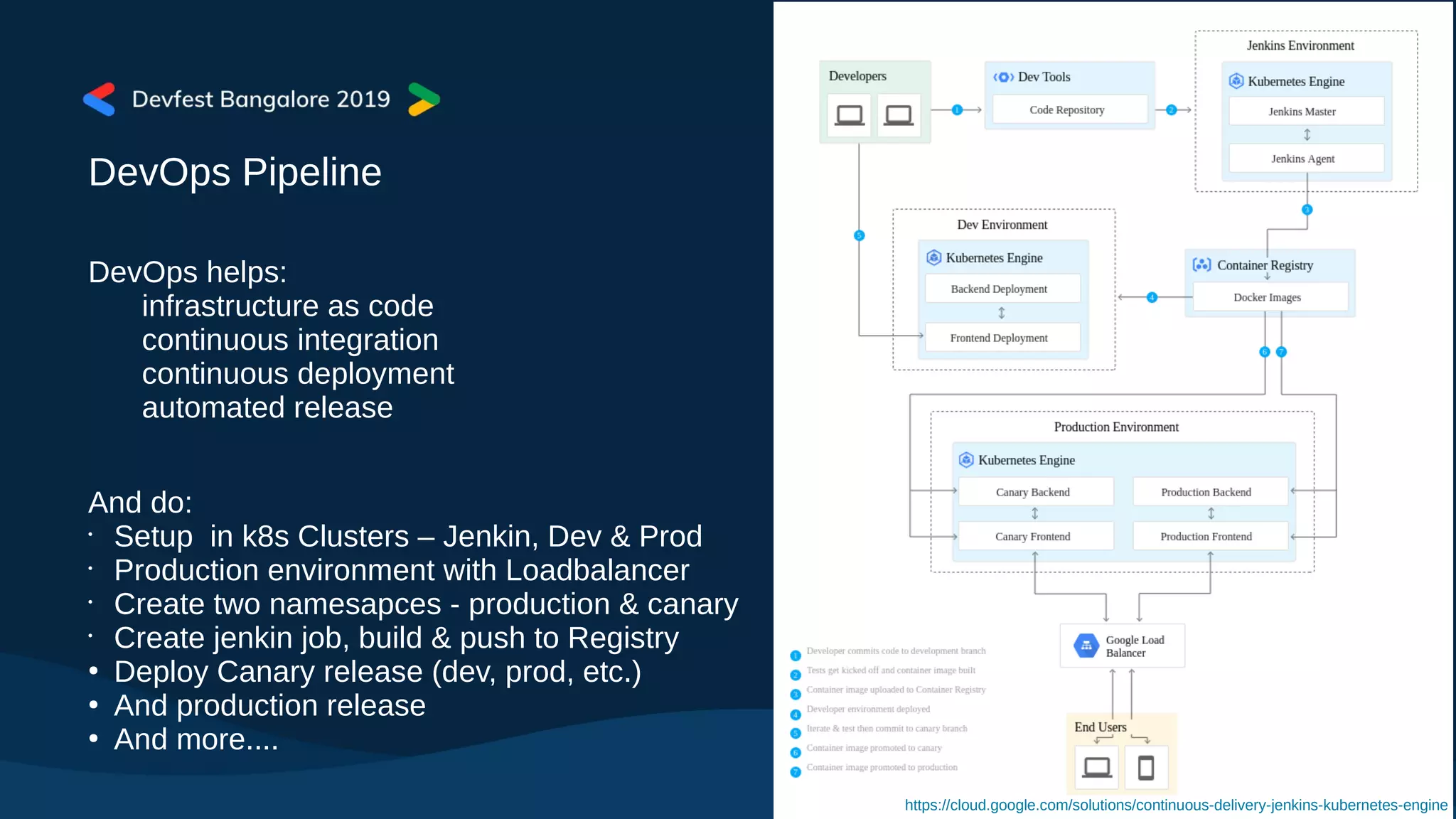
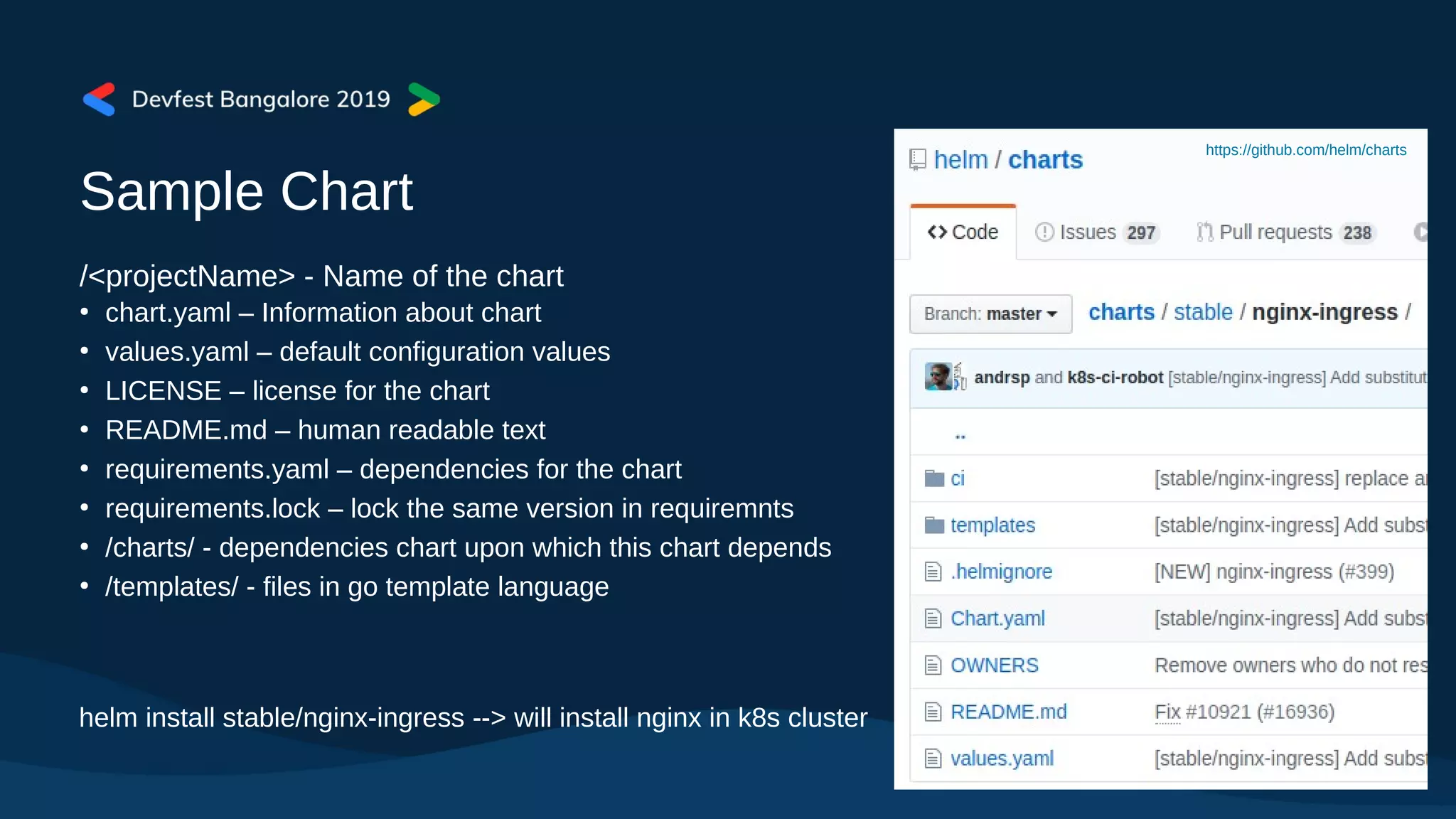
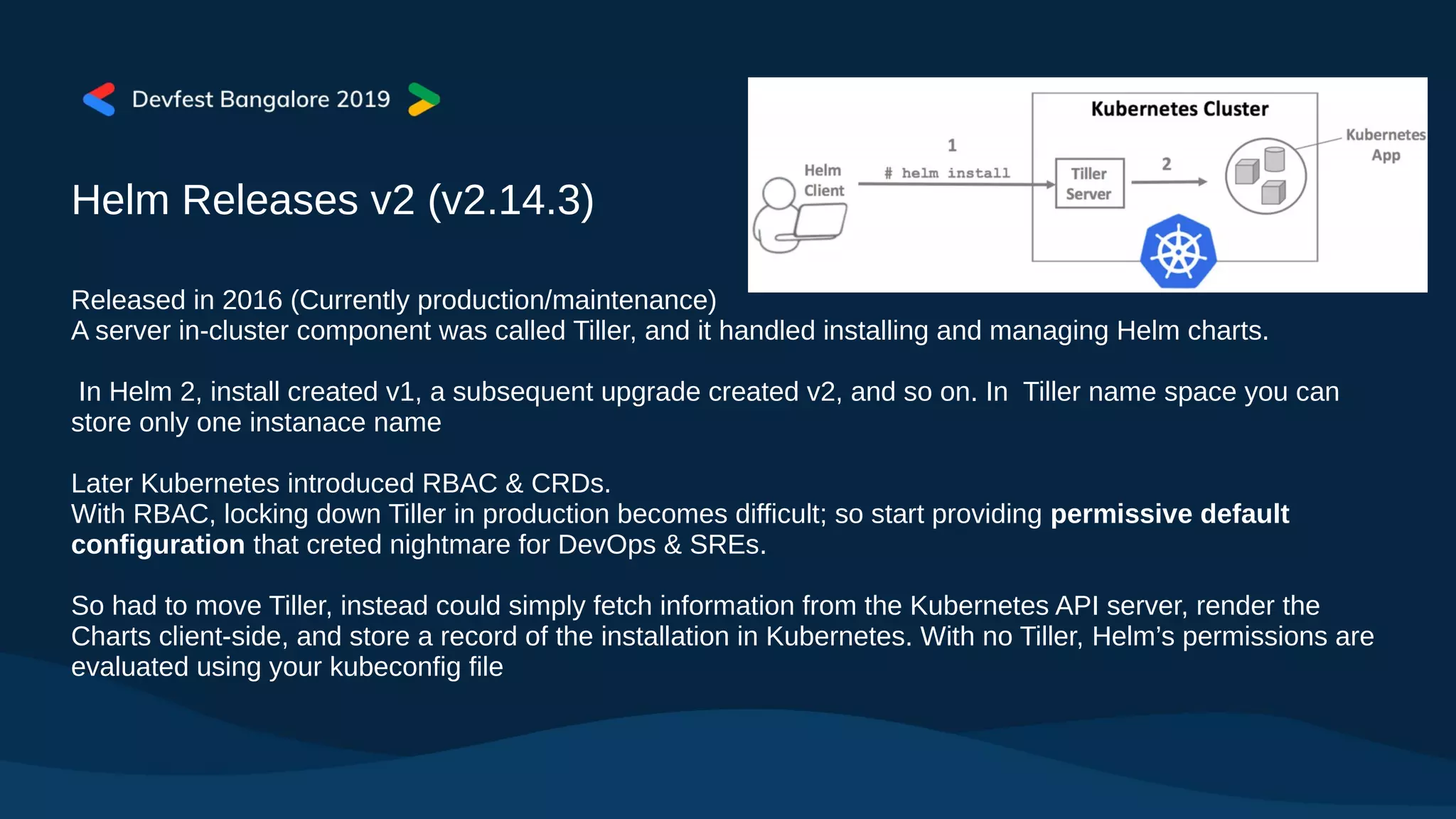
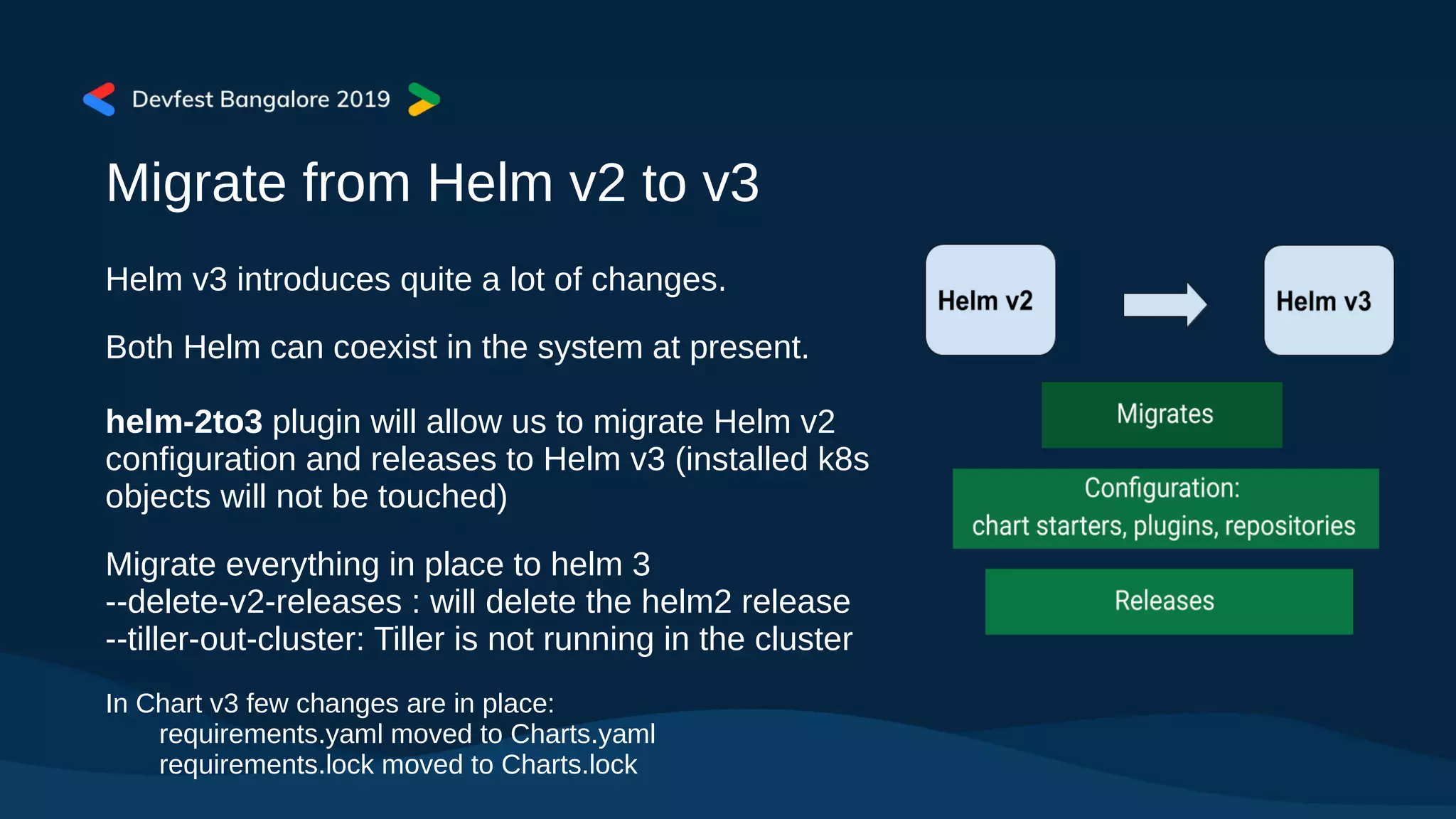
The document covers Kubernetes application deployment methods, focusing on Helm as a package manager that facilitates managing Kubernetes applications. It outlines various deployment strategies and introduces Helm 3, highlighting its significant updates such as the removal of the Tiller component, enhancements with library charts, and plans for migration from Helm 2. The content also includes a demo of deploying applications using Helm on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE).