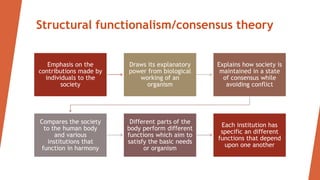
The document discusses key sociological theories of education including structural functionalism/consensus theory, conflict theory, symbolic interactionalism theory, and labelling theory. Structural functionalism views society as a system of interconnected parts that work together in harmony. Conflict theory emphasizes social divisions and power struggles over resources. Symbolic interactionism focuses on how people interact through symbols and follow social norms. Labelling theory examines how individuals are labeled and how those labels can shape their behavior and self-perception. The implications of these theories for education include maintaining social stability, addressing conflicts, using appropriate symbols for interaction, and avoiding negative labeling of students.