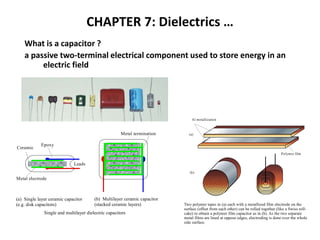
4661898.ppt
- 1. CHAPTER 7: Dielectrics … What is a capacitor ? a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field Metal termination Metal electrode Ceramic Epoxy Leads (b) Multilayer ceramic capacitor (stacked ceramic layers) (a) Single layer ceramic capacitor (e.g. disk capacitors) Single and multilayer dielectric capacitors (b) Al metallization Polymer film (a) Two polymer tapes in (a) each with a metallized film electrode on the surface (offset from each other) can be rolled together (like a Swiss roll- cake) to obtain a polymer film capacitor as in (b). As the two separate metal films are lined at oppose edges, electroding is done over the whole side surface.
- 2. Capacitors What is a dielectric material ? an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field What are the ways of increasing capacitance? d A ε ε C . . . dV dQ C r o Co +Qo Qo E V +Q Q C E V Dielectric i (t) V
- 3. Polarization Polarization … polar molecules vs. non-polar molecules Can non-polar molecules become polar ? â Q p The origin of electronic polarization. (a) A neutral atom in E = 0. (b) Induced dipole moment in a field Electron cloud Atomic nucleus pinduced E Center of negative charge x C O The definition of electric dipole mome Electric Dipole Moment,
- 4. Polarization How do dielectrics increase the capacitance of a capacitor ? A Q P P Co +Qo Qo E V +Q Q C E V Dielectric i (t) V +Q E Q V Area =A p total P QP +QP d (c) QP +QP Boundpolarization chargesonthesurfaces Polarization,
- 5. Polarization Susceptibility, Χe: A proportionality constant that indicates the degree of polarization of a dielectric material in response to an applied electric field. (dimesnionless) Permittivity: A measure of how an electric field affects, and is affected by, a dielectric medium. (F/m) polarizability … dielectric constant … are material properties. In a way they are equivalent to what mobility is for conductors and semiconductors. A Q P P E ε χ P o e r e ε 1 χ αE pinduced
- 6. Polarization Mechanism Dependence of ε’r & ε”r frequency depends on polarization mechanism: a. Electronic b. Ionic c. Interfacial d. Orientational
- 7. POLARIZATION MECHANISMS Ionic: polarization caused by relative displacements between positive and negative ions in ionic crystals p+ p- x p'+ p'- E Cl Ð Na + (a) (b) (a) A NaCl chain in the NaCl crystal without an applied field. Average or net dipole moment per ion is zero. (b) In the presence of an applied field the ions become slightly displaced which leads to a net average dipole moment per ion.
- 8. POLARIZATION MECHANISMS Electronic: the stretching of atoms/electronic clouds under an applied E-field (in covalent solids) (a) Valence electrons in covalent bonds in the absence of an applied field. (b) When an electric field is applied to a covalent solid, the valence electrons in the covalent bonds are shifted very easily with respect to the positive ionic cores. The whole solid becomes polarized due to the collective shift in the negative charge distribution of the valence electrons.
- 9. POLARIZATION MECHANISMS Interfacial: charge accumulation at defective interfaces (2 material or 2 regions of same material) leads to the formation of a net polarization vector E Accumulated charge (b) Electrode Dielectric Electrode Fixed charge Mobile charge (a) E Grain boundary or interface (c) (a) A crystal with equal number of mobile positive ions and fixed negative ions. In the basence of a field there is no net separation between all the
- 10. POLARIZATION MECHANISMS Orientational (Dipolar): in “rigid polarized molecule” materials, an applied field aligns the permanent dipoles to yield a net polarization vector Cl H+ po (a) (b) pav = 0 q +Q Q F = Q E F po = aQ t E pav ¹ 0 E (c) (d)
- 12. DIELECTRIC LOSS The dielectric constant is frequency dependent … why ? The polarization process is not instantaneous … i.e. it takes a finite amount of time for the molecules to align themselves. If the applied field is changing so fast that the molecules cannot respond to it at all … then the polarization is … zero! Therefore ε is frequency dependent … ' ' r ' r r jε ε ε
- 13. DIELECTRIC LOSS The imaginary part represents dielectric “losses” due to “slow” polarization. v = Vo sint P = Po sin(t - ) E = Eo sint (a) r '' r ' r (0) 1 1/ 10/ 100/ 0.01/ 0.1/ r' and r'' (b) ' ' r ' r r jε ε ε t t E Eo E p d(0)E pÐd(0)E d(0)Eo 0 The dc field is suddenly changed from Eo to E at time t = 0. The induced dipole moment p has to decrease from d(0)Eo to a final value of d(0)E. The decrease is achieved by random collisions of molecules in the gas.
- 14. DIELECTRIC LOSS ' ' r ' r r jε ε ε d ε ωAε d ε Aε jω d )A jε (ε ε jω C jω Y ' ' r o ' r o ' ' r ' r o ' r ' ' r ε ε tanδ ... tangent loss v = Vo sint P = Po sin(t -) C Conductance = Gp = 1/Rp v = Vo sint tanδ ε ε ωE ε ωε d V dA 1 R V W ' r o 2 " r o 2 2 2 P vol Dielectric Loss per unit volume,
- 15. DIELECTRIC LOSS f ε 10 MHz 0 ε’r ε”r 1 2 1. For the dielectric material as in the figure, calculate the loss tangent at 10 MHz frequency. If the parallel plate capacitor is formed with the material, where the separation is 1mm, plate area is 1mm2 and 1V is applied across… 2. Calculate the value of resistance and capacitance. 3. Calculate the power loss per unit volume. ' r ' ' r ε ε tanδ tangent loss 1. ' ' r o P ε ωAε d R 2. d ε Aε C ' r o P tanδ ε ε ωE ε ωε d V W 3. ' r o 2 " r o 2 2 vol =0.5 =1.8x106 ohm =1.7x10-14 F =556 Wcm-3
- 16. Matter Polarization & Permittivity C C Q Q ε 0 0 r a Q p ˆ The definition of electric dipole moment. Electric Dipole Moment, The origin of electronic polarization. (a) A neutral atom in E = 0. (b) Induced dipole moment in a field Electron cloud Atomic nucleus pinduced E Center of negative charge x C O αE pinduced β x Fr Ze E Fe )E β e Z ( (Ze)x pe 2 2 Induced Electric Dipole Moment, Spring action
- 17. Matter Polarization & Permittivity The origin of electronic polarization. (a) A neutral atom in E = 0. (b) Induced dipole moment in a field Electron cloud Atomic nucleus pinduced E Center of negative charge x C O )E e Z ( (Ze)x pe 2 2 Induced Electric Dipole Moment, Removal of applied E field cause the vibration with a resonant frequency… 2 2 dt x d Zm x e t) (ω x x(t) o 0 cos 2 0 e Zm β ω Electronic polarization resonance frequency 2 2 0 2 e e m ω Ze Electronic Polarizability F=ma
- 18. Permittivity: Electronic Polarization Area = A ptotal P -QP +QP (c) -QP +QP Bound polarization charges on the surfaces (b) d +Q E -Q V (a) (a) When a dilectric is placed in an electric field, bound polarization charges appear on the opposite surfaces. (b) The origin of these polarization charges is the polarization of the molecules of the medium. (c) We can represent the whole dielectric in terms of its surface polarization charges +QP and -QP. Total Polarization A Q Ad d Q volume p P p p total E P o e p E N Np P e induced e o e N 1 Also, total polarization Total Polarization =surface polarization charge density!
- 19. Permittivity: Electronic Polarization Area = A ptotal P -QP +QP (c) -QP +QP Bound polarization charges on the surfaces (b) d +Q E -Q V (a) (a) When a dilectric is placed in an electric field, bound polarization charges appear on the opposite surfaces. (b) The origin of these polarization charges is the polarization of the molecules of the medium. (c) We can represent the whole dielectric in terms of its surface polarization charges +QP and -QP. before insertion of dielectric medium 0 0 o o o o A Q d C Q d V E free surface charge density A Qo o after insertion of dielectric medium p o Q Q Q dividing by the area, A p E 0
- 20. Permittivity: Electronic Polarization Area = A ptotal P -QP +QP (c) -QP +QP Bound polarization charges on the surfaces (b) d +Q E -Q V (a) (a) When a dilectric is placed in an electric field, bound polarization charges appear on the opposite surfaces. (b) The origin of these polarization charges is the polarization of the molecules of the medium. (c) We can represent the whole dielectric in terms of its surface polarization charges +QP and -QP. Substitution for surface charge density Relative permittivity o o r Q Q E e 0 ) 1 ( e r 1 0 1 e r N Relation between polarization mechanism to relative permittivity
- 21. Clausius-Mossotti Equation The bulk electric field assumption is not valid in the atomic level P ε E Elocal 0 3 1 0 1 1 e r r N Relation between polarization mechanism to relative permittivity Clausius-Mossotti Equation For electronic polarization Eloc x Electric field at atomic scale E = V/d E Eloc The electric field inside a polarized dielectric at the atomic scale is not uniform. The local field is the actual field that acts on a molecules. It can be calculated by removing that molecules and evaluating the field at that point from the charges on the plates and the dipoles surrounding the point. Lorentz Field
- 22. Total Polarization 0 3 1 1 i i r r N Clausius-Mossotti Equation For ionic polarization loc d loc i loc e av E E E p i i e e r r N N 0 3 1 1 1 Total Polarization Relative permittivity due to ionic and electronic polarization
- 23. Total Polarization 7.9 Electronic and ionic polarization in KCl KCl has the FCC crystal structure. Lattice parameter is 0.629 nm. The ionic polarizability per ion pair (per K+-Cl- ion) is 4.58 10-40 F m2. The electronic polarizability of K+ is 1.264 10-40 F m2 and Cl- is 3.408 10-40 F m2. Calculate the dielectric constant under dc operation and at optical frequencies. Experimental values are 4.84 and 2.19. FCC… 4 KCl ion pairs per unit cell. The number of ion pairs, or individual ions, per unit volume (N) is: 3 9 3 m 10 629 . 0 4 4 a N = 1.607 1028 m-3 i i e i e i r r N Cl N K N ) ( ) ( 3 1 1 1 0 under dc operation ) ( ) ( 3 1 1 1 0 Cl N K N e i e i rop rop under optical frequency r(op) = 2.18 Example 7.2, 7.3