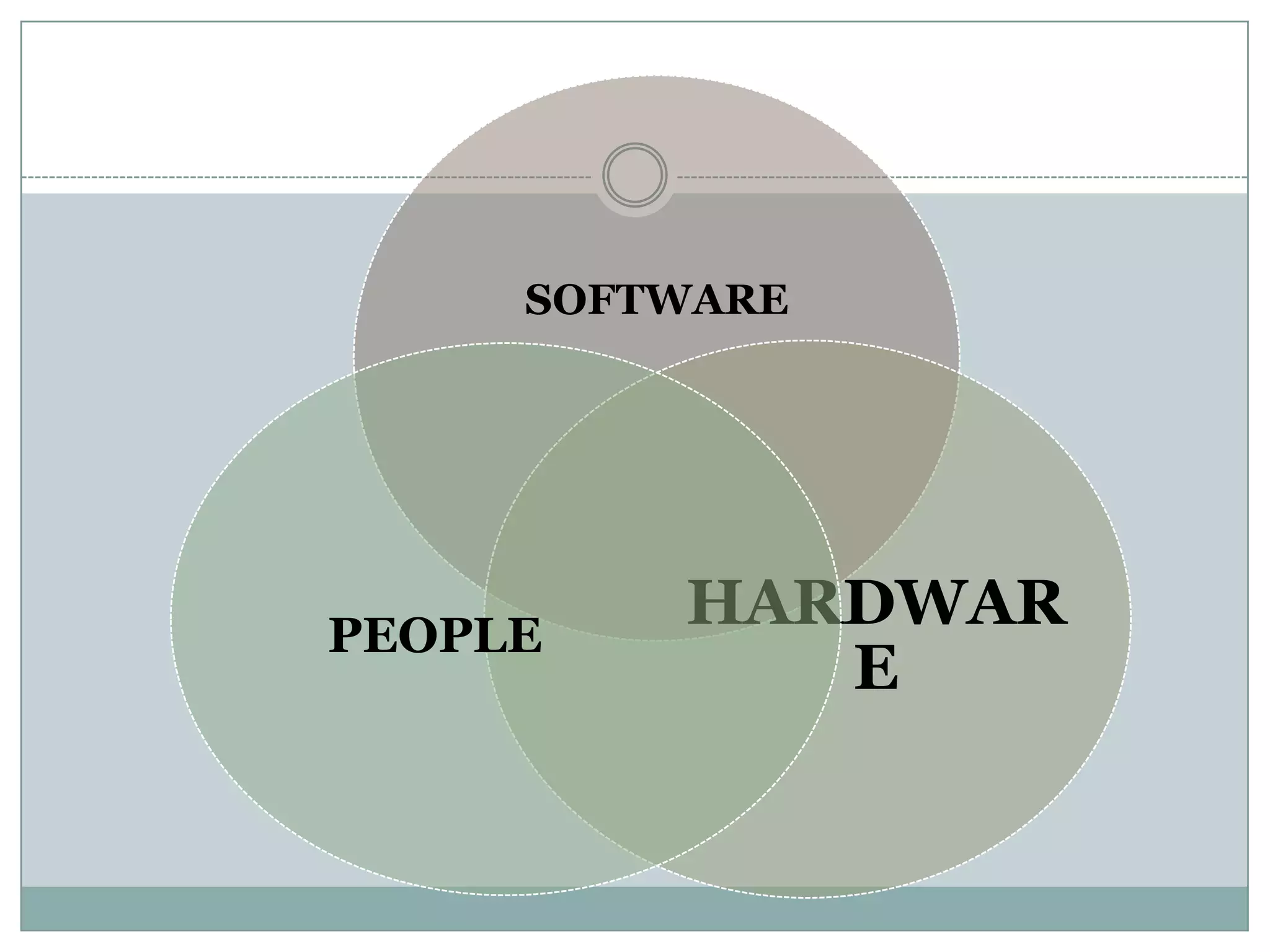
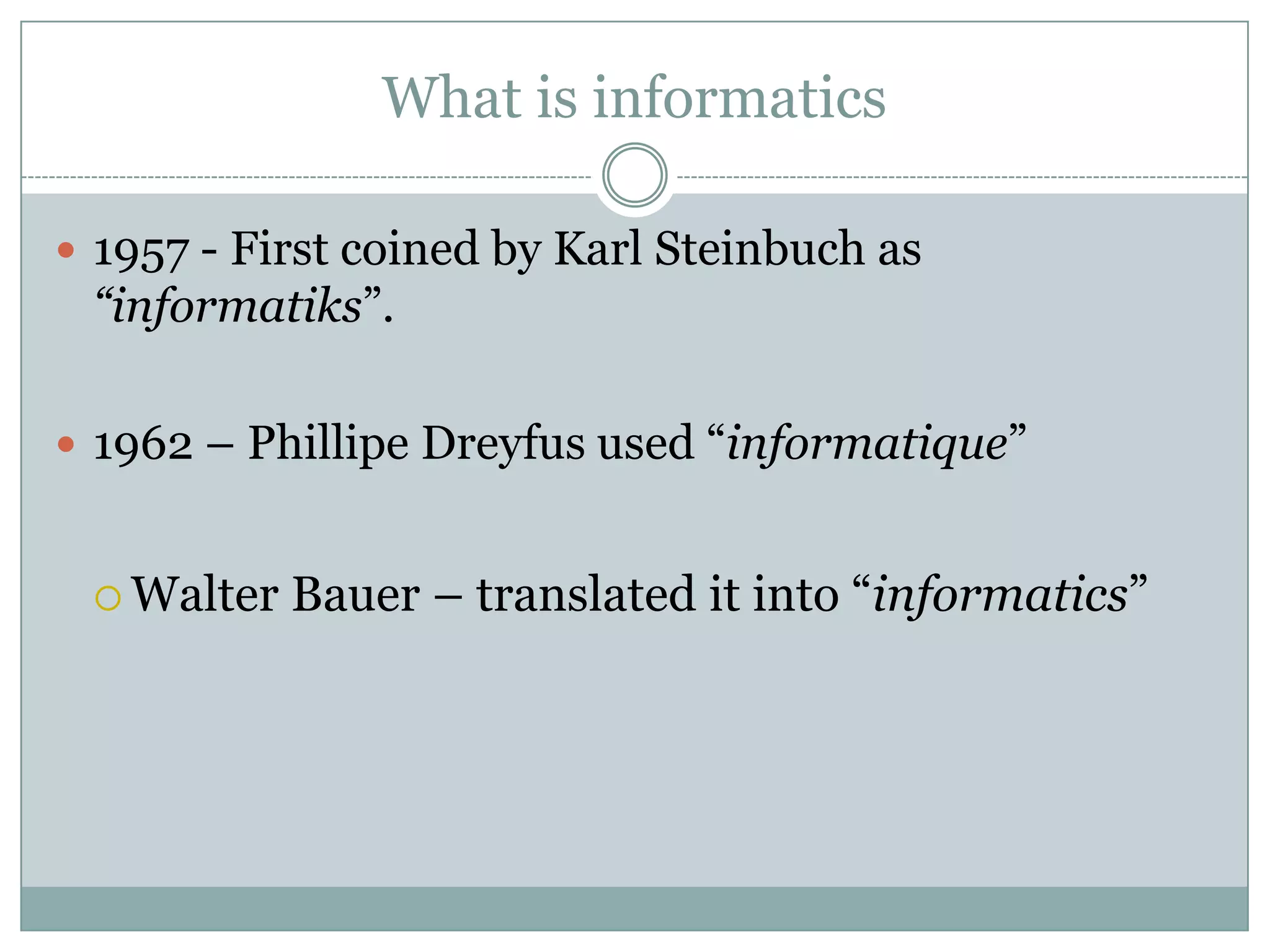
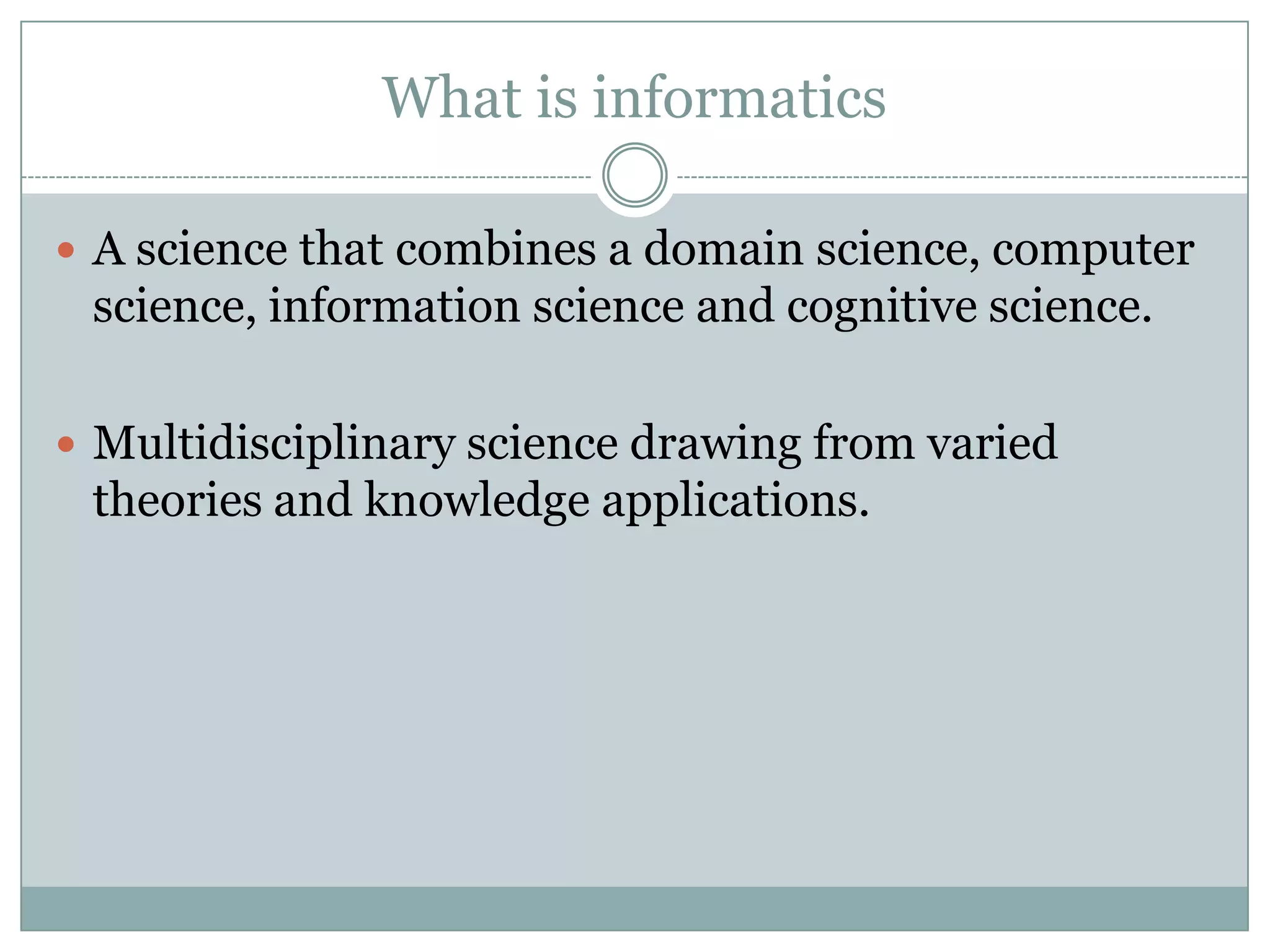
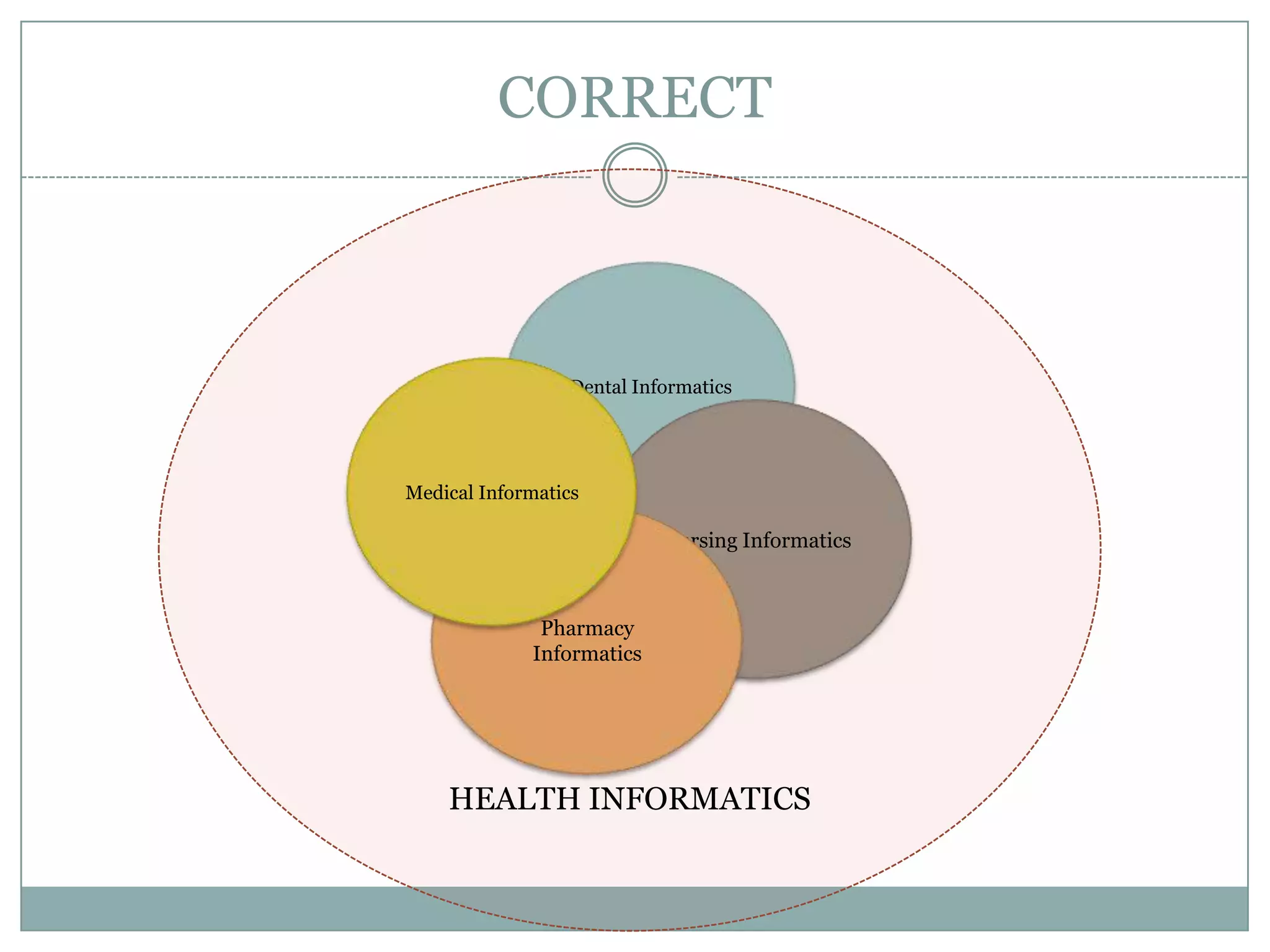
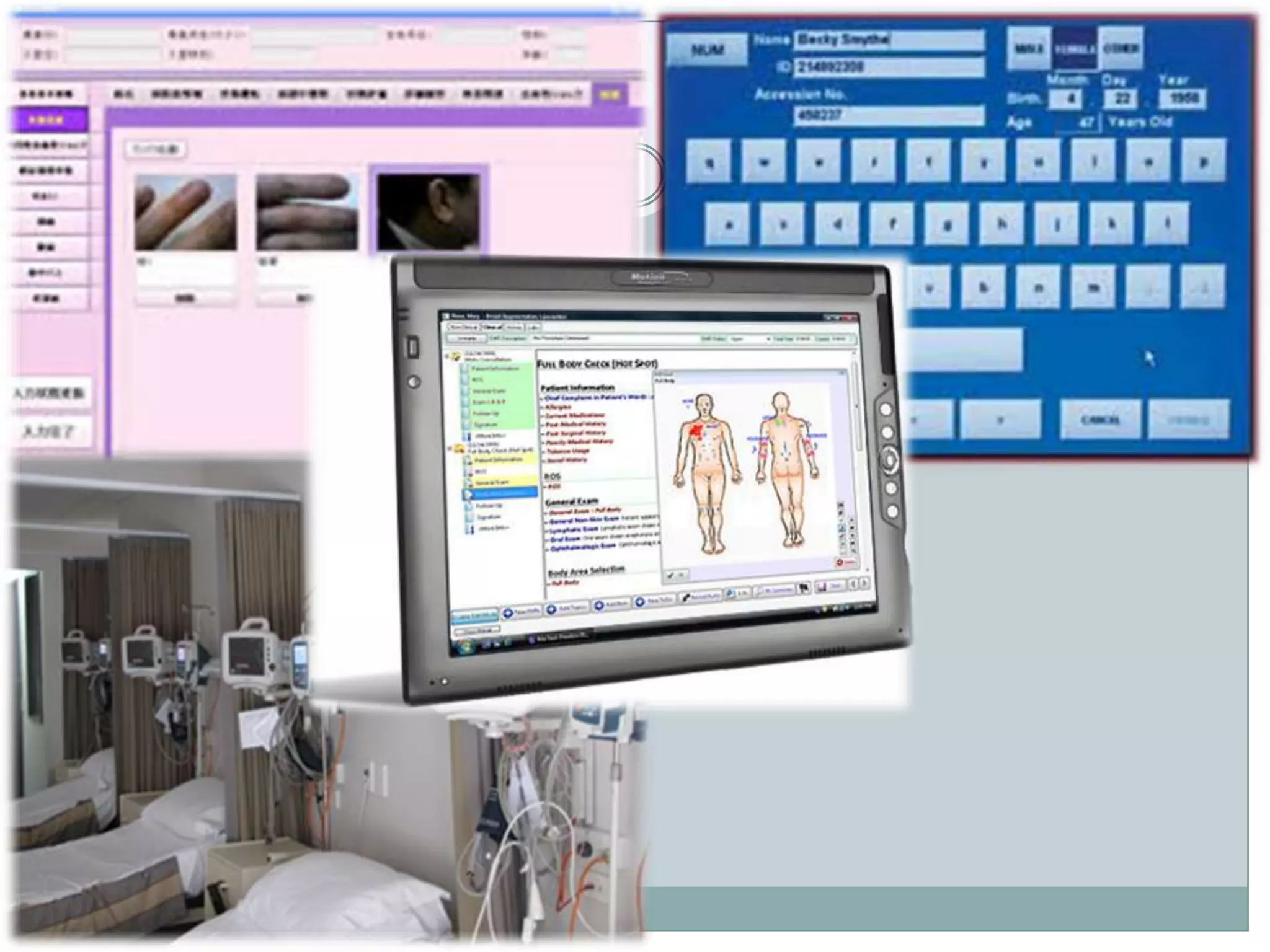
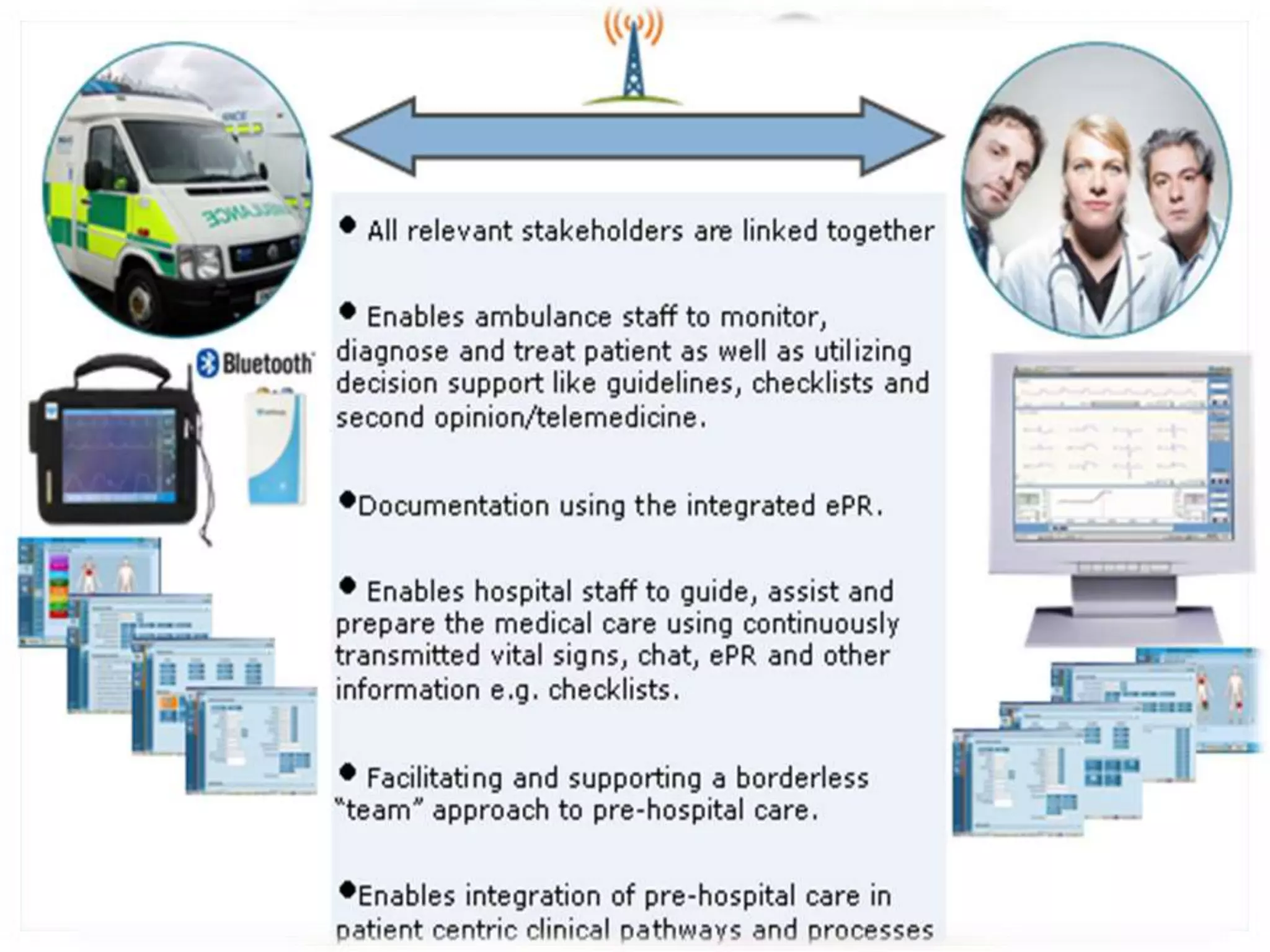
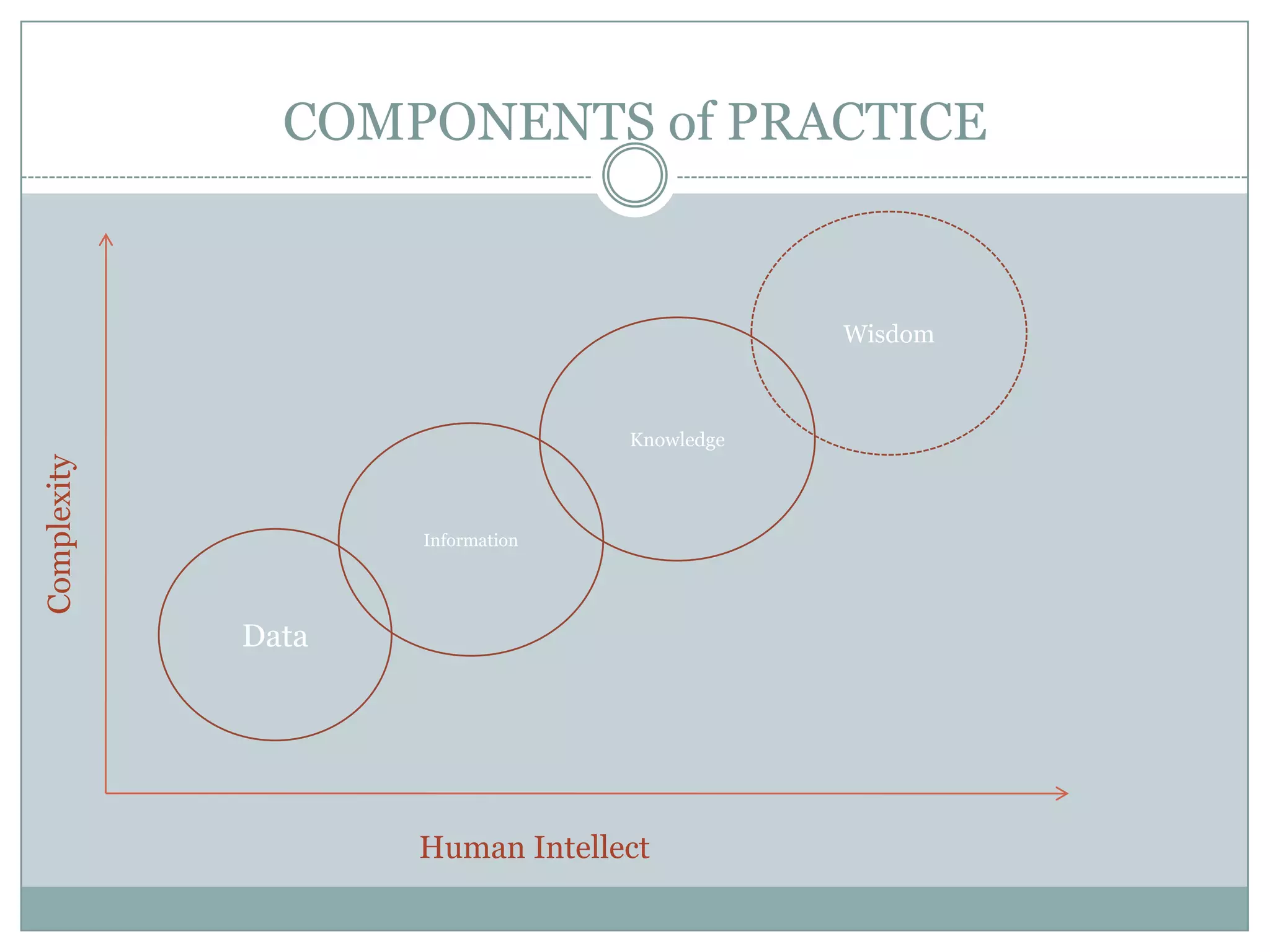
Nursing informatics is an established and growing specialty area in nursing that employs information technologies. It combines nursing science, computer science, and information science. Nursing informatics helps manage and communicate data, information, and knowledge to support decision-making by patients, nurses, and other providers. The goal is to improve care through the effective use of information technology.