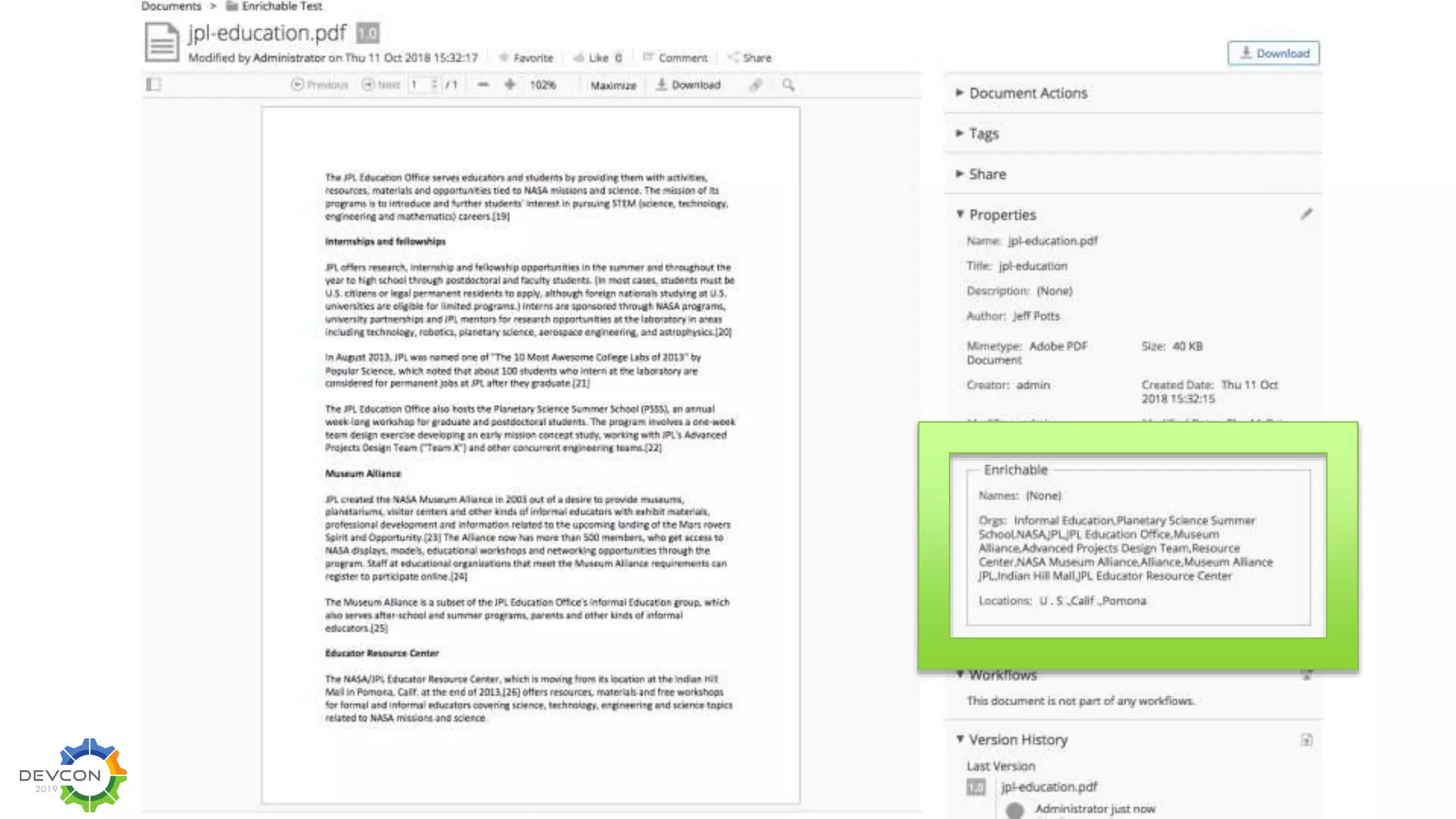
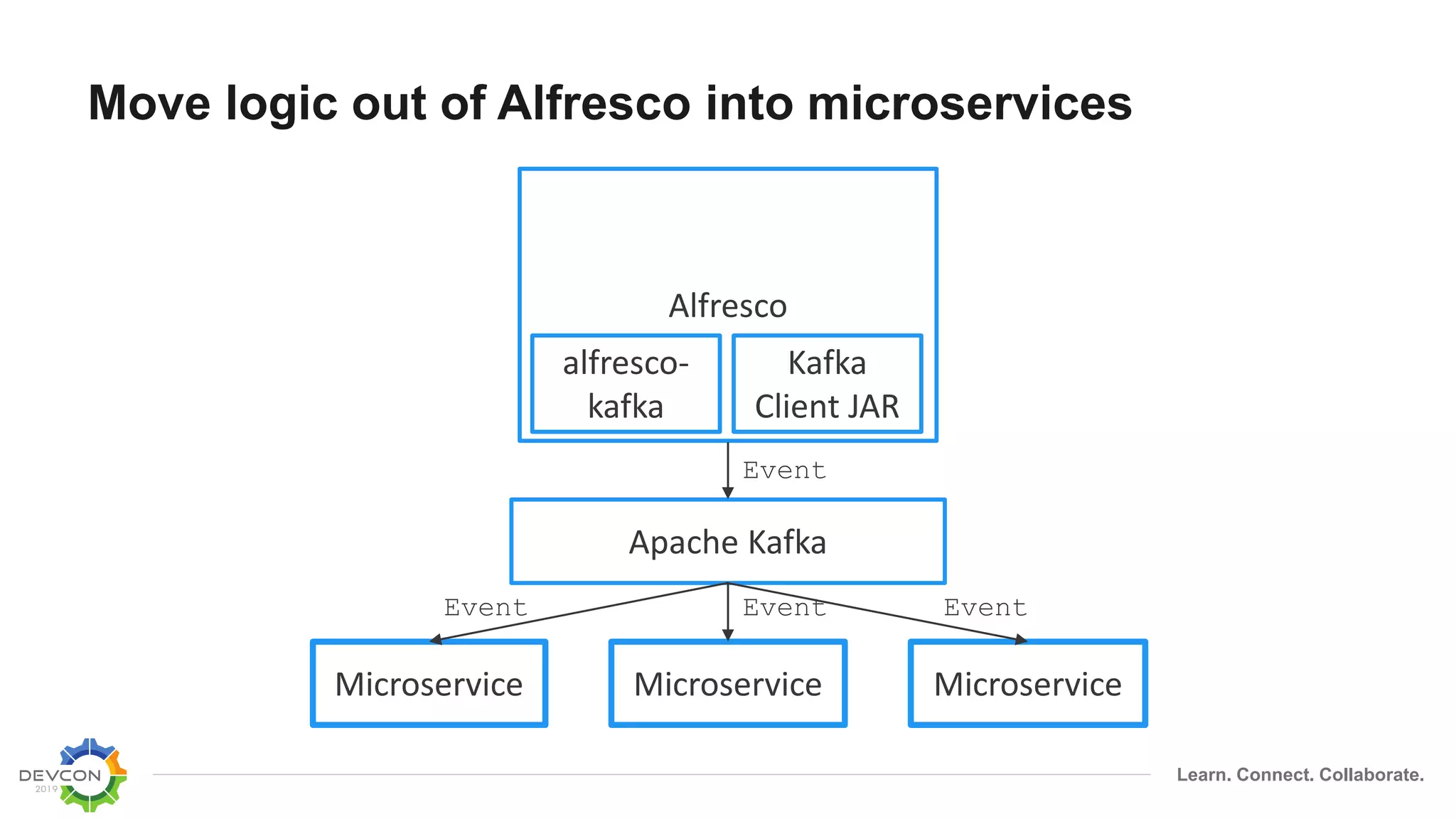
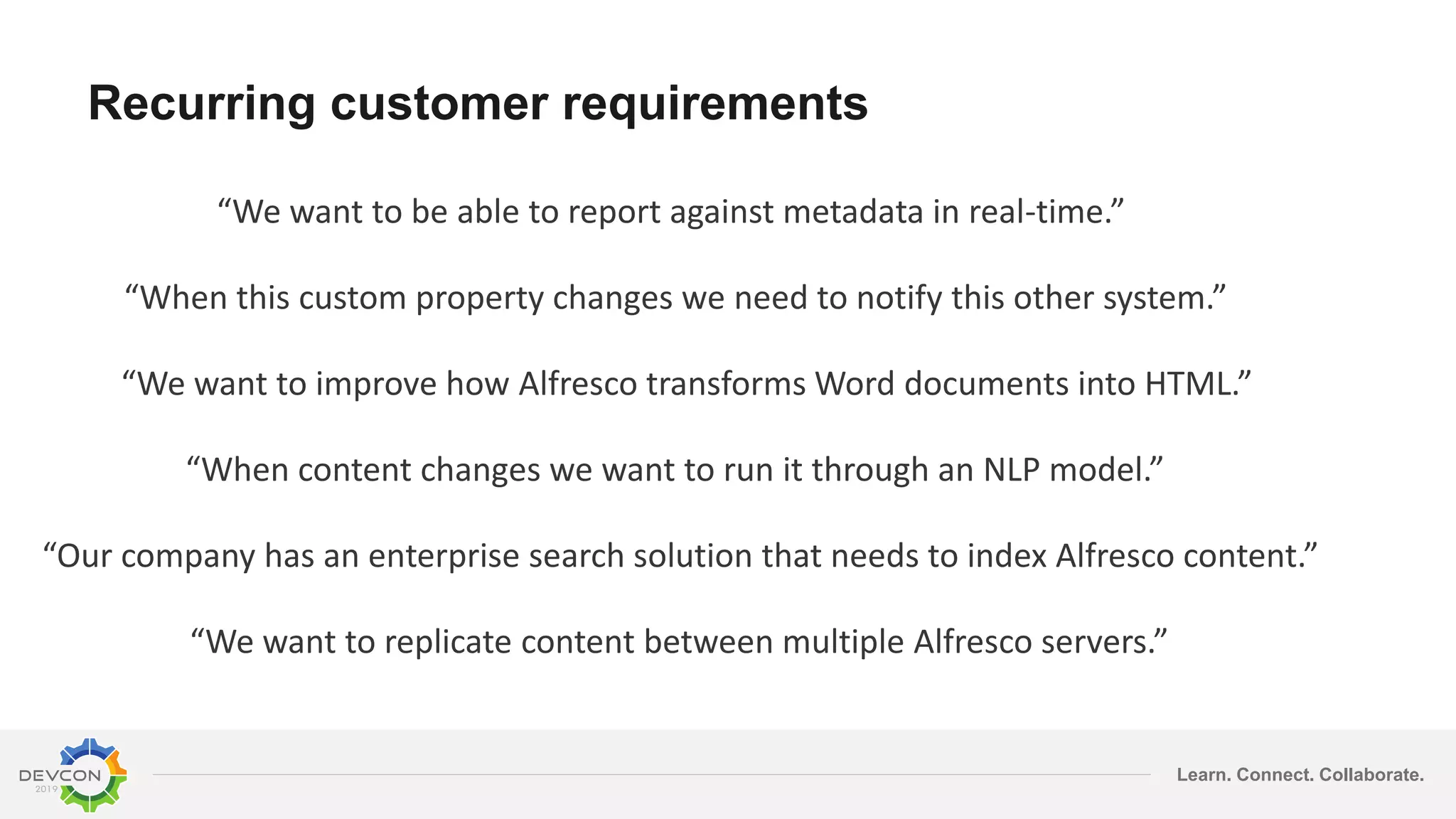
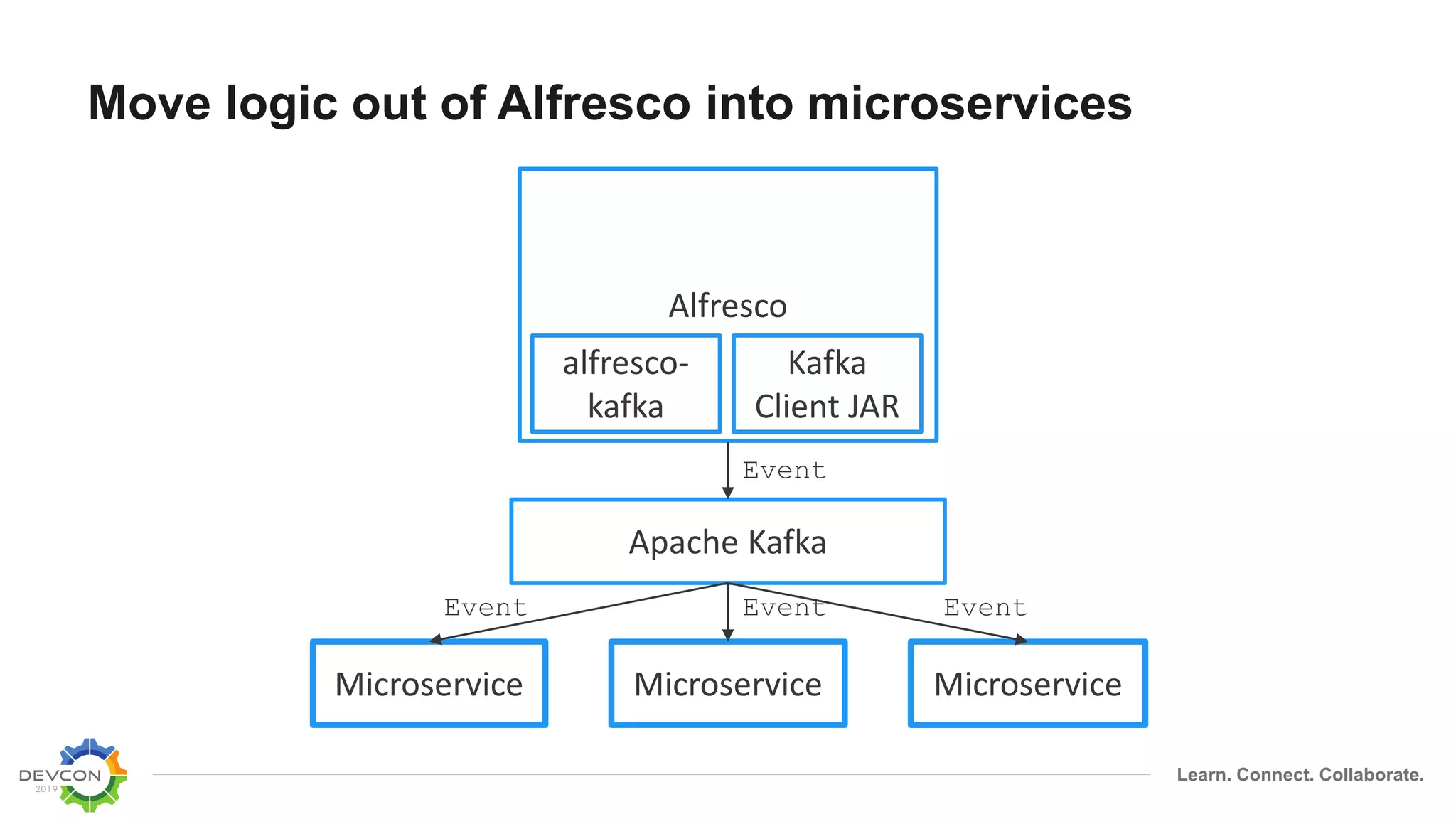
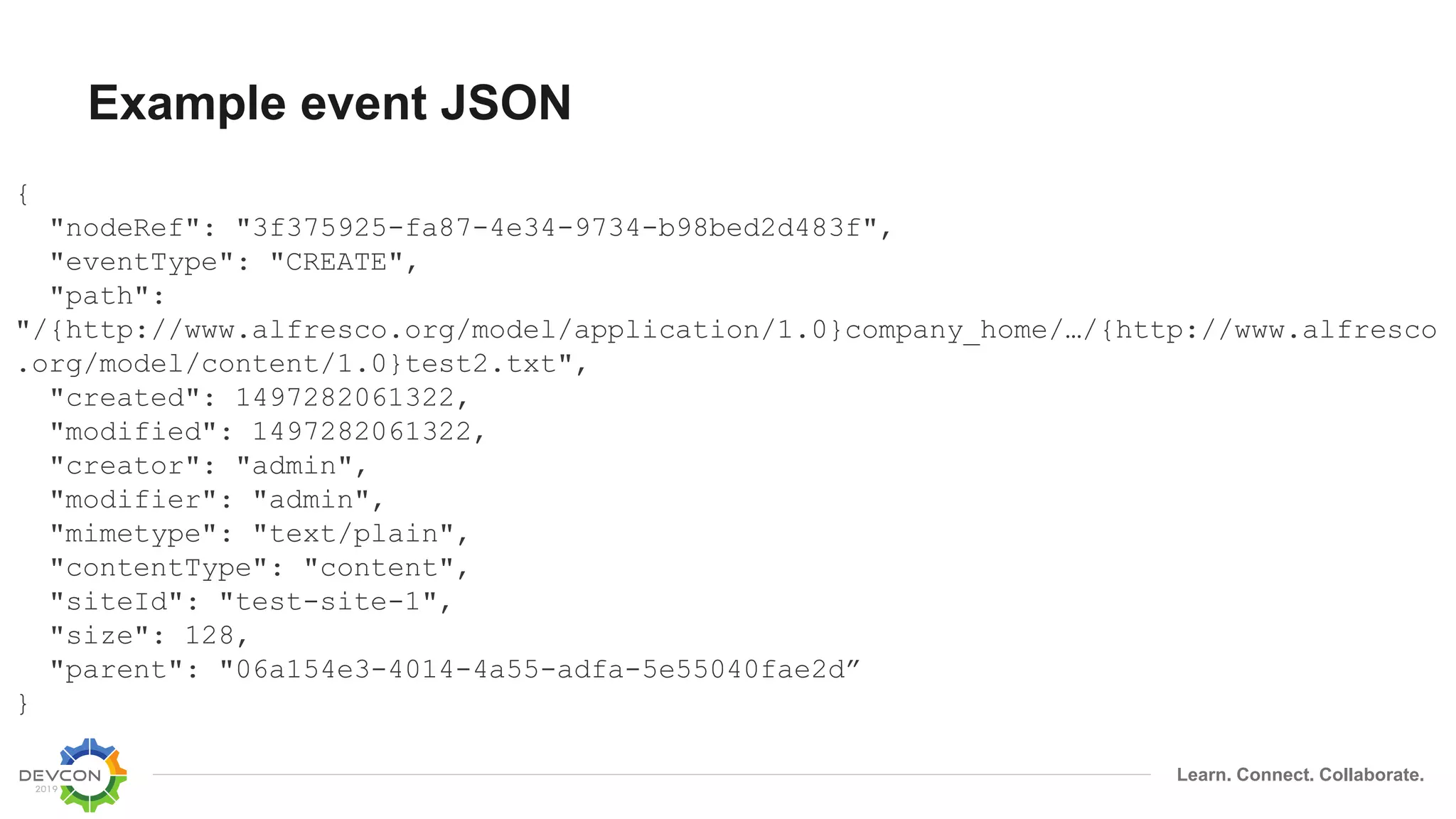
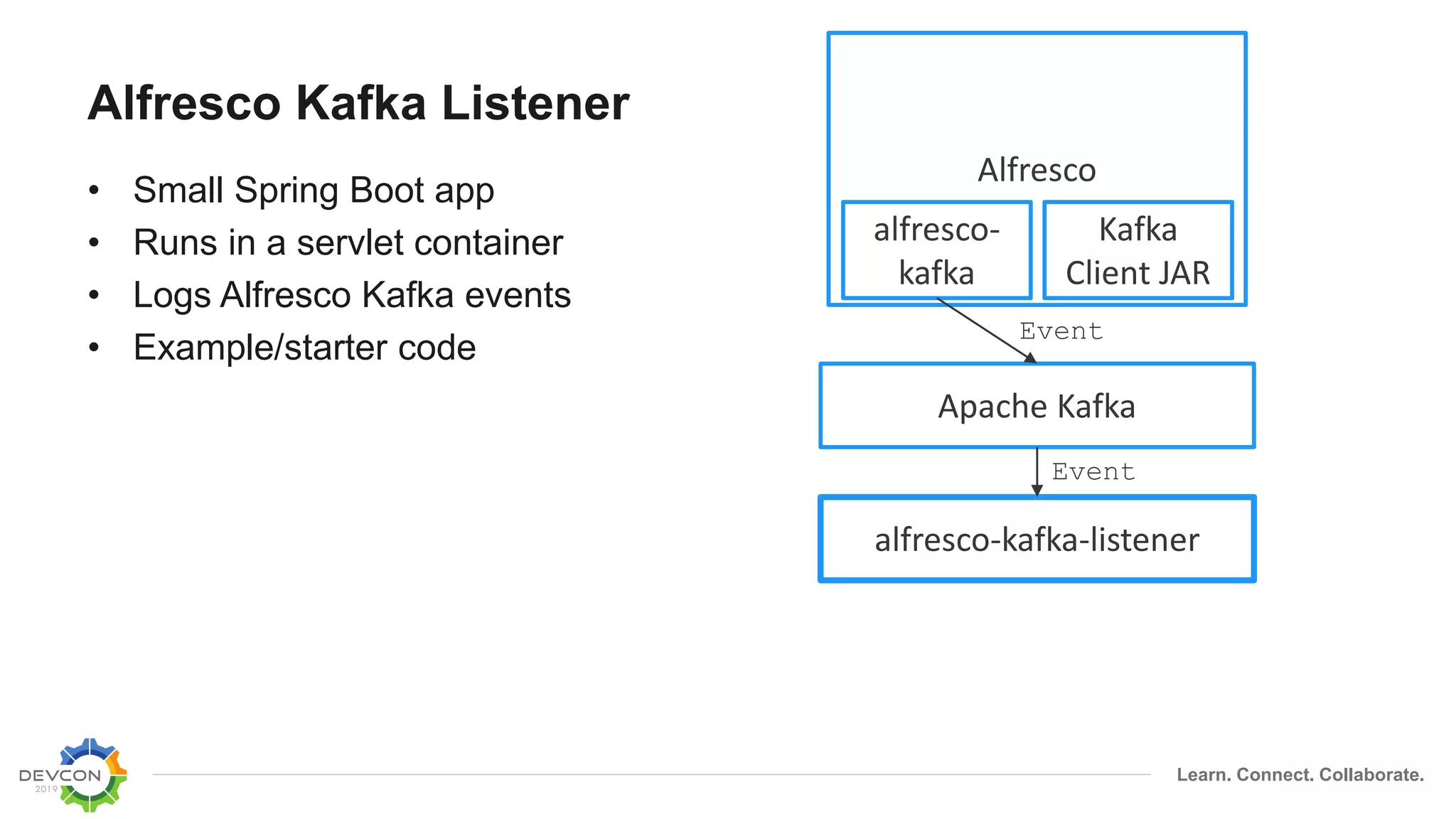
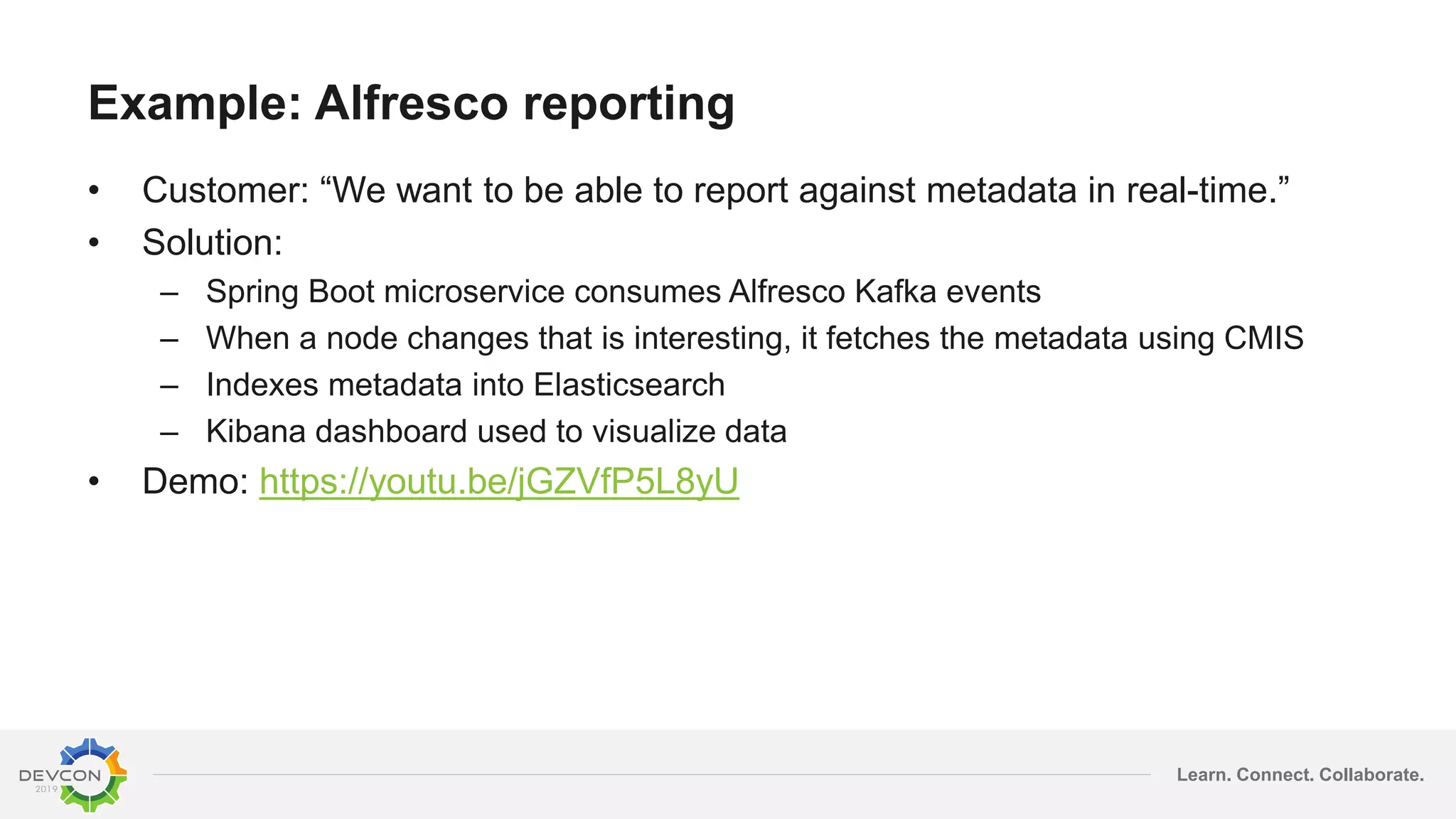
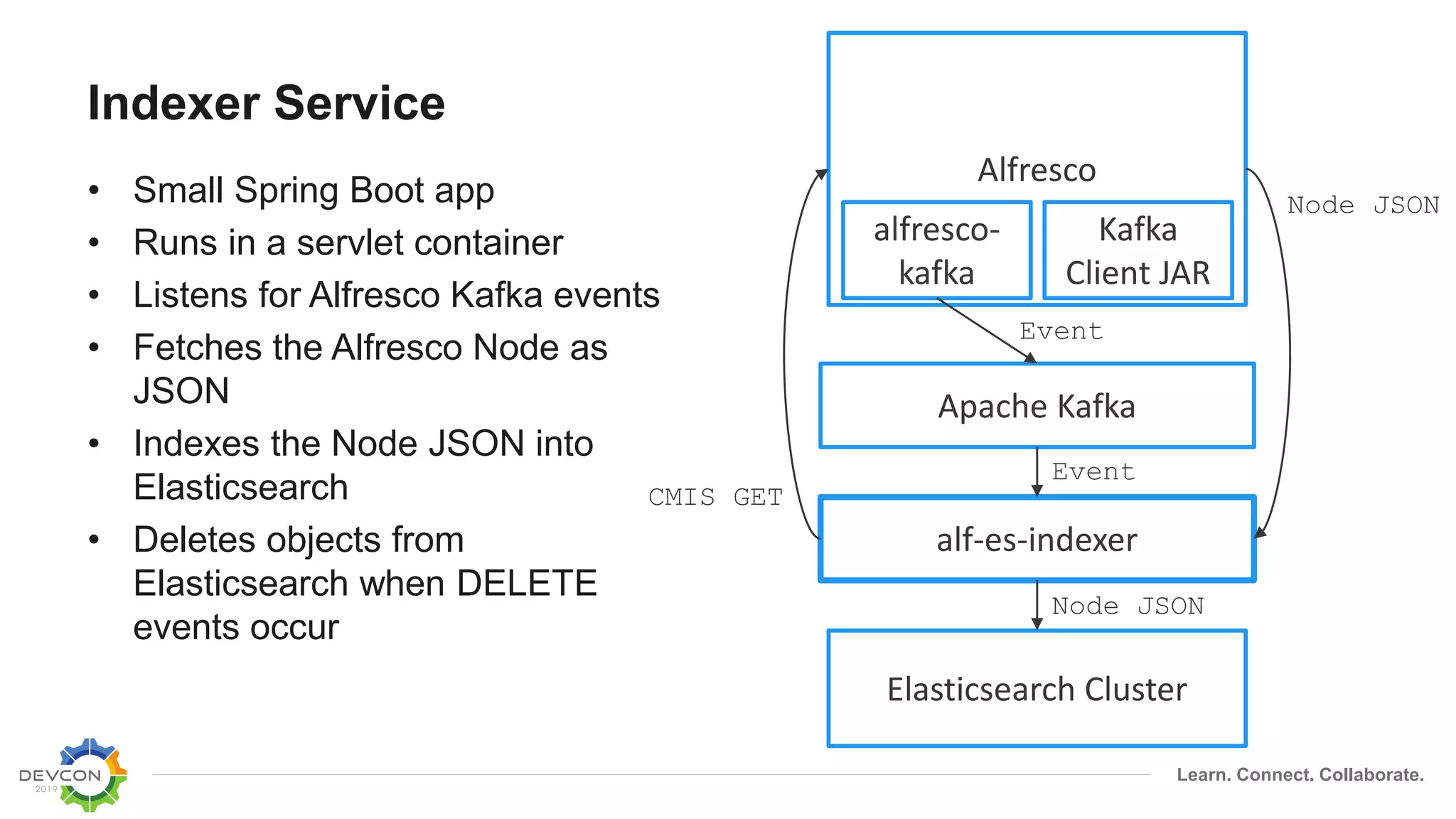
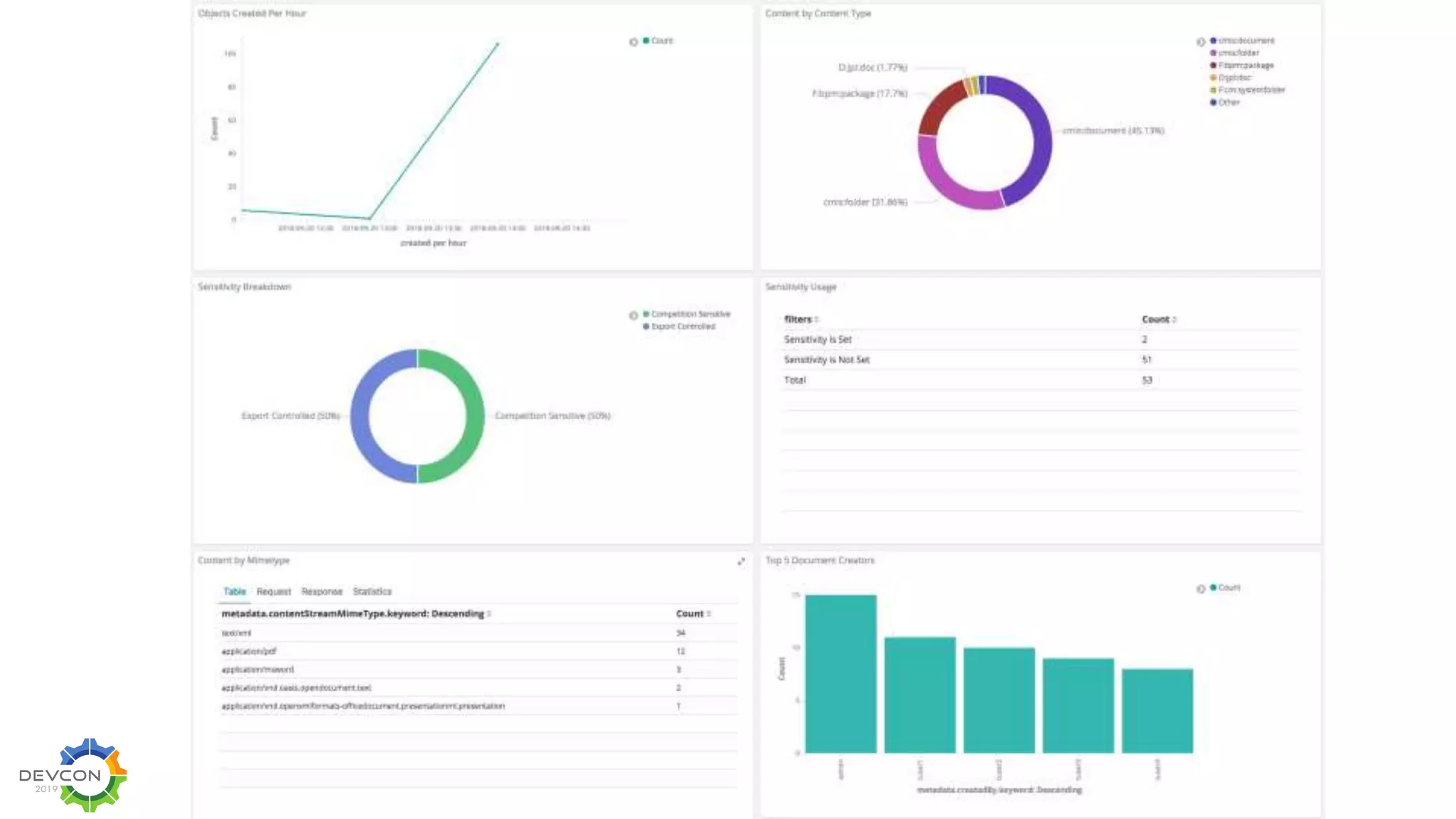
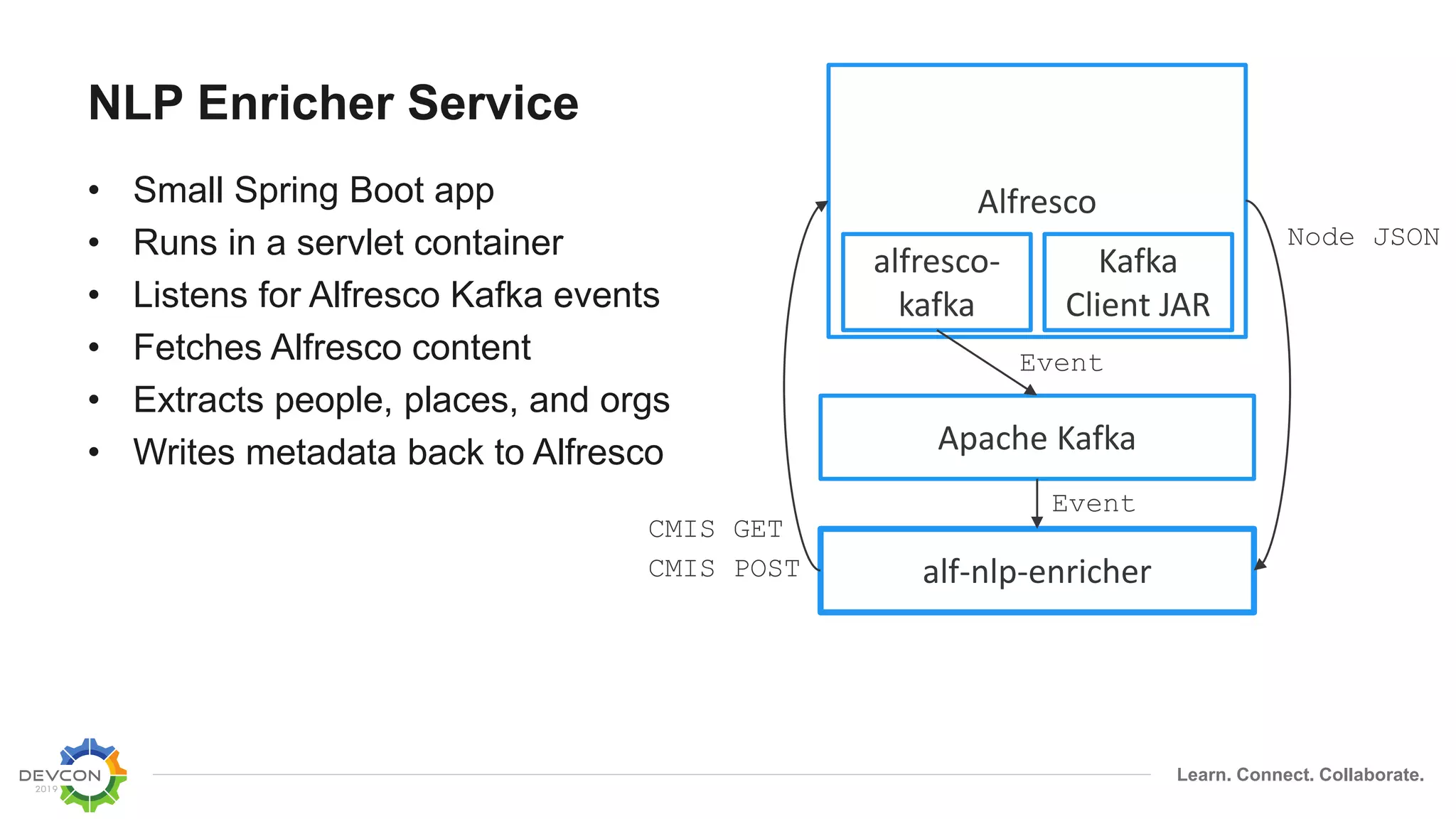
The document discusses the transition from traditional integration methods within Alfresco to an event-based microservices architecture using Apache Kafka. It highlights customer requirements such as real-time metadata reporting, content indexing, and NLP for metadata enrichment, providing examples and demonstrations of microservices that process events generated from Alfresco. The advantages of this approach include reduced code complexity, scalability, and flexibility in integration technology choices, though it also introduces increased complexity and coding efforts.

















![Learn. Connect. Collaborate.
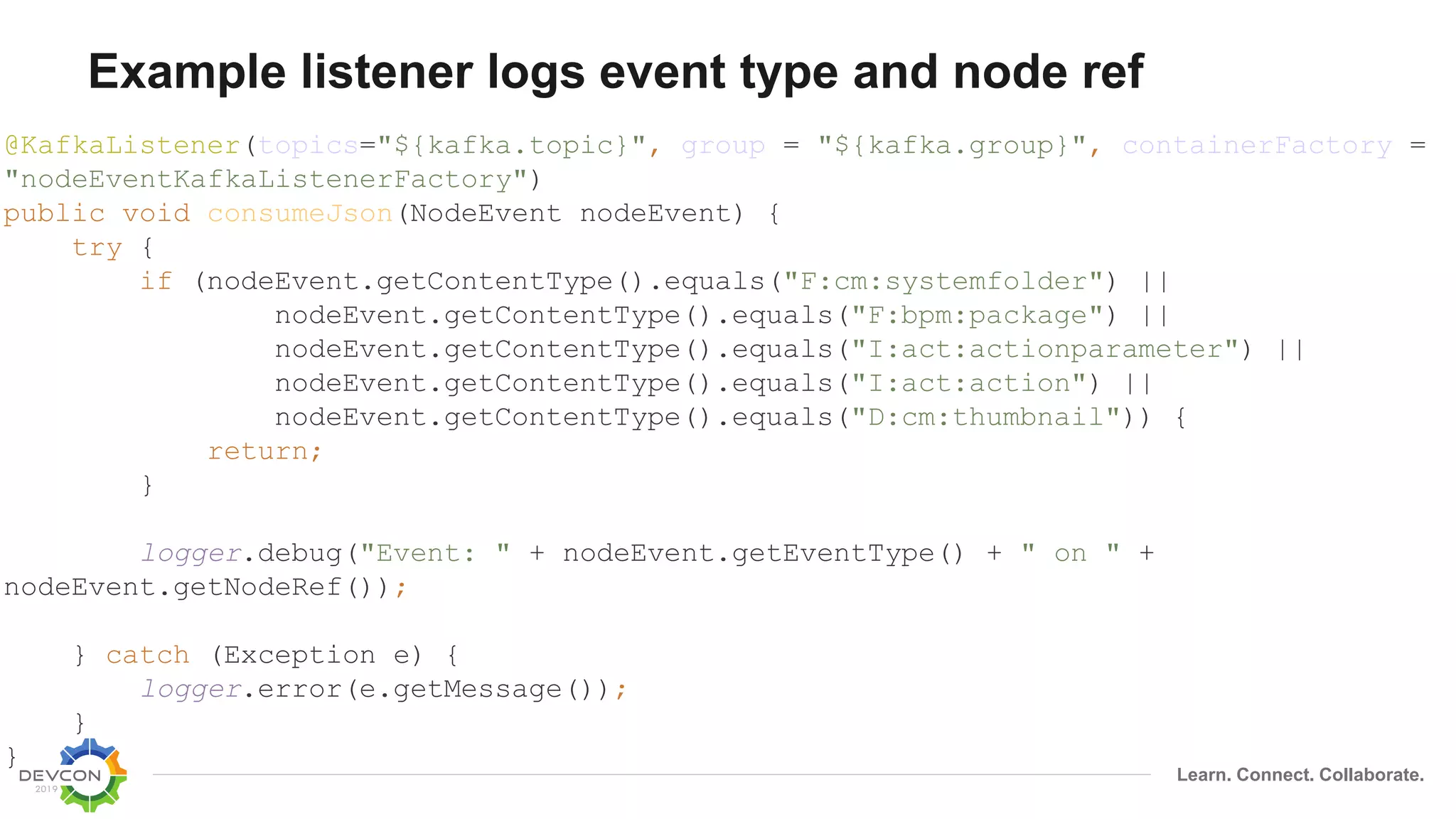
Detect sentences, call OpenNLP, update metadata
String sentences[] = sentenceDetector.detect(text);
for (String sentence : sentences) {
locations = addToSet(locationExtractor.extract(sentence), locations);
orgs = addToSet(orgExtractor.extract(sentence), orgs);
names = addToSet(nameExtractor.extract(sentence), names);
}
HashMap<String, Serializable> properties = new HashMap<>();
properties.put(PROP_LOCATIONS, toArrayList(locations));
properties.put(PROP_ORGS, toArrayList(orgs));
properties.put(PROP_NAMES, toArrayList(names));
try {
alfrescoService.updateNode(id, properties);
} catch (AlfrescoServiceException ase) {
logger.error(ase.getMessage());
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/moving-from-actions-behaviors-190127154747/75/Moving-From-Actions-Behaviors-to-Microservices-28-2048.jpg)