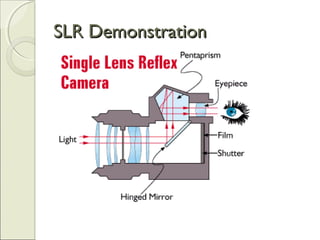
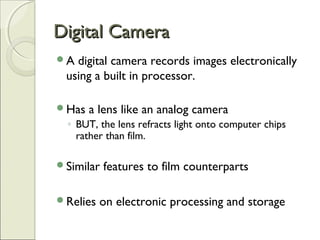
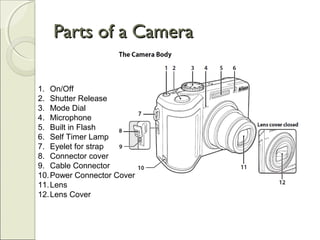
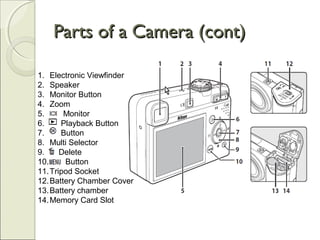
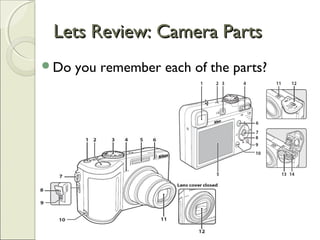
This document provides an overview of camera basics, including the different types of cameras and their components. It discusses analog film cameras, which use chemical and mechanical processes to capture images on film, and digital cameras, which use an image sensor and electronic storage. Digital cameras can be point-and-shoot or single-lens reflex (SLR) models. The document also reviews camera parts, the basic process for taking a photo, and viewing and transferring images. It emphasizes removing lens caps, setting the mode dial, stabilizing the camera, and half-pressing the shutter button to focus before fully pressing it to capture an image.