Recommended
PDF
PDF
OpenStackをさらに”使う”技術 概要と基礎操作
PDF
PDF
Japan OpenStack User Group 34th Meetup - Handson Environment
PDF
Control distribution of virtual machines
PDF
H26第1回 沖縄オープンラボラトリ・ハンズオンセミナー:OpenStack入門
PDF
HAクラスタで PostgreSQLレプリケーション構成の 高可用化
PDF
クラウドオーケストレーション「OpenStack Heat」に迫る!
PDF
バックアップことはじめ JPUG第29回しくみ+アプリケーション分科会(2014-05-31)
PDF
OpenStackでも重要な役割を果たすPacemakerを知ろう!
PDF
About OpenStack DBaas (trove)
PDF
PDF
PostgreSQLの運用・監視にまつわるエトセトラ
PDF
BigDataを迎え撃つ! PostgreSQL並列分散ミドルウェア「Stado」の紹介と検証報告
PDF
各スペシャリストがお届け!データベース最新情報セミナー -PostgreSQL10-
PDF
「今そこにある危機」を捉える ~ pg_stat_statements revisited
PDF
PDF
PostgreSQLアーキテクチャ入門(INSIGHT OUT 2011)
PDF
PDF
OSC2012 Tokyo/Spring JOSUG
PDF
PDF
シンプルでシステマチックな Linux 性能分析方法
PDF
PDF
RHEL7/CentOS7 NetworkManager徹底入門
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
The invitation to Infrastructure CI
PDF
The NoOps strategy and tactics
More Related Content
PDF
PDF
OpenStackをさらに”使う”技術 概要と基礎操作
PDF
PDF
Japan OpenStack User Group 34th Meetup - Handson Environment
PDF
Control distribution of virtual machines
PDF
H26第1回 沖縄オープンラボラトリ・ハンズオンセミナー:OpenStack入門
PDF
HAクラスタで PostgreSQLレプリケーション構成の 高可用化
PDF
クラウドオーケストレーション「OpenStack Heat」に迫る!
What's hot
PDF
バックアップことはじめ JPUG第29回しくみ+アプリケーション分科会(2014-05-31)
PDF
OpenStackでも重要な役割を果たすPacemakerを知ろう!
PDF
About OpenStack DBaas (trove)
PDF
PDF
PostgreSQLの運用・監視にまつわるエトセトラ
PDF
BigDataを迎え撃つ! PostgreSQL並列分散ミドルウェア「Stado」の紹介と検証報告
PDF
各スペシャリストがお届け!データベース最新情報セミナー -PostgreSQL10-
PDF
「今そこにある危機」を捉える ~ pg_stat_statements revisited
PDF
PDF
PostgreSQLアーキテクチャ入門(INSIGHT OUT 2011)
PDF
PDF
OSC2012 Tokyo/Spring JOSUG
PDF
PDF
シンプルでシステマチックな Linux 性能分析方法
PDF
PDF
RHEL7/CentOS7 NetworkManager徹底入門
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
More from irix_jp
PDF
The invitation to Infrastructure CI
PDF
The NoOps strategy and tactics
PDF
The practical guide of Infrastructure CI
PDF
The strategy from the Iserlohn fortress at JTF2018
PDF
PDF
OSC2016.Enterprise OpenStack & Cloud Native Applications
PDF
OSC2016 Kyoto Heat + Ansible + Jupyter
PDF
JTF2016 The strategy and Sun Tzu
PDF
Hot の書き方(Template Version 2015-04-30) 前編
PDF
PDF
クラウド時代のエンジニア魂と企業に必要なカルチャーチェンジ(前半)
PDF
Josug 20th meetup アンケート集計
PDF
OSC@Kyoto2014 OpenStack概要
PDF
H26第1回 沖縄オープンラボラトリ・ハンズオンセミナー:ボリューム操作編
PDF
H26第1回 沖縄オープンラボラトリ・ハンズオンセミナー:OpenStack 基礎操作編
PDF
JTF2014:OpenStackの概要と最新技術動向
PDF
Interop2014 - OpenStackの概要と最新技術動向(Icehouse)
PDF
Okinawa Open Days - OpenStack Overview
PDF
OSC2013 Tokyo Spring OpenStack Overview
PDF
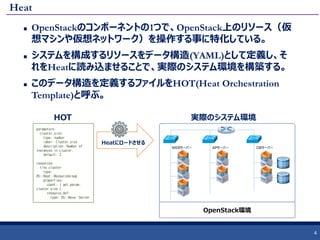
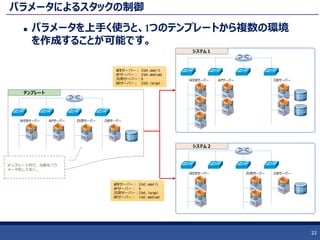
JOSUG Meetup 28th Heat 101 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. HOTとは?
Heatで利用するシステム構成をデータ構造(YAML)で記述したファイルを
指す。
Heat が定めるデータ構造
YAML形式で記述
作成するリソース、設定するパラメータなどのシステム構造を定義する。
多段ネスト可能
リソース間の依存関係を定義
暗黙の依存関係
明示的な依存関係
定義された依存関係に基づいてリソースの作成順序が決まる
依存関係がないものは平行で作成される
作成された全てのリソースは「状態」を持つ
Heatが検知する状態
ユーザーが外部から与える状態
条件文はかけない(if 系、for系は可能)
6
7. 8. Heatを使うための条件
イメージ
特にOSに関係なく利用できます。以下の導入ツールの有無によってインスタンスに対して操作できる範
囲が異なってきます。
前提ツール
cloud-init
インストールされていなくてもHeatは利用できますが、利用可能であればより高度な設定が可能です。
heat-cfntools
AWSのCFN互換コマンド群です。インストールされていなくてもHeatは利用できますが、利用可能であれ
ばより高度な設定が可能です。
userdata で 連携を行うため cloud-init が導入されていることが前提です。
boot-config(os-xxxx-config ツール群)
インストールされていなくてもHeatは利用可能。
主にTripleOで活用されている。高度なソフトウェア設定を行うためのツールです。このツールが導入された
イメージは、スタックの状態変化をフックして、様々な処理を実行させることが可能になります。
cloud-init の導入が前提
ネットワーク
Heat管理下で作成するインスタンスは外部ネットワーク(OpenStackのエンドポイント)へ接続できる
ように構成するのが推奨です。
閉じたネットワークでも利用可能ですが、一部の機能が制限される。
これは状態の通知がエンドポイント経由で行われるためです。
8
9. HOTの基本
OpenStack上で行える操作がほぼ全て行えます。
例)
仮想サーバーの作成
キーペアの作成
仮想ネットワーク、サブネットの作成
仮想ルーターの作成、ネットワークとの接続
Floating IPの作成、割当て
論理ポートの作成
セキュリティグループの作成
仮想ボリュームの作成、アタッチ
「リソース」をYAMLで記述することで作成できます。
このYAMLファイルを「テンプレート」と呼びます。
9
resources:
server1:
type: OS::Nova::Server
properties:
name: "Heat_Deployed_Server"
image: { get_param: ImageID }
flavor: "m1.small"
key_name: "temp-key-001"
networks:
- network: { get_param: NetID }
web_server_security_group:
type: OS::Neutron::SecurityGroup
properties:
name: web_server_security_group
rules:
- protocol: icmp
- protocol: tcp
port_range_min: 22
port_range_max: 22
- protocol: tcp
port_range_min: 443
port_range_max: 443
- protocol: tcp
port_range_min: 80
port_range_max: 80
private_subnet:
type: OS::Neutron::Subnet
properties:
network_id: { get_resource: private_network }
cidr: 10.10.20.0/24
dns_nameservers:
- 8.8.8.8
- 8.8.4.4
セキュリティグループの作成
仮想サーバーの作成
サブネットの作成
10. テンプレートに記述できるリソース
heat resource-type-list コマンドで一覧を確認できます。
利用できるリソースはHeatのバージョンに依存します。
またHeatのバージョンによって同じリソースでも仕様が異なっている場合があります。
例)
パラメータのバリデーション方法など。
これにより、前のバージョンでは動いていたのに、新しいバージョンではエラーになるという場合があります。
以下は利用できるリソースの一部を表示したものです。
10
$ heat resource-type-list
+------------------------------------------+
| resource_type |
+------------------------------------------+
| AWS::AutoScaling::AutoScalingGroup |
| AWS::AutoScaling::LaunchConfiguration |
| AWS::AutoScaling::ScalingPolicy |
| AWS::CloudFormation::Stack |
| AWS::CloudFormation::WaitCondition |
| AWS::CloudFormation::WaitConditionHandle |
| AWS::CloudWatch::Alarm |
| AWS::EC2::EIP |
| AWS::EC2::EIPAssociation |
| AWS::EC2::Instance |
| AWS::EC2::InternetGateway |
| AWS::EC2::NetworkInterface |
| AWS::EC2::RouteTable |
| AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup |
| AWS::EC2::Subnet |
| AWS::EC2::SubnetRouteTableAssociation |
| AWS::EC2::VPC |
| AWS::EC2::VPCGatewayAttachment |
| AWS::EC2::Volume |
| AWS::EC2::VolumeAttachment |
| AWS::ElasticLoadBalancing::LoadBalancer |
| AWS::IAM::AccessKey |
| AWS::IAM::User |
| AWS::RDS::DBInstance |
| AWS::S3::Bucket |
| OS::Ceilometer::Alarm |
| OS::Ceilometer::CombinationAlarm |
| OS::Cinder::Volume |
| OS::Cinder::VolumeAttachment |
| OS::Glance::Image |
| OS::Heat::AccessPolicy |
| OS::Heat::AutoScalingGroup |
| OS::Heat::CWLiteAlarm |
| OS::Heat::CloudConfig |
| OS::Heat::HARestarter |
| OS::Heat::InstanceGroup |
| OS::Heat::MultipartMime |
| OS::Heat::RandomString |
| OS::Heat::ResourceGroup |
| OS::Heat::ScalingPolicy |
| OS::Heat::SoftwareComponent |
| OS::Heat::SoftwareConfig |
| OS::Heat::SoftwareDeployment |
| OS::Heat::SoftwareDeployments |
| OS::Heat::Stack |
| OS::Heat::StructuredConfig |
| OS::Heat::StructuredDeployment |
| OS::Heat::StructuredDeployments |
| OS::Heat::SwiftSignal |
| OS::Heat::SwiftSignalHandle |
| OS::Heat::UpdateWaitConditionHandle |
| OS::Heat::WaitCondition |
| OS::Heat::WaitConditionHandle |
| OS::Neutron::Firewall |
| OS::Neutron::FirewallPolicy |
| OS::Neutron::FirewallRule |
| OS::Neutron::FloatingIP |
| OS::Neutron::FloatingIPAssociation |
| OS::Neutron::HealthMonitor |
| OS::Neutron::IKEPolicy |
| OS::Neutron::IPsecPolicy |
| OS::Neutron::IPsecSiteConnection |
| OS::Neutron::LoadBalancer |
| OS::Neutron::MeteringLabel |
| OS::Neutron::MeteringRule |
| OS::Neutron::Net |
| OS::Neutron::NetworkGateway |
| OS::Neutron::Pool |
| OS::Neutron::PoolMember |
| OS::Neutron::Port |
| OS::Neutron::ProviderNet |
| OS::Neutron::Router |
| OS::Neutron::RouterGateway |
| OS::Neutron::RouterInterface |
heat_template_version: 2015-04-30
11. テンプレートのバージョン
Heatはバージョンごとサポートされるリソース種別と、Heat関数の機能が
異なっています。
基本的に新しいHeatは過去のテンプレートバージョンをサポートしています。
テンプレートの先頭にどのバージョンを利用するか宣言して利用します。
利用可能なバージョンは以下
年月日の部分がバージョン番号です。
11
2013-05-23
Icehouse
2014-10-16
Juno
2015-04-30
Kilo
2015-10-15
Liberty
2016-04-08
Mitaka
DSLで利用でき
る関数
get_attr
get_file
get_param
get_resource
list_join
resource_facade
str_replace
Fn::Base64
Fn::GetAZs
Fn::Join
Fn::MemberListTo
Map
Fn::Replace
Fn::ResourceFaca
de
Fn::Select
Fn::Split
Ref
get_attr
get_file
get_param
get_resource
list_join
resource_facade
str_replace
Fn::Select
get_attr
get_file
get_param
get_resource
list_join
repeat
digest
resource_facade
str_replace
Fn::Select
get_attr
get_file
get_param
get_resource
list_join
repeat
digest
resource_facade
str_replace
str_split
digest
get_attr
get_file
get_param
get_resource
list_join
map_merge
repeat
resource_facade
str_replace
str_split
http://docs.openstack.org/developer/heat/template_guide/hot_spec.html#heat-template-version
12. 参考:利用できるテンプレートバージョンの確認
Liberty以降では、以下のコマンドでサポートバージョンが確認
できます。
12
# heat template-version-list
+--------------------------------------+------+
| version | type |
+--------------------------------------+------+
| AWSTemplateFormatVersion.2010-09-09 | cfn |
| HeatTemplateFormatVersion.2012-12-12 | cfn |
| heat_template_version.2013-05-23 | hot |
| heat_template_version.2014-10-16 | hot |
| heat_template_version.2015-04-30 | hot |
| heat_template_version.2015-10-15 | hot |
+--------------------------------------+------+
13. シンプルなテンプレート
以下は1台のインスタンスを作成するテンプレートです。
nova boot コマンドと同じようなパラメータを与えています。
テンプレートにはシステムの構造を定義します。
システムの構造とは、以下のような情報を指します。
そのシステムがどのようなネットワークをいくつ持つか、そのシステムはどのような役割のインスタンスをいくつ持つか
システムの起動順序、システムが障害を起こした際にどうするか?そのシステムを制御するための変数は何か?
テンプレートを実行すると「スタック(stack)」が作成されます。
13
heat_template_version: 2015-04-30
resources:
server1:
type: OS::Nova::Server
properties:
image: d33f51a3-6a18-4b96-bde6-2a68782336ca
flavor: "m1.small"
key_name: "temp-key-001"
networks:
- network: 1a684f4a-4f06-4741-b4f9-daa28676f74b
single-instance.yaml
テンプレートのバージョンを宣言します。
操作するリソースについて記述します。
ここれは1台のインスタンスを作成しています。
ここでは1つのリソースのみ記述していますが、実際
にはいくつでも記載可能です。
# heat stack-create -f single-instance.yaml test-stack
+--------------------------------------+------------+--------------------+----------------------+
| id | stack_name | stack_status | creation_time |
+--------------------------------------+------------+--------------------+----------------------+
| b4b8d078-7f84-4ab3-b8ca-87dc80d2480e | test-stack | CREATE_IN_PROGRESS | 2015-12-21T14:52:57Z |
+--------------------------------------+------------+--------------------+----------------------+
# nova list
+--------------------------------------+---------------------------------+--------+------------+-------------+----------------------+
| ID | Name | Status | Task State | Power State | Networks |
+--------------------------------------+---------------------------------+--------+------------+-------------+----------------------+
| abbbbc96-f301-4d63-b13b-b9733d3b6404 | test-stack-server1-cg4vev4dgxga | ACTIVE | - | Running | work-net=10.10.10.16 |
+--------------------------------------+---------------------------------+--------+------------+-------------+----------------------+
14. 15. スタックの状態
作成されたスタックは状態を持ちます。
管理するリソースの状態、操作の状況によってスタックは様々
な状態へ変化します。
以下は状態の一例です。
15
init_in_progress
init_complete
init_failed
create_in_progress
create_complete
create_failed
delete_in_progress
delete_complete
delete_failed
update_in_progress
update_complete
update_failed
snapshot_in_progress
snapshot_complete
snapshot_failed
check_in_progress
check_complete
check_failed
rollback_in_progress
rollback_complete
rollback_failed
suspend_in_progress
suspend_complete
suspend_failed
resume_in_progress
resume_complete
resume_failed
adopt_in_progress
adopt_complete
adopt_failed
16. 17. 18. HOTの構造
先にシンプルなテンプレート例を紹介しましたが、実際のテン
プレートはもっと多くの情報を含んでいます。
ここではトップレベルの構造を紹介します。現在のテンプレート
は5つのセクションをテンプレート内に持ちます。
heat_template_version, resources 以外は省略可能です。
18
heat_template_version: 2015-04-30
description: Demo template for the 09th lecture.
parameters:
image:
type: string
label: Image name or ID
description: Image to be used for the server.
default: CentOS-7-x86_64-GenericCloud-1509-witn-cfntools-1.3.0-2
resources:
private_network:
type: OS::Neutron::Net
outputs:
instance_ip:
description: The IP address of the deployed instance
value: { get_attr: [floating_ip, floating_ip_address] }
テンプレートのバージョン
テンプレートの説明
外部から変更可能なパラメータを定義する
作成するリソースを記述する。最も重要。
スタック内の情報を外部へ出力する
19. テンプレート例
以下は仮想ルーター、仮想ネットワークを作成・接続し、論理ポートを作
成した後で、インスタンスを一台起動して、Floating IPを与える例です。
19
parameters:
image:
type: string
label: Image name or ID
description: Image to be used for the server.
default: CentOS-7-x86_64-GenericCloud-1509-witn-cfntools-1.3.0-2
flavor:
type: string
label: Flavor
description: Type of instance (flavor) to be used on the compute instance.
default: m1.small
key:
type: string
label: Key name
description: Name of key-pair to be installed on the compute instance.
default: temp-key-001
public_network:
type: string
label: Public network name or ID
description: Public network with floating IP addresses.
default: public
ext_router:
type: string
label: Router name
description: Router name or ID to connect to an external network.
default: Ext-Router
secgroup:
type: string
label: Secgroup name
description: Security group name.
default: web_server_security_group
resources:
private_network:
type: OS::Neutron::Net
private_subnet:
type: OS::Neutron::Subnet
properties:
network_id: { get_resource: private_network }
cidr: 10.10.20.0/24
dns_nameservers:
- 8.8.8.8
- 8.8.4.4
router-interface:
type: OS::Neutron::RouterInterface
properties:
router_id: { get_param: ext_router }
subnet: { get_resource: private_subnet }
neutron-port:
type: OS::Neutron::Port
properties:
network: { get_resource: private_network }
security_groups:
- { get_param: secgroup }
test-instance:
type: OS::Nova::Server
properties:
image: { get_param: image }
flavor: { get_param: flavor }
key_name: { get_param: key }
networks:
- port: { get_resource: neutron-port }
floating_ip:
type: OS::Neutron::FloatingIP
properties:
floating_network: { get_param: public_network }
floating_ip_assoc:
type: OS::Neutron::FloatingIPAssociation
properties:
floatingip_id: { get_resource: floating_ip }
port_id: { get_resource: flasky_port }
20. Parameters セクション
定義したパラメーターの値はテンプレート内から get_param
関数で参照可能です。
パラメーターにはデフォルト値を設定することが可能です。
デフォルト値は、スタック作成時に上書き可能です。
20
parameters:
image:
type: string
label: Image name or ID
description: Image to be used for the server.
default: CentOS-7-x86_64-GenericCloud-1509-witn-cfntools-1.3.0-2
flavor:
type: string
label: Flavor
description: Type of instance (flavor) to be used on the compute
instance.
default: m1.small
$ heat stack-create -f heat.yaml -P 'image=Ubuntu14.04lts;flavor=m1.medium' stack-name
test-instance:
type: OS::Nova::Server
properties:
image: { get_param: image }
flavor: { get_param: flavor }
key_name: { get_param: key }
networks:
- port: { get_resource: neutron-port }
パラメーターの値を参照
(通常はデフォルト値が参
照される)
パラメーターを上書きしてスタックを作成
する例
21. Resources セクション
作成するリソースを記述していく。
リソースは作成する単位ごとに1つのタイプを持つ。
作成したリソースの値は get_resource, get_attr 関数で値を参照できます。
21
resources:
wait_condition:
type: OS::Heat::WaitCondition
properties:
handle: { get_resource: wait_handle }
count: 1
timeout: 600
wait_handle:
type: OS::Heat::WaitConditionHandle
web_server_security_group:
type: OS::Neutron::SecurityGroup
properties:
name: web_server_security_group
rules:
- protocol: icmp
- protocol: tcp
port_range_min: 22
port_range_max: 22
- protocol: tcp
port_range_min: 443
port_range_max: 443
- protocol: tcp
port_range_min: 80
port_range_max: 80
private_network:
type: OS::Neutron::Net
private_subnet:
type: OS::Neutron::Subnet
properties:
network_id: { get_resource: private_network }
cidr: 10.10.20.0/24
dns_nameservers:
- 8.8.8.8
- 8.8.4.4
router-interface:
type: OS::Neutron::RouterInterface
properties:
router_id: { get_param: ext_router }
subnet: { get_resource: private_subnet }
neutron-port:
type: OS::Neutron::Port
properties:
network: { get_resource: private_network }
security_groups:
- { get_resource: web_server_security_group }
test-instance:
type: OS::Nova::Server
properties:
image: { get_param: image }
flavor: { get_param: flavor }
key_name: { get_param: key }
networks:
- port: { get_resource: neutron-port }
user_data_format: RAW
user_data:
str_replace:
params:
wc_notify: { get_attr: ['wait_handle', 'curl_cli'] }
template: |
#!/bin/bash -ex
sleep 3
echo "Hello"
wc_notify --data-binary '{"status": "SUCCESS"}'
echo '--- end ---'
22. 23. Outputs セクション
作成したスタックの情報を外部に出力する。
他のプログラムとの連携や、別のテンプレートで仕様する。
23
outputs:
instance_name:
description: Name of the instance
value: { get_attr: [test-instance, name] }
instance_ip:
description: The IP address of the deployed instance
value: { get_attr: [floating_ip, floating_ip_address] }
[
{
"output_value": "test3-test-instance-2xmjvlijsyrz",
"description": "Name of the instance",
"output_key": "instance_name"
},
{
"output_value": "172.16.0.104",
"description": "The IP address of the deployed instance",
"output_key": "instance_ip"
}
]
テンプレート
出力
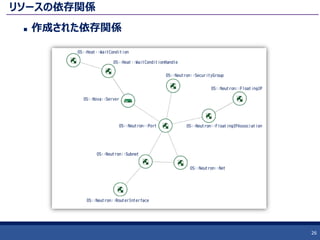
24. リソースの依存関係
Resourcesセクションでは get_resource, get_attr で他のリソースを参照した場合に、Heat側で依存関係が設定されます。
リソース作成時に、 depend_on パラメーターを与える事で、ユーザーが依存関係を設定することも可能。
依存関係が設定されている場合、依存元のリソースの作成が完了してから、リソースの作成が行われる。
それ以外のリソースは平行で作成されていく。
以下のテンプレートからスタックを作成した場合・・・
24
heat_template_version: 2015-04-30
description: Demo template for the 09th lecture.
parameters:
image:
type: string
label: Image name or ID
description: Image to be used for the server.
default: CentOS-7-x86_64-GenericCloud-1509-witn-cfntools-1.3.0-2
flavor:
type: string
label: Flavor
description: Type of instance (flavor) to be used on the compute instance.
default: m1.small
key:
type: string
label: Key name
description: Name of key-pair to be installed on the compute instance.
default: temp-key-001
public_network:
type: string
label: Public network name or ID
description: Public network with floating IP addresses.
default: public
ext_router:
type: string
label: Router name
description: Router name or ID to connect to an external network.
default: a3f094b5-fe83-4a92-a161-dece054ff0b0
resources:
wait_condition:
type: OS::Heat::WaitCondition
properties:
handle: { get_resource: wait_handle }
count: 1
timeout: 600
wait_handle:
type: OS::Heat::WaitConditionHandle
web_server_security_group:
type: OS::Neutron::SecurityGroup
properties:
name: web_server_security_group
rules:
- protocol: icmp
- protocol: tcp
port_range_min: 22
port_range_max: 22
- protocol: tcp
port_range_min: 443
port_range_max: 443
- protocol: tcp
port_range_min: 80
port_range_max: 80
private_network:
type: OS::Neutron::Net
(続く)
25. リソースの依存関係
右下図の依存関係が自動で設定される。
25
(続き)
private_subnet:
type: OS::Neutron::Subnet
properties:
network_id: { get_resource: private_network }
cidr: 10.10.20.0/24
dns_nameservers:
- 8.8.8.8
- 8.8.4.4
router-interface:
type: OS::Neutron::RouterInterface
properties:
router_id: { get_param: ext_router }
subnet: { get_resource: private_subnet }
neutron-port:
type: OS::Neutron::Port
properties:
network: { get_resource: private_network }
security_groups:
- { get_resource: web_server_security_group }
test-instance:
type: OS::Nova::Server
properties:
image: { get_param: image }
flavor: { get_param: flavor }
key_name: { get_param: key }
networks:
- port: { get_resource: neutron-port }
user_data_format: RAW
user_data:
str_replace:
params:
wc_notify: { get_attr: ['wait_handle', 'curl_cli'] }
template: |
#!/bin/bash -ex
sleep 3
echo "Hello"
wc_notify --data-binary '{"status": "SUCCESS"}'
echo '--- end ---'
floating_ip:
type: OS::Neutron::FloatingIP
properties:
floating_network: { get_param: public_network }
floating_ip_assoc:
type: OS::Neutron::FloatingIPAssociation
properties:
floatingip_id: { get_resource: floating_ip }
port_id: { get_resource: neutron-port }
outputs:
instance_name:
description: Name of the instance
value: { get_attr: [test-instance, name] }
instance_ip:
description: The IP address of the deployed instance
value: { get_attr: [floating_ip, floating_ip_address] }
26. 27. 28. スタックのアップデート
一度作成したスタックはリソースのプロパティ変更してアップデート可能です。
プロパティをアップデートした時の挙動はリソースごとに決められています。
例)
インスタンスを操作する OS:Nova:Server において、 flavor プロパティをアップデートした場合、RESIZE 処理がデフォルトで
実行されます。
この値はリソース作成時に変更可能です。
28
$ heat resource-type-show OS::Nova::Server
(抜粋)
"flavor_update_policy": {
"description": "Policy on how to apply a flavor update; either by requesting a server resize or by replacing the entire server.",
"default": "RESIZE",
"required": false,
"update_allowed": true,
"type": "string",
"immutable": false,
"constraints": [
{
"allowed_values": [
"RESIZE",
"REPLACE"
]
(省略)
[centos@console ~]$ heat stack-create -f 15_02_simple_server.yaml ¥
-P image=cirros ¥
-P flavor=m1.tiny ¥
-P private_network=heat-handson-net ¥
-P key=heat-key ¥
-P sec_group=sg-for-heat ¥
simple-server
[centos@console ~]$ heat stack-update -f 15_02_simple_server.yaml ¥
-P image=cirros ¥
-P flavor=m1.smll ¥
-P private_network=heat-handson-net ¥
-P key=heat-key ¥
-P sec_group=sg-for-heat ¥
simple-server
+-------------------------------------+--------+------------+-------------+
| Name | Status | Task State | Power State |
+-------------------------------------+--------+------------+-------------+
| simple-server-instance-5xnnypou2f25 | ACTIVE | - | Running |
+-------------------------------------+--------+------------+-------------+
+-------------------------------------+--------+---------------+-------------+
| Name | Status | Task State | Power State |
+-------------------------------------+--------+---------------+-------------+
| simple-server-instance-3nflhxpgmq5z | RESIZE | resize_finish | Running |
+-------------------------------------+--------+---------------+-------------+
29. テンプレートのネスト
テンプレートはネスト可能で、1つのテンプレートを別のテンプレート内で1つのリソースとし
て扱うことができます。
この時、パラメータがリソースのプロパティになり、アウトプット値をリソースの属性値とし
て取り出すことが可能になります。
29
(省略)
resources:
server1:
type: 15_02_simple_server.yaml
properties:
image: { get_param: image }
flavor: { get_param: flavor }
key: { get_param: key }
sec_group: { get_param: sec_group }
private_network: { get_param: private_network }
server2:
type: 15_02_simple_server.yaml
properties:
image: { get_param: image }
flavor: { get_param: flavor }
key: { get_param: key }
sec_group: { get_param: sec_group }
private_network: { get_param: private_network }
outputs:
instance_name:
description: Name of the instance
value:
- { get_attr: [ server1, instance_name ] }
- { get_attr: [ server2, instance_name ] }
instance_ip:
description: The IP address of the deployed instance
value:
- { get_attr: [ server1, instance_ip ] }
- { get_attr: [ server2, instance_ip ] }
(省略)
parameters:
image:
type: string
default: CentOS7-1509
flavor:
type: string
default: m1.small
private_network:
type: string
default: work-net
sec_group:
type: string
default: open_all
key:
type: string
default: my-key
resources:
instance:
type: OS::Nova::Server
properties:
image: { get_param: image }
flavor: { get_param: flavor }
key_name: { get_param: key }
security_groups:
- { get_param: sec_group }
networks:
- network: { get_param: private_network }
outputs:
instance_name:
description: Name of the instance
value: { get_attr: [instance, name] }
instance_ip:
description: The IP address of the deployed instance
value: { get_attr: [ instance, first_address ] }
15_02_simple_server.yaml
30. 環境定義ファイル
テンプレートをネストする際に、
ファイル名を独自のリソース名に
マッピングすることが可能です。
30
resource_registry:
My::SimpleServer::file: 15_02_simple_server.yaml
My::SimpleServer::github: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/irixjp/topse-tools/master/hands-on/15_02_simple_server.yaml
15_environment.yaml
$ heat stack-create -f 15_03_nested_temp_from_env.yaml -e 15_environment.yaml nested-stack-from-env
(省略)
resources:
instance:
type: OS::Nova::Server
properties:
image: { get_param: image }
flavor: { get_param: flavor }
key_name: { get_param: key }
security_groups:
- { get_param: sec_group }
networks:
- network: { get_param: private_network }
outputs:
instance_name:
description: Name of the instance
value: { get_attr: [instance, name] }
instance_ip:
description: The IP address of the deployed instance
value: { get_attr: [ instance, first_address ] }
15_02_simple_server.yaml
(省略)
resources:
server1:
type: My::SimpleServer::file
properties:
image: { get_param: image }
flavor: { get_param: flavor }
key: { get_param: key }
sec_group: { get_param: sec_group }
private_network: { get_param: private_network }
(省略)
15_03_nested_temp_from_env.yaml
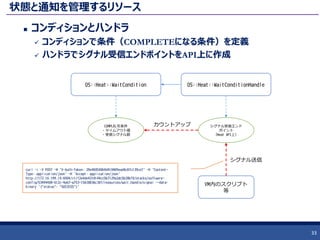
31. 32. 33. 状態と通知を管理するリソース
コンディションとハンドラ
コンディションで条件(COMPLETEになる条件)を定義
ハンドラでシグナル受信エンドポイントをAPI上に作成
33
OS::Heat::WaitCondition OS::Heat::WaitConditionHandle
シグナル受信エンド
ポイント
(Heat API上)
COMPLELTE条件
・タイムアウト値
・受信シグナル数
VM内のスクリプト
等
カウントアップ
シグナル送信
curl -i -X POST -H 'X-Auth-Token: 29e480500b9d410489ead0c87c139ce7' -H 'Content-
Type: application/json' -H 'Accept: application/json'
http://172.16.199.10:8004/v1/f2e4de4318144cc5b7129a2dc5b28bf0/stacks/software-
config/53494408-612c-4eb7-a753-15630836c30f/resources/wait_handle/signal --data-
binary '{"status": "SUCCESS"}'
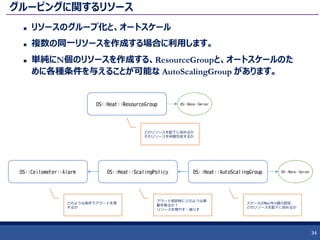
34. グルーピングに関するリソース
リソースのグループ化と、オートスケール
複数の同一リソースを作成する場合に利用します。
単純にN個のリソースを作成する、ResourceGroupと、オートスケールのた
めに各種条件を与えることが可能な AutoScalingGroup があります。
34
OS::Ceilometer::Alarm OS::Heat::ScalingPolicy OS::Heat::AutoScalingGroup
どのような条件でアラートを発
するか
アラート受診時にどのような挙
動を取るか?
リソースを増やす・減らす
スケールのMax/Min値の設定
どのリソースを配下に収めるか
OS::Nova::Server
OS::Heat::ResourceGroup OS::Nova::Server
どのリソースを配下に収めるか
そのリソースを何個生成するか
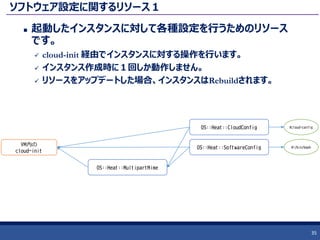
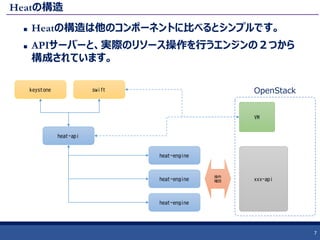
35. 36. ソフトウェア設定に関するリソース2
起動したインスタンスに対して各種設定を行うためのリソース
です。
boot-config に含まれる各種ツールとMetadataサーバー、シグナル受信
機によって動作します。
https://github.com/openstack/heat-templates/tree/master/hot/software-config/boot-config
実行順序の定義が可能で、スタックをアップデートした際に特定の処理
のみを再実行することも可能です。
36
OS::Heat::CloudConfig
VM内の
boot-config
OS::Heat::SoftwareConfig
OS::Heat::MultipartMime
#cloud-config
#!/bin/bash
OS::Heat::SoftwareDeployment
OS::Heat::SoftwareDeployment
OS::Heat::SoftwareDeployment
Nova Metadata
Server
Signal Reciever
(Heat API/Swift)
37. 38. まとめ
Heat を利用するとOpenStack上のリソースを操作可能
HOT形式でリソースの表現する。
リソースは依存関係を持ち、依存関係の末端から処理が実
行されていく。
インスタンスに関する操作は cloud-init か boot-config で実
行される。
ただし、リブートのハンドリング等、苦手なこともあるのでインスタンスの
操作はAnsible等に比べると苦手。
38
39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45.













![HOTの構造
先にシンプルなテンプレート例を紹介しましたが、実際のテン
プレートはもっと多くの情報を含んでいます。
ここではトップレベルの構造を紹介します。現在のテンプレート
は5つのセクションをテンプレート内に持ちます。
heat_template_version, resources 以外は省略可能です。
18
heat_template_version: 2015-04-30
description: Demo template for the 09th lecture.
parameters:
image:
type: string
label: Image name or ID
description: Image to be used for the server.
default: CentOS-7-x86_64-GenericCloud-1509-witn-cfntools-1.3.0-2
resources:
private_network:
type: OS::Neutron::Net
outputs:
instance_ip:
description: The IP address of the deployed instance
value: { get_attr: [floating_ip, floating_ip_address] }
テンプレートのバージョン
テンプレートの説明
外部から変更可能なパラメータを定義する
作成するリソースを記述する。最も重要。
スタック内の情報を外部へ出力する](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/josug28thv1-160621113755/85/JOSUG-Meetup-28th-Heat-101-18-320.jpg)


![Resources セクション
作成するリソースを記述していく。
リソースは作成する単位ごとに1つのタイプを持つ。
作成したリソースの値は get_resource, get_attr 関数で値を参照できます。
21
resources:
wait_condition:
type: OS::Heat::WaitCondition
properties:
handle: { get_resource: wait_handle }
count: 1
timeout: 600
wait_handle:
type: OS::Heat::WaitConditionHandle
web_server_security_group:
type: OS::Neutron::SecurityGroup
properties:
name: web_server_security_group
rules:
- protocol: icmp
- protocol: tcp
port_range_min: 22
port_range_max: 22
- protocol: tcp
port_range_min: 443
port_range_max: 443
- protocol: tcp
port_range_min: 80
port_range_max: 80
private_network:
type: OS::Neutron::Net
private_subnet:
type: OS::Neutron::Subnet
properties:
network_id: { get_resource: private_network }
cidr: 10.10.20.0/24
dns_nameservers:
- 8.8.8.8
- 8.8.4.4
router-interface:
type: OS::Neutron::RouterInterface
properties:
router_id: { get_param: ext_router }
subnet: { get_resource: private_subnet }
neutron-port:
type: OS::Neutron::Port
properties:
network: { get_resource: private_network }
security_groups:
- { get_resource: web_server_security_group }
test-instance:
type: OS::Nova::Server
properties:
image: { get_param: image }
flavor: { get_param: flavor }
key_name: { get_param: key }
networks:
- port: { get_resource: neutron-port }
user_data_format: RAW
user_data:
str_replace:
params:
wc_notify: { get_attr: ['wait_handle', 'curl_cli'] }
template: |
#!/bin/bash -ex
sleep 3
echo "Hello"
wc_notify --data-binary '{"status": "SUCCESS"}'
echo '--- end ---'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/josug28thv1-160621113755/85/JOSUG-Meetup-28th-Heat-101-21-320.jpg)
![Outputs セクション
作成したスタックの情報を外部に出力する。
他のプログラムとの連携や、別のテンプレートで仕様する。
23
outputs:
instance_name:
description: Name of the instance
value: { get_attr: [test-instance, name] }
instance_ip:
description: The IP address of the deployed instance
value: { get_attr: [floating_ip, floating_ip_address] }
[
{
"output_value": "test3-test-instance-2xmjvlijsyrz",
"description": "Name of the instance",
"output_key": "instance_name"
},
{
"output_value": "172.16.0.104",
"description": "The IP address of the deployed instance",
"output_key": "instance_ip"
}
]
テンプレート
出力](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/josug28thv1-160621113755/85/JOSUG-Meetup-28th-Heat-101-23-320.jpg)

![リソースの依存関係
右下図の依存関係が自動で設定される。
25
(続き)
private_subnet:
type: OS::Neutron::Subnet
properties:
network_id: { get_resource: private_network }
cidr: 10.10.20.0/24
dns_nameservers:
- 8.8.8.8
- 8.8.4.4
router-interface:
type: OS::Neutron::RouterInterface
properties:
router_id: { get_param: ext_router }
subnet: { get_resource: private_subnet }
neutron-port:
type: OS::Neutron::Port
properties:
network: { get_resource: private_network }
security_groups:
- { get_resource: web_server_security_group }
test-instance:
type: OS::Nova::Server
properties:
image: { get_param: image }
flavor: { get_param: flavor }
key_name: { get_param: key }
networks:
- port: { get_resource: neutron-port }
user_data_format: RAW
user_data:
str_replace:
params:
wc_notify: { get_attr: ['wait_handle', 'curl_cli'] }
template: |
#!/bin/bash -ex
sleep 3
echo "Hello"
wc_notify --data-binary '{"status": "SUCCESS"}'
echo '--- end ---'
floating_ip:
type: OS::Neutron::FloatingIP
properties:
floating_network: { get_param: public_network }
floating_ip_assoc:
type: OS::Neutron::FloatingIPAssociation
properties:
floatingip_id: { get_resource: floating_ip }
port_id: { get_resource: neutron-port }
outputs:
instance_name:
description: Name of the instance
value: { get_attr: [test-instance, name] }
instance_ip:
description: The IP address of the deployed instance
value: { get_attr: [floating_ip, floating_ip_address] }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/josug28thv1-160621113755/85/JOSUG-Meetup-28th-Heat-101-25-320.jpg)

![スタックのアップデート
一度作成したスタックはリソースのプロパティ変更してアップデート可能です。
プロパティをアップデートした時の挙動はリソースごとに決められています。
例)
インスタンスを操作する OS:Nova:Server において、 flavor プロパティをアップデートした場合、RESIZE 処理がデフォルトで
実行されます。
この値はリソース作成時に変更可能です。
28
$ heat resource-type-show OS::Nova::Server
(抜粋)
"flavor_update_policy": {
"description": "Policy on how to apply a flavor update; either by requesting a server resize or by replacing the entire server.",
"default": "RESIZE",
"required": false,
"update_allowed": true,
"type": "string",
"immutable": false,
"constraints": [
{
"allowed_values": [
"RESIZE",
"REPLACE"
]
(省略)
[centos@console ~]$ heat stack-create -f 15_02_simple_server.yaml ¥
-P image=cirros ¥
-P flavor=m1.tiny ¥
-P private_network=heat-handson-net ¥
-P key=heat-key ¥
-P sec_group=sg-for-heat ¥
simple-server
[centos@console ~]$ heat stack-update -f 15_02_simple_server.yaml ¥
-P image=cirros ¥
-P flavor=m1.smll ¥
-P private_network=heat-handson-net ¥
-P key=heat-key ¥
-P sec_group=sg-for-heat ¥
simple-server
+-------------------------------------+--------+------------+-------------+
| Name | Status | Task State | Power State |
+-------------------------------------+--------+------------+-------------+
| simple-server-instance-5xnnypou2f25 | ACTIVE | - | Running |
+-------------------------------------+--------+------------+-------------+
+-------------------------------------+--------+---------------+-------------+
| Name | Status | Task State | Power State |
+-------------------------------------+--------+---------------+-------------+
| simple-server-instance-3nflhxpgmq5z | RESIZE | resize_finish | Running |
+-------------------------------------+--------+---------------+-------------+](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/josug28thv1-160621113755/85/JOSUG-Meetup-28th-Heat-101-28-320.jpg)
![テンプレートのネスト
テンプレートはネスト可能で、1つのテンプレートを別のテンプレート内で1つのリソースとし
て扱うことができます。
この時、パラメータがリソースのプロパティになり、アウトプット値をリソースの属性値とし
て取り出すことが可能になります。
29
(省略)
resources:
server1:
type: 15_02_simple_server.yaml
properties:
image: { get_param: image }
flavor: { get_param: flavor }
key: { get_param: key }
sec_group: { get_param: sec_group }
private_network: { get_param: private_network }
server2:
type: 15_02_simple_server.yaml
properties:
image: { get_param: image }
flavor: { get_param: flavor }
key: { get_param: key }
sec_group: { get_param: sec_group }
private_network: { get_param: private_network }
outputs:
instance_name:
description: Name of the instance
value:
- { get_attr: [ server1, instance_name ] }
- { get_attr: [ server2, instance_name ] }
instance_ip:
description: The IP address of the deployed instance
value:
- { get_attr: [ server1, instance_ip ] }
- { get_attr: [ server2, instance_ip ] }
(省略)
parameters:
image:
type: string
default: CentOS7-1509
flavor:
type: string
default: m1.small
private_network:
type: string
default: work-net
sec_group:
type: string
default: open_all
key:
type: string
default: my-key
resources:
instance:
type: OS::Nova::Server
properties:
image: { get_param: image }
flavor: { get_param: flavor }
key_name: { get_param: key }
security_groups:
- { get_param: sec_group }
networks:
- network: { get_param: private_network }
outputs:
instance_name:
description: Name of the instance
value: { get_attr: [instance, name] }
instance_ip:
description: The IP address of the deployed instance
value: { get_attr: [ instance, first_address ] }
15_02_simple_server.yaml](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/josug28thv1-160621113755/85/JOSUG-Meetup-28th-Heat-101-29-320.jpg)
![環境定義ファイル
テンプレートをネストする際に、
ファイル名を独自のリソース名に
マッピングすることが可能です。
30
resource_registry:
My::SimpleServer::file: 15_02_simple_server.yaml
My::SimpleServer::github: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/irixjp/topse-tools/master/hands-on/15_02_simple_server.yaml
15_environment.yaml
$ heat stack-create -f 15_03_nested_temp_from_env.yaml -e 15_environment.yaml nested-stack-from-env
(省略)
resources:
instance:
type: OS::Nova::Server
properties:
image: { get_param: image }
flavor: { get_param: flavor }
key_name: { get_param: key }
security_groups:
- { get_param: sec_group }
networks:
- network: { get_param: private_network }
outputs:
instance_name:
description: Name of the instance
value: { get_attr: [instance, name] }
instance_ip:
description: The IP address of the deployed instance
value: { get_attr: [ instance, first_address ] }
15_02_simple_server.yaml
(省略)
resources:
server1:
type: My::SimpleServer::file
properties:
image: { get_param: image }
flavor: { get_param: flavor }
key: { get_param: key }
sec_group: { get_param: sec_group }
private_network: { get_param: private_network }
(省略)
15_03_nested_temp_from_env.yaml](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/josug28thv1-160621113755/85/JOSUG-Meetup-28th-Heat-101-30-320.jpg)