Microeconomics #03: Individual Firm Decisions
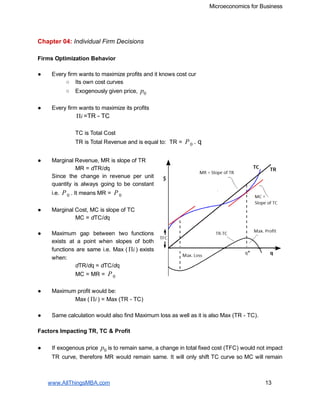
- 1. Microeconomics for Business Chapter 04: Individual Firm Decisions Firms Optimization Behavior ● Every firm wants to maximize profits and it knows cost cur ○ Its own cost curves ○ Exogenously given price, p0 ● Every firm wants to maximize its profits =TR TCiΠ TC is Total Cost TR is Total Revenue and is equal to: TR = . qP0 ● Marginal Revenue, MR is slope of TR MR = d TR/ d q Since the change in revenue per unit quantity is always going to be constant i.e. . It means MR = P0 P0 ● Marginal Cost, MC is slope of TC MC = d TC/ d q ● Maximum gap between two functions exists at a point when slopes of both functions are same i.e. Max ( ) exists iΠ when: d TR/ d q = d TC/ d q MC = MR = P0 ● Maximum profit would be: Max ( ) = Max (TR TC)iΠ ● Same calculation would also find Maximum loss as well as it is also Max (TR TC). Factors Impacting TR, TC & Profit ● If exogenous price is to remain same, a change in total fixed cost (TFC) would not impact p0 TR curve, therefore MR would remain same. It will only shift TC curve so MC will remain www.AllThingsMBA.com 13
- 2. Microeconomics for Business same as well. However the profit i.e. Max (TR TC) will increase or decrease depending on fixed cost decrease or increase. ● If exogenous price is to remain same, a change in TVC would change the TC curve and p0 so MC will change as well. TR curve will remain same and so would MR. Profit i.e. Max (TR TC) will change depending on the change in TC curve. ● A change in exogenous price only will either make the TR curve less or more steep, p0 therefore MR would change. TC curve and MC would remain same. The profit will increase or decrease depending on whether the new price is less or more. Marginal Revenue (MR) & Marginal Cost (MC) ● For an exogenous price , Total p0 Revenue (TR) is a linear line with fixed slope, therefore MR is constant and is equal to .P0 ● Maximum profit exists when MC & MR are equal as shown in graph. ● TR at this point can be calculated as = q* x P0 ● MC has no information about TFC, therefore it is not possible to calculate TC from this graph. Marginal Revenue (MR), Marginal Cost MC) & Average Total Cost ● TC = ATC * q ● It means that by plotting ATC on MC and MR graph, total profit can be calculated. Π = TR TC = (q* x ) (ATC x q*)P0 = q* ( ATC)P0 Negative Profit (Loss) & Its Impact ● If ATC is above MR at all points at exogenous price , it means the firm is generatingP0 negative profit i.e. TC is always going to be higher than TR. www.AllThingsMBA.com 14
- 3. Microeconomics for Business ● In the Long Run (where no factor of production is fixed), if profit goes in negative, it means exit for the firm. ● In the Short Run (where a firm cannot change its fixed cost), if profit goes into negative it needs to decide: ○ Whether to continue producing q* at MR = MC. OR ○ Shutdown i.e. Stop production until exit. It means waiting to enter Long Run. ● Decision to whether continue or stop production can be made using following condition: ○ If TR < VC while producing q* when MR = MC Then Stop Production ● When TR < VC, it means that not only FC is loss but production is resulting into additional loss due to higher VC. Example: ● In this case, TR is less than VC which means that not only FC is a loss, but firm cannot cover VC either. This means running production is generating even more loss. ○ Area (Z) = Total Revenue ○ Area (Y+Z) = Total Variable Cost ○ Area (X) = Total Fixed Cost ● It shows that running production is producing additional loss, therefore it is better to shut down. ● If however TR > VC, then it means there is the revenue is greater than VC and it can help offset FC loss. ● In example: ○ Area Z = TVC ○ Area (X+Y) = TC ○ Area (Y+Z) = TR Here the TR > TVC by quantity Y which means this profit is going to cover some of TFC. www.AllThingsMBA.com 15
- 4. Microeconomics for Business References: 1. Lectures by Prof. Larry DeBrock 2. http://economics.fundamentalfinance.com/micro_outputdecision.php 3. https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Microeconomics/Perfect_Competition 4. https://www.boundless.com/economics/textbooks/boundlesseconomicstextbook/competitive markets10/productiondecisionsinperfectcompetition67/marginalcostprofitmaximizations trategy25112348/ Notes by Fraz Tajammul www.AllThingsMBA.com 16
