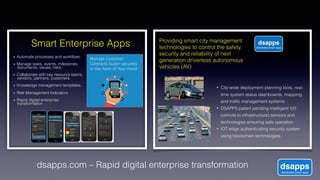
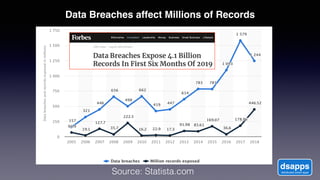
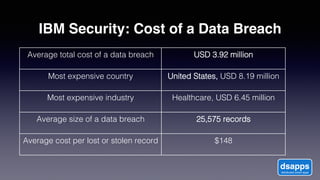
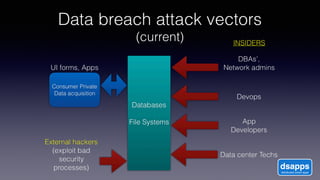
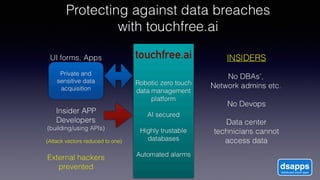
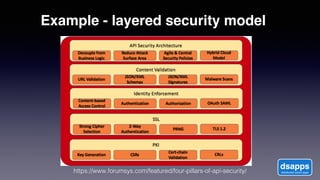
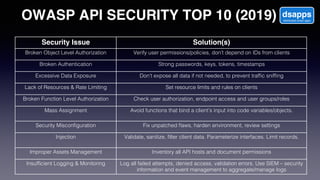
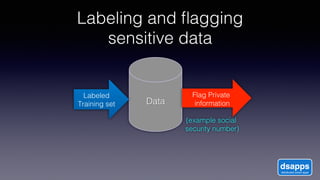
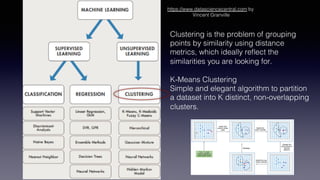
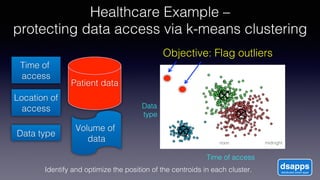
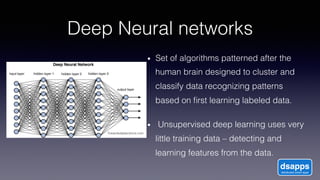
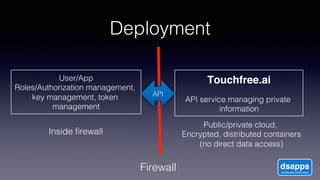
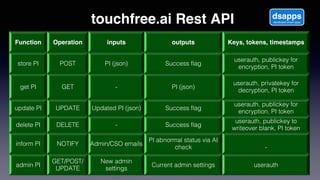
The document discusses introducing a new data security model using APIs and AI pattern recognition. It notes that data breaches cost enterprises millions of dollars and new regulations like GDPR and CCPA have increased data security urgency. The proposed model uses minimal human touch, APIs to access data, and AI to learn, detect, and flag abnormalities in data access patterns to better secure sensitive enterprise data.