Difference between humoral and cell mediated immunity Dr. ihsan edan abdulkareem alsaimary
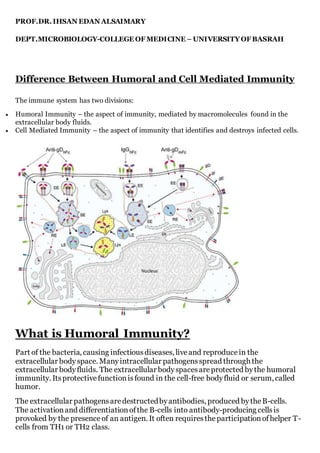
- 1. PROF.DR.IHSAN EDAN ALSAIMARY DEPT.MICROBIOLOGY-COLLEGE OF MEDICINE – UNIVERSITYOF BASRAH Difference Between Humoral and Cell Mediated Immunity The immune system has two divisions: Humoral Immunity – the aspect of immunity, mediated by macromolecules found in the extracellular body fluids. Cell Mediated Immunity – the aspect of immunity that identifies and destroys infected cells. What is Humoral Immunity? Part of the bacteria, causing infectiousdiseases, liveand reproducein the extracellular body space. Manyintracellular pathogensspread through the extracellular bodyfluids. The extracellular bodyspacesareprotected bythe humoral immunity. Itsprotectivefunctionisfound in the cell-free bodyfluid or serum, called humor. The extracellular pathogensaredestructedbyantibodies, produced bytheB-cells. The activationand differentiationofthe B-cells into antibody-producing cellsis provoked by the presenceof an antigen. It often requirestheparticipationofhelper T- cells from TH1 or TH2 class.
- 2. Antibodieseliminatethepathogensby neutralization, or by facilitating theworkof the phagocyticcells. The type of the effector mechanism that willbe used depends on the type of the produced antibodies. In order to enter the cells, viruses and bacteria bind tocertainmolecules, located on the cells’ surface. By binding with thepathogentheantibodyobstructsthisprocess and protectsthecells. Thistype of eliminationofthe pathogensis called neutralization. Antibodiesfacilitatetheuptakeof the bacteriabyphagocytic cells. They bind to the antigen’ssurfaceand help phagocytesrecognizethepathogens. Thisprocess is called opsonization. By binding tothe surfaceof a pathogenthe antibodiescanactivate complement system’s proteins. Thecomplement system is a group of plasma proteins which attackextracellular pathogens. It can activatespontaneouslyor by antibody, bind to a pathogen. The activationofthese proteinsenables them to bind to the pathogens’surface. Thus they facilitate thework of phagocytes. Report this ad What is Cell Mediated Immunity? Pathogen within a living cell is not recognized by the humoral immunity. For this reason the antibodies are not effective when the pathogens infect cells. The cell-mediated immune response is the one, able to identify and destroy infected cells. Thus, it prevents the further invasion of viruses or bacteria.
- 3. T-cells develop in the thymus. From there they enter the blood and circulate between the peripheral lymphoid tissue and the blood until they found their specific antigen. The so called naive T-cells are mature recirculating cells that haven’t met their specific antigen. When such cell encounters an antigen it starts to multiply and differentiate into armed effector T-cells. These cells are able to contribute to the termination of the antigen. When they meet their antigen on other (target) cell they act rapidly. The naive T-cells activate and form armed effector T-cells when they meet their antigen in the form of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) on the top of an activated antigen-presenting cell. Examples of antigen- presenting cells are the dendritic cells. They are highly specialized cells, ingesting antigen at sites of infection. They migrate to a local lymphoid tissue where they present the antigen to the recirculating T-cells. Macrophages and B-cells can act as antigen-presenting cells. Effector T-cells recognize peptide antigens from different pathogens. MHC class I molecules carry to the cell surface the peptides from pathogens in the cells and present them to CD8 T-cells. These cells differentiate into cytotoxic T-cells which kill the infected cells. Pathogens proliferating in vesicles inside the cells, toxins, and peptide antigens from extracellular bacteria, are transported to the surface of the cell by МНC class II molecules. They present the pathogens to the СD4 Т-cells, which differentiate into TH1 and TH2. Pathogens accumulating inside dendritic cells and macrophage stimulate the production of TH1 cells. The extracellular antigens stimulate the differentiation of TH2 cells. The infected cells are destroyed by cytotoxic T-cells, while the intracellular pathogens are terminated by macrophages. After the termination of an infection the number of T-cells decreases but a small number is maintained for years. That’s why the re-infection with a
- 4. microbe results in a more profound and rapid proliferation of effector T- cells and leads to vast clearance of the organism. Report this ad Difference Between Humoral and Cell Mediated Immunity 1. Definition of Humoral and Cell Mediated Immunity Humoral Immunity: The aspect of immunity, mediated by macromolecules found in the extracellular body fluids is called humoral immunity. Cell Mediated Immunity: The aspect of immunity that identifies and destroys infected cells is called cell mediated immunity. 2.Pathogens Humoral Immunity: The humoral immunity protects against extracellular pathogens. Cell Mediated Immunity: The cell mediated immunity protects against intracellular pathogens. 3.Main cells Humoral Immunity: The main cells, involved in the humoral immunity are the B-cells. Thеse cells are generated and mature in the bone marrow. Cell Mediated Immunity: The main cells, involved in the cell mediated immunity are the T-cells. Thеse cells are generated in the bone marrow and complete their development in the thymus. 4.Activation Humoral Immunity: The end result of the activation is the differentiation of plasma B-cells, secreting antibodies.
- 5. Cell Mediated Immunity: The end result of the activation is the secretion of cytokines. 5.Onset Humoral Immunity: The onset is rapid. Cell Mediated Immunity: The onset is delayed. Difference between Humoral and Cell Mediated Immunity in Tabular form
- 6. Summary of Humoral Vs. Cell Mediated Immunity The immune system has two divisions – humoral immunity and cell mediated immunity. The aspect of immunity, mediated by macromolecules found in the extracellular body fluids is called humoral immunity. The aspect of immunity that identifies and destroys infected cells is called cell mediated immunity. The humoral immunity protects against extracellular pathogens, while the cell mediated immunity protects against intracellular pathogens. The main cells, involved in the humoral immunity are the B-cells. These cells are generated and mature in the bone marrow. The main cells, involved in the cell mediated immunity are the T-cells. These cells are generated in the bone marrow and complete their development in the thymus. The end result of the activation is the differentiation of plasma B-cells, secreting antibodies. The end result of the activation is the secretion of cytokines. The humoral immunity has a rapid onset, while the cell mediated immunity has a delayed onset
- 7. Comparison of Humoral and Cell Mediated Immunity Humoral Immunity Cell mediated Immunity Maincells B lymphocytes T lymphocytes Maturation Generatedandmatured in bone marrow Originate inbone marrow and complete development inthymus Protect against Extracellular microbes and their toxins 1. toxininduceddiseases 2. infections (virulence relatedto polysaccharide capsule) Intracellular microbes 1. viruses 2. parasites (leishmania) 3. bacteria (mycobacteria, listeria) 4. kill tumor cells %age of lymphocytes 10-20% circulating peripheral lymphocyte population 60-70% Locationin lymph nodes Superficial cortex Paracortical areas Locationin spleen White pulp Periarteriolar sheaths Receptors B-cell antigenreceptor complex consisting of mainly IgM and IgD immunoglobulins In 95% T cells à alpha/betaTCR In minority à gamma, T cells Accessory surface molecules Igα, Igβ, Fc receptors, CD40, CD21 CD3 molecular complex Dimer of ∑ chain CD4, CD8, CD2, CD28 integrins End result of activation Differentiationof B cells intoantibody secreting Secrete locally acting proteins calledcytokines
- 8. cells calledplasmacells Hypersensitivity reactions I, II, III are antibody mediated IV is cell mediated Role of MHC molecules Antigenreceptor recognizes whole unprocessedproteins and has no requirement for presentationby MHC protein Antigenreceptor recognizes only processedpeptides in associationwithMHC protein Regulator of antibody synthesis No Yes Onset Rapid Delayedtype hypersensitivity Antibodies Formed Not formed Evaluation From plasma level of antibodies Skin test for development of delayed type of hypersensitivity Cells involved Ab synthesisrequires 3 cells: 1. t lymphocytes 2. b lymphocytes 3. macrophage 1. macrophage 2. helper T cells 3. natural killer T cells 4. cytotoxic Tcells
- 9. Difference Between T cells and B cells The immune system is formed by a complex network of cells, organs, and processes interacting together to constitute the main defense line of the human body against foreign organisms and diseases. One of its main components are lymphocytes, a subtype of white blood cells which include two types of cells, T cells and B cells. T cells and B cells are both generated from the lymphoid common progenitor in the bone marrow. What are T cells? T cells, also called thymocytes, are lymphocytes generated from a stem cell precursor, the lymphoid common progenitor, in the bone marrow. They migrate afterward to the thymus, a lymphoid organ situated in the chest, where they undergo their maturation. Mature T cells circulate continually in an inactive state between the blood and the peripheral lymphoid organs (the lymph nodes, the spleen, and the mucosal lymphoid tissues) until they encounter foreign antigens from the sites of infection. In this case, they are activated and differentiate into effector cells.
- 10. Two classes of effector T cells with distinct functions exist – cytotoxic T cells and helper T cells. Cytotoxic T cells are capable of attacking and killing other cells infected with an intracellular pathogen or a virus. Helper T cells, on the other hand, present an indirect immune response by stimulating other defense mechanisms and cells such as macrophages, B cells, and cytotoxic T cells. They are effective against intracellular and extracellular pathogens as well. Cytotoxic T cells and helper T cells alike, are characterized by the presence of membrane-bound antigen receptors and are activated through a direct contact with an antigen-presenting cell. Cytotoxic T cells act by inducing their target pathogen-infected cell to undergo apoptosis through the activation of the caspase cascade. Helper T cells, when activated by an antigen-presenting cell, act by secreting different cytokines and by expressing specific stimulatory proteins on their surface. They can differentiate into two types of helper cells – TH1 and TH2 cells. TH1 cells function by activating macrophages and cytotoxic T cells, while TH2 cells function by activating B cells. Report this ad What are B cells?
- 11. B cells are lymphocytes generated from the lymphoid common progenitor in the bone marrow. They undergo their maturation in the bone marrow as well, at the same site of their formation, hence their name B cells. Upon maturation, B cells enter the bloodstream before migrating to the peripheral lymphoid organs. B cells are characterized by the presence of antigen receptors on their membrane. When activated, they differentiate into plasma cells and secrete antibodies or immunoglobulins, which are mainly the secreted form of their membrane antigen receptors. While some antigens can trigger a direct response from the B cells, their main mechanism of action depends on their interaction with the helper T cells. Activated helper T cells are responsible for triggering the proliferation of B cells and the secretion of the specific antibodies. The secreted antibodies can therefore recognize pathogenic antigens and bind specifically to them. The pathogen is either directly neutralized by the antibody, or tagged to be destroyed subsequently by other components of the immune system such as macrophages. Difference between T cells and B cells? T cells and B cells are both generated in the bone marrow from stem cells or more precisely form the lymphoid common progenitor. T cells or thymocytes maturate in the thymus, a lymphoid organ situated in the chest, while B cells mature in the bone marrow, at the same site of their generation. Both T cells and B cells migrate to the bloodstream after their maturation and circulate between the peripheral lymphoid organs in an inactive state. There are two types of activated T cells: Cytotoxic T cells responsible of the destruction of cells infected by intracellular pathogens, and helper T cells responsible of activating cytotoxic T cells, macrophages, and B cells. B cells, on the other side, differentiate upon activation by helper T cells into one cell type, plasma cells capable of secreting antigen-specific antibodies. Activated T cells present antigen receptors on their membrane and are not capable of secreting antibodies, whereas activated B cells are responsible for antibody secretion. T cells versus B cells: Comparison Table
- 12. Summary of T cells versus B cells T cells and B cells are two cellularcomponents of the complex network that constitutes the immune system.They are the main actors of the adaptive immunity against foreign pathogens. While both are generated in the bone marrow from a common lymphoid progenitor, their main differences reside in their maturation sites and their mechanism of action: T cells undergo maturation in the thymus,while B cells undergo their maturation in the bone marrow. T cells present antigen receptors in their membrane and are not capable of secreting antibodies. They can act as cytotoxic T cells by directly attacking cells infected with intracellularpathogens, or as helper T cells by indirectly activating other immune cells including cytotoxic T cells, macrophages, and B cells. B cells present antigen receptors on their membranes but are also responsible for secreting antibodies when activated by helper T cells. The secreted antibodies are highly specific and attach to the antigens provoking the destruction of the infectingpathogen either directly, or indirectly through the subsequent recruitment of other immune cells such as macrophages.
- 13. Differences Between Immunoglobulin and Antibodies Immunoglobulin vs Antibodies Ever wonder why we don’t get sick easily even if the surroundings are more polluted than before? It’s because we have tiny soldiers inside our body, and they are called immunoglobulin. There has been confusion that immunoglobulin and antibodies are different things. However, as I do my research on the Internet, immunoglobulin and antibodies are pretty much the same when it comes to their function.An antibody is a Y-shaped protein which has the task to determine and neutralize certain bacteria and viruses that try to invade our immune system. Immunoglobulin is also a protein that carries the same function as antibodies. In this regard, the terms immunoglobulin and antibodies are often used interchangeably.The Y- shape of the antibody enables its key to unlock it and release the antibodies inside the immune system. This key is known as an antigen. The antigen helps the antibody to determine the foreign object within our body. It also comes in the shape of a “Y” enabling the antibody to activate and perform its neutralizing function. In this case, the antibody or immunoglobulin will be found in the bloodstream, tissues, and other bodily fluids. The antibodies or immunoglobulin come from the plasma cells which can be derived from the immune system’s B cells. The B cells become plasma cells when an antigen binds to its structure. Sometimes, the T cells help the B cells to activate. There are five types of immunoglobulin: IgM, IgG, IgA, IgD, and IgE. These immunoglobulin, or antibodies, have similar, basic structures. They contain four polypeptide chains which are fused together by disulfide bonds forming a symmetrical molecular structure. The immunoglobulin, or antibodies, can really work wonders. When activated, they signal other cells of the immune system to be on the alert whenever there are invading foreign bodies like bacteria and viruses. The
- 14. antigen plays a very important role in the activation of the antibodies. Without it, we would always catch a cold, flu, and other types of diseases. If you have seen TV commercials that encourage mothers to let their toddlers play in muddy terrains or seemingly dirty surroundings, that is one way of boosting the child’s immune system. As long as they properly clean their children after playing, they don’t have anything to worry about. And because the body has immunoglobulin, or antibodies, a child cannot easily catch colds and the flu. The immunoglobulin, or antibodies, work day and night to keep you out of reach of bacteria and viruses. But under certain conditions, foreign bodies can still make you sick. This is where you need to eat plenty of nutritious foods and Vitamin C rich foods like citrus fruits to enhance your immune system. To be able to get the most out of our little soldiers’ protection, you also need to take care of them through eating the right food and drinking plenty of fluids.Remember that our immunoglobulin, or antibodies, can also get sick if we don’t take care of them. As a responsible person who always keeps an eye on your health, you have to properly take care of your body. Summary: 1. Immunoglobulin and antibodies are terms used interchangeably. 2. An antibody, or immunoglobulin, is a Y-shaped protein that helps to combat and fight diseases in our bodies. 3. Antibodies, or immunoglobulin, are generally found in our bloodstream, tissues, and other forms of bodily fluids. They are produced by plasma cells of the immune system. 4. With the help of antigens, the antibodies, or immunoglobulin, can perform their function. Antigens are like keys unlocking the antibodies. 5. People don’t easily acquire diseases because of the presence of antibodies.
- 15. Differences Between Vaccine and Toxoid In our modern world, we tend to be assailed by too many terms than we can care to count. Oftentimes, we hear people use a certain term and sometimes associate it with another and we assume that they are the same. Two of these terms that we tend to use equally are vaccine and toxoid. The use of vaccines and toxoid these days is quite due to the fact that there are simply too many illnesses and diseases that are ‘there,’ so when a baby is born, it is imperative that he would be vaccinated with the necessary ‘antigen’ that would help his body in producing the antibody. There are so many types of medical what-not that are simply too many for us laymen to fully understand. So when we get to meet terms like vaccine and toxoid, especially when heard in almost the same usage and conversation, we would put two and two together and assume that such terms are similar in meaning, hence, they can be used one with the other. What is vaccine? Vaccine is an antigenic material. Antigenic is from the term ‘antigen,’ which is a substance that is introduced and brought to one’s body. Its purpose is to be able to produce the antibody internally. The antigens that are injected or introduced to your body can be toxins. It can also be bacteria, foreign blood cells, and even cells of transplanted organs. The main purpose of a vaccination is to stimulate, increase, or even promote your body’s immune system to come up with an adaptive immunity to whatever vaccine it is that you are about to take it for. Examples of vaccines that have been created are influenza vaccine, chicken pox vaccine, polio vaccines, measles, and many more. What is toxoid? Toxoid, on the other hand, is introducing a bacterial toxin to your body. The toxic has been made ‘inactive’ by use of a chemical or heat treatment. The most common toxoid that is probably being administered is the diphtheria, botulism, and tetanus. Toxoids are used as vaccines because
- 16. they help the individual in stimulating an immune response to the toxin. Another reason for using toxoid as vaccine is to increase the antigen in one’s body. With those different definitions above, it might be easier to now grasp how one is different from the other. Then again, as one layman to another, it is really easier to comprehend medical terms when used as examples. Simply put, vaccines help your body by increasing the antibodies. Toxoid helps your body by putting the virus in, in a modified version, and allowing your body to produce the antibody to deflect and kill it, naturally. SUMMARY: Vaccine and toxoid are both committed to helping your body in coming up with ‘something’ to fight the virus, the bacteria, or the illness. They would both vary in how your body would ‘accept’ the virus, for toxoid; or antigen, for vaccine, and come up with how to fight them naturally. Your immune system has its ways of coming up with a powerful ‘method’ in killing the antigen or virus. This is why some doctors deem it best on how to go about curing you through any of these methods. The bottom line is that vaccine uses antigens that should help produce the antibody against the virus. Toxoid is introducing the modified version of the virus to your body, and allowing your body to create the ‘immune response’ to the virus. Since doctors would know best on how to prevent, cure, and improve your health, it is always best to consult with them with any problem that you might have. Better yet, for any questions regarding proper care and achieving a healthier you, or family, get in touch with your family doctor now.
- 17. Differences Between a Toxin and a Toxoid Toxin vs Toxoid The human body is a vulnerable vessel among harmful diseases. Without a healthy body, these harmful diseases can invade our system. However, harmful bacteria do not only come from the outside, but they can also emerge from within or inside our body system. “Toxin” and “toxoid” always ring a bell whenever we are caught up with a very bad disease. In this article, let us determine the meaning and differences between “toxin” and “toxoid.” The term “toxin” came from the Ancient Greek word “toxikon.” Toxins are the poisonous substances that have been produced within the cells of living organisms. Ludwig Brieger, an organic chemist, was the first one to use the term “toxin.” If the poisonous substance is not produced within the cells of a living organism, it is called “toxicant” or “toxics,” instead of “toxin.” These toxins can come in the form of small molecules, peptides, or proteins, and they are capable of causing disease. These poisonous chemical compounds are also produced naturally by plants and animals. Toxins can also be used as a protective and offensive mechanism by the living organism. However, these toxins can also disrupt or interfere with the natural body processes of the organism in order to survive. Toxins can affect the nervous system or even the digestive system. Examples of toxins are botulinum toxins from the bacteria, Clostridium botulinum. This is the most common and most poisonous substance. You may have heard the term “botulism,” or popularly known as “food poisoning.” Poorly preserved foods attract the bacteria Clostridium botulinum, thus producing the botulinum toxins. When you ingest the contaminated food, you will experience stomach discomforts or mild to excessive pain. Toxins are dangerous, so to speak. In response to eliminating harmful toxins, several studies have been conducted. Scientists have developed
- 18. ways to fight these toxins – and these are toxoids. Toxoids fight toxins. They are the medicine or the cure when someone ingests harmful toxins. Toxins and toxoids have similar structures since a toxoid was derived from a toxin. However, a toxoid’s composition has been altered in order to remove the harmful effects. This is usually done in the process of heating the toxin. If toxins are naturally made, toxoids are man-made. Toxoids are synthetic compounds which are given to animals and people in order to develop long-term resistance to toxins. If you are given a specific type of toxoid, you will be immune to a specific type of toxin. Though it is meant to defend your body from a harmful toxin, your body’s immune system will still see the toxoid as a threat to your body since its structure is also similar to that of a toxin. The next time your body is invaded by a particular toxin, your immune system will already know how to fight it since it has already learned its experience from fighting against the toxoid. Toxoids are only given in small doses which are enough to be countered by the body’s immune system. Summary: 1. Toxins are poisonous substances that have been produced within the cells of living organisms. 2. Ludwig Brieger, an organic chemist, was the first one to use the term “toxin.” 3. Examples of toxins are botulinum toxins from the bacteria, Clostridium botulinum. This is the most common and most poisonous substance which causes botulism or food poisoning. 4. Toxoids fight toxins. You will develop an immunity against a particular toxin if you take the corresponding toxoid. 5. Your body’s immune system will still see the toxoid as a threat to your body since its structure is also similar to that of a toxin, but your immune system will learn how to fight the real toxins when encountered the next time.
- 19. Difference Between Antigens and Antibodies Antigens vs Antibodies Antigen comes from the root term antibody generator and is an organic substance that initiates the creation of antibodies thereby bringing about a prompt immunity retort. On the other hand, antibodies which are also termed as immunoglobulins comprise of gamma globulin proteins that are contained in the various body fluids and the blood stream in all vertebrates. Antibodies essentially make use of the immune system to recognize and fight foreign elements that can cause harm to the system like viruses or bacteria. Antigens are made of either polysaccharides or proteins. This may contain components like cell walls, capsules, flagella, toxins or fimbrae of viruses, bacteria and other microorganisms. On the other hand antibodies are made of organic structural units including a couple of large heavy chains and a couple of small light chains. Antibodies develop from plasma cells in the blood. The purpose that the antibody serves is that it is produced by the body in order to bind and thereon render all foreign particles into an inactivated state in the body. When the entire process of binding goes unhindered the
- 20. antibody manages to bind specifically the particular antigen in question. The particle that is formed in the process is called the antigen. Antigens on the other hand precisely serve the purpose of stimulating a state of alertness in the body initiating immediate immune response. So the basic difference between an antigen and an antibody is that the emergence of the former leads to the production of the latter, both functioning in an antagonistic organic process to each other. Antibody is the particular protein purposely produced to counter a specific antigen. There are five basic kinds of antibodies, 1. Immunoglobulin M 2. Immunoglobulin G 3. Immunoglobulin E 4. Immunoglobulin D 5. Immunoglobulin A Report this ad Now coming to antigens, there exist three primary kinds of professional antigen cells including, 1. Dendritic Cells 2. Macrophages 3. B-cells Other than these three there is another distinctive kind of antigen called the T-independent antigen. Antibodies are always Y-shaped with a differencein the higher branch.This is due tothe structural difference existing amongst the aminoacids in the antibodies that help in exact antigen recognition.On the other hand the antigen has a surface that acts a s the binding site for the antibody . Once combined by the y branches of the anti body , the antigen gets destroy ed. Summary : 1 . Antigen is an organicsubstance that initiates the creation of antibodies, whereas antibodies make use of the immune sy ste m to recognize and fight foreign elements. 2. There are fiv e basic kinds of antibodies and three basic kinds of antigens. 3. Antigens aremade of either polysaccharides or proteins. Antibodies, on the other hand, are made of organic structural uni ts.
- 21. Difference Between MHC and HLA MHC vs. HLA “MHC” stands for “major histocompatibility complex,” while “HLA” is the short version of “human leukocyte antigen.” Both are groups of antigens or proteins found on the surface of cells and in the genetic makeup or DNA. Their functions are also very similar – they identify and prevent a foreign protein or cell from entering or spreading in an organism’s body. This often happens in coordination with the immune system, which attacks these foreign bodies. Both groups of proteins regulate the immune system itself as well as its response. The main difference between the two groups is that MHC is often found in vertebrates, while HLA is only found in humans. To simplify, HLA is the human body’s version of MHC. Part of the responsibility of these antigens is to detect cells entering the body. Upon detection, cells are recognized as either local or foreign. Local cells carrying viruses and other harmful organisms are often identified and attacked. This is also true for foreign cells introduced to the body.
- 22. These antigens are often involved when an organ transplant is planned for an organism or a human being. Certain tests are carried out to determine the compatibility between an organ and a recipient’s body. Near perfect or perfect matches are desirable in these situations in order to lessen the risk of the recipient’s body rejecting the organ. Aside from organ transplants, both MHC and HLA are very useful in strengthening a body and its immune system. In humans, the HLA is also used in paternity tests to determine the parentage of a child; this is done by comparing antigens from the child, father, and mother. A disadvantage of MHC and HLA is that they carry certain hereditary diseases like cancer, diabetes, and lupus. Both antigens are also responsible for preventing inbreeding or the state of excessive similar genetic material in a person. They favor diversity in the genetic makeup but, at the same time, are responsible for cooperation in terms of kin recognition, dual recognition, and transplant matching. Both MHC and HLA have four classifications of antigens. However, only the first and second classes of antigens are responsible for identification and a response to any cell, whether local or foreign. Class I antigens deal with the destruction of foreign or infected local cells; this occurs in all types of cells except for red blood cells. Meanwhile, class II antigens mediate specific immunization to the antigen. Class II antigens are found in B cells, macrophages, and antigen-presenting
- 23. cells (APCs). MHC and HLA both act as shields of defense and protection of an organism’s body. Summary: 1.MHC and HLA are slightly different, but their functions are basically the same. 2.Both MHC and HLA are classified as proteins and antigens. They are both located in an organism’s cells and work hand-in-hand with the body’s immune system. 3.MHC is found in many vertebrates, while HLA is only found in humans; HLA is basically the human MHC. 4.Both MHC and HLA are identifiers of local and foreign cells in a body. Foreign and infected cells are attacked and immunized. MHC and HLA regulate the immune system and its responses. 5.These antigens play a key role in organ transplants; an organ can be rejected by the recipient’s body if its MHC or HLA is not a near or perfect match. Aside from immunization and histocompatibility, these antigens are also responsible for a body’s defense against foreign organisms. 6.Only two classes out of four are responsible for the body’s immunity responses. 7.HLA can be used in identifying a child’s father and can also function as a carrier of hereditary diseases. It also prevents inbreeding among people.
- 24. Difference Between Active and Passive Immunity Active vs Passive Immunity Throughout the world, people are now more aware of the dangers of viral outbreaks and the effects to humanity. All of us were aghast to hear or even read reports of previous viral epidemics that have plagued different countries. Their ability to cause damage to the body is very serious indeed. Nevertheless, doctors are in constant search for ways to combat these viruses. They are always looking for ways for boosting a person’s immune system to prevent outbreaks from occurring again. They are taking into consideration an individual’s own immunity. Now, you might ask, what is immunity? It indicates your body’s ability to fight pathogens or foreign organisms from causing damage to your body. It involves your immune system and its primary defense, considered as antibodies. Antibodies come in different types and they will attack any foreign compound that comes into your body. Furthermore, your immunity is divided into two major types, active and passive immunity. Both types are also divided further into sub-types, which are, active-natural, active-artificial, passive-natural, and passive-artificial immunity. The differences will be discussed here. First of all, active immunity indicates that you directly form antibodies upon contact with an antigen, which is another term for foreign organisms that cause reactions to the body’s defense mechanisms. Only with the presence of antigens will your body form such antibodies. In active-natural immunity, a direct exposure to disease conditions, such as measles, will enable your body to ‘memorize’ this antigen and then create antibodies. This will prevent you from contracting measles again. On the other hand, in active-artificial immunity, you are given live-attenuated antigens for your body to form antibodies to attack the antigens. For
- 25. example, a vaccine to prevent hepatitis B would be given to you beforehand for your body to prevent the actual disease from occurring. Take into consideration that in active immunity, your body itself is making the antibodies to protect you. In passive immunity, individuals do not have the antibodies, but rather, are passed down to them naturally or through human intervention. The antibodies given are already working and can protect the recipient from illness. In passive-natural, there is a direct transfer of antibody from one person to another without any conscious effort. One very good example for this kind of immunity is the transfer of antibodies from a mother to her baby during its development in the womb. When the baby is born, it is protected from antigens for a specific time. In passive-artificial immunity, a person is given antibodies through medical means, such as, an immuno-suppressed individuals receiving antibodies through intravenous therapy. Summary: 1. Active immunity indicates the formation of antibodies through direct exposure to an antigen. 2. Active immunity is divided into 2 subtypes, active-natural and active- artificial. 3. Passive immunity means that antibodies are passed down to a recipient, even without exposure to an antigen. 4. Passive immunity has 2 subtypes, passive-natural and passive-artificial.