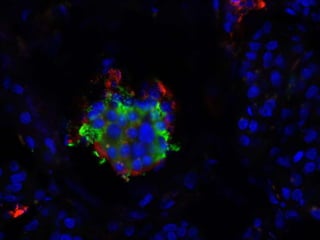
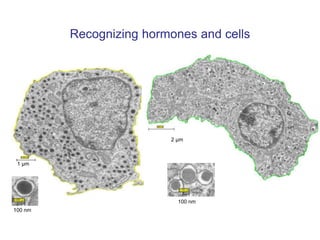
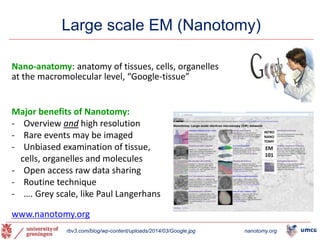
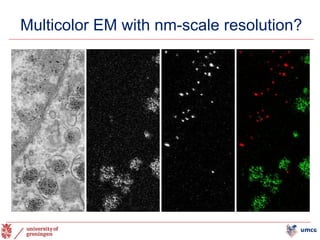
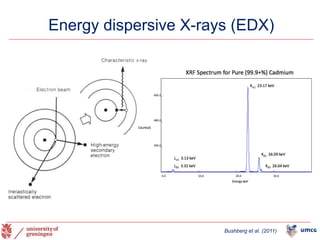
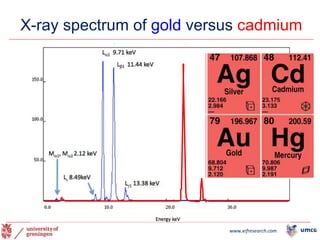
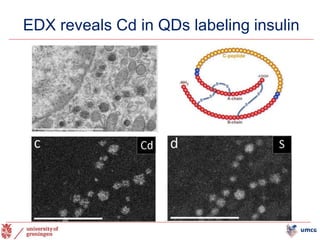
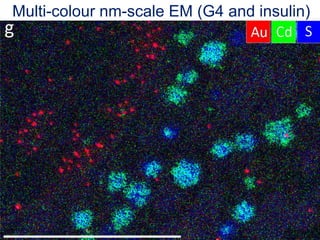
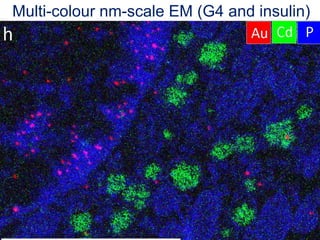
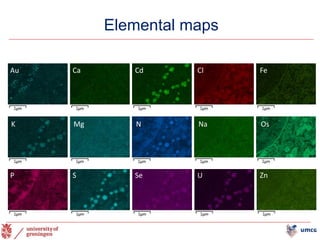
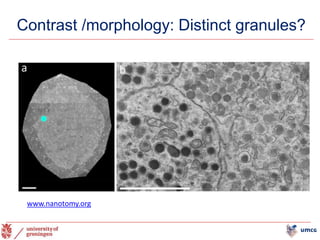
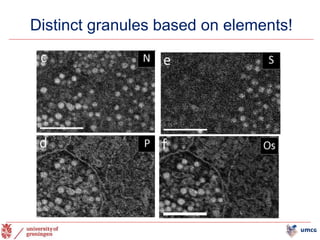
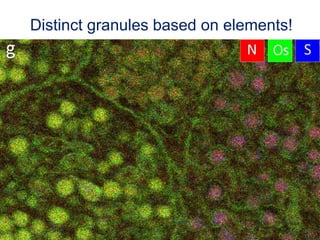
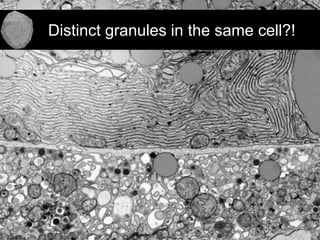
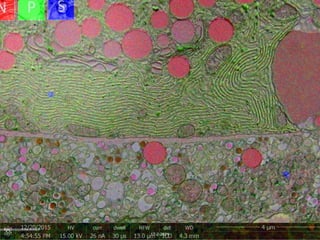
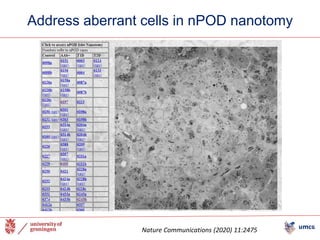
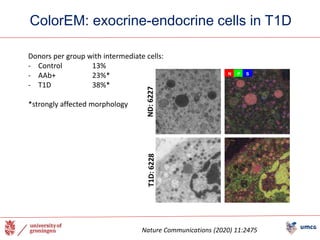
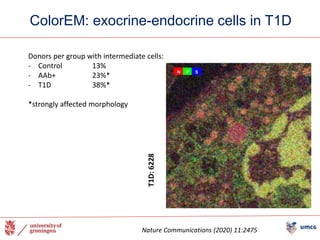
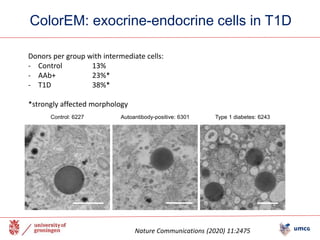
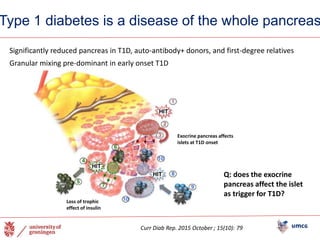
The document outlines the NPOD Nanotomy project, focusing on large-scale electron microscopy (EM) for understanding type 1 diabetes (T1D). It emphasizes the benefits of nanotomy, including high-resolution imaging and open data access, facilitating research on pancreatic tissues and cells affected by diabetes. The project involves a global network, allowing for the examination of donor tissues and the sharing of EM data to further insights into T1D pathology.