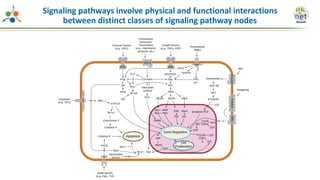
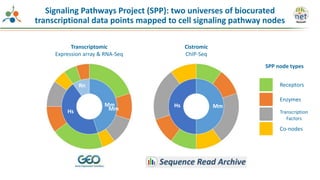
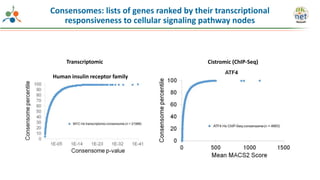
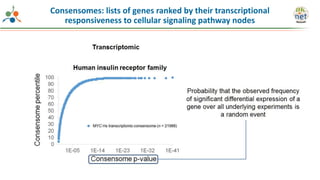
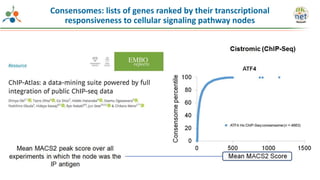
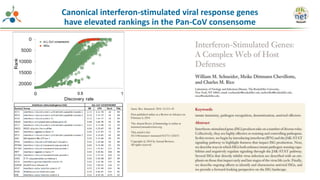
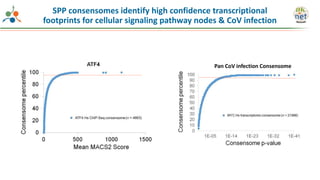
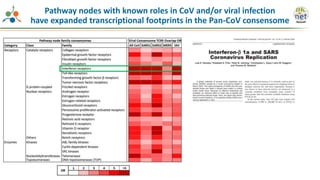
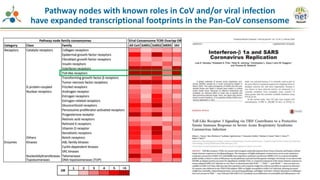
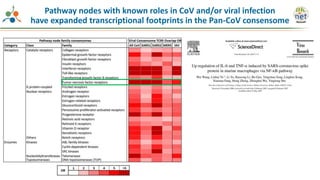
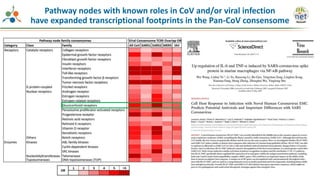
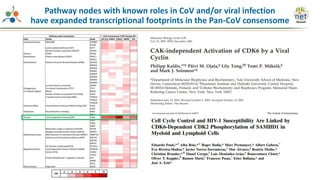
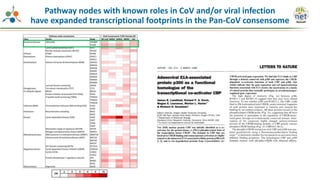
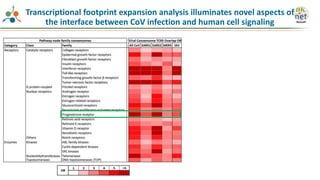
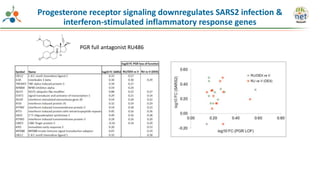
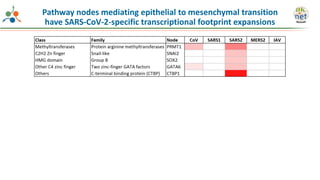
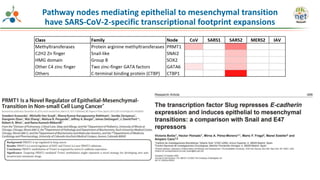
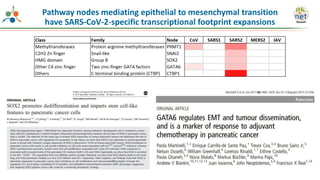
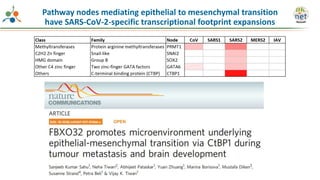
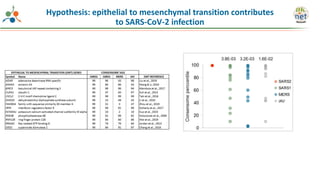
The Signaling Pathways Project (SPP) is an integrated knowledgebase that aims to make mammalian cellular signaling 'omics datasets fair and accessible for researchers. It includes biocurated data on transcriptional responses to various cellular signaling nodes, particularly in relation to COVID-19 and its impact on human cellular signaling pathways. The project emphasizes the development of consensomes to identify significant transcriptional footprints related to coronavirus infections, potentially aiding in hypothesis generation for further research.