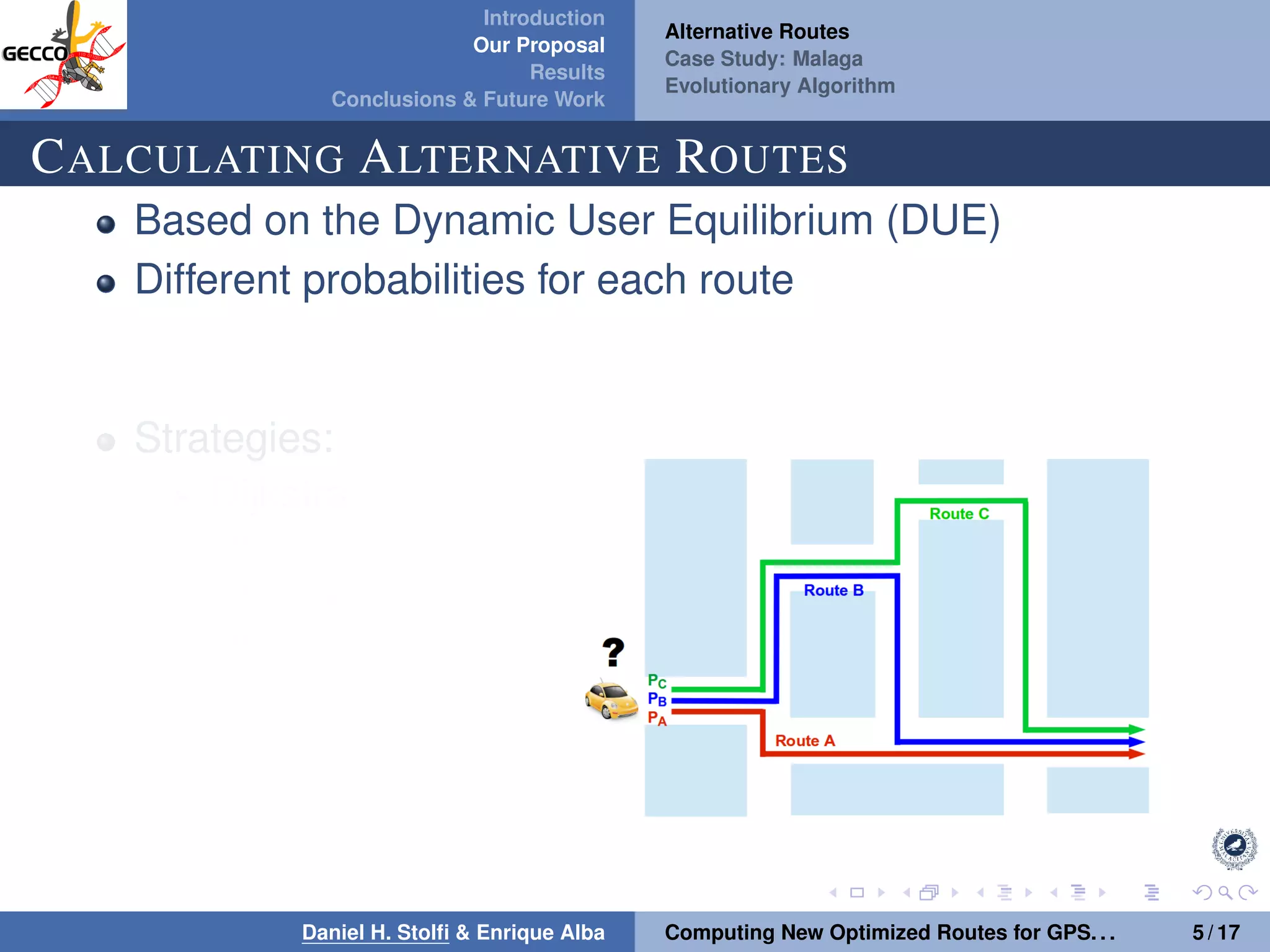
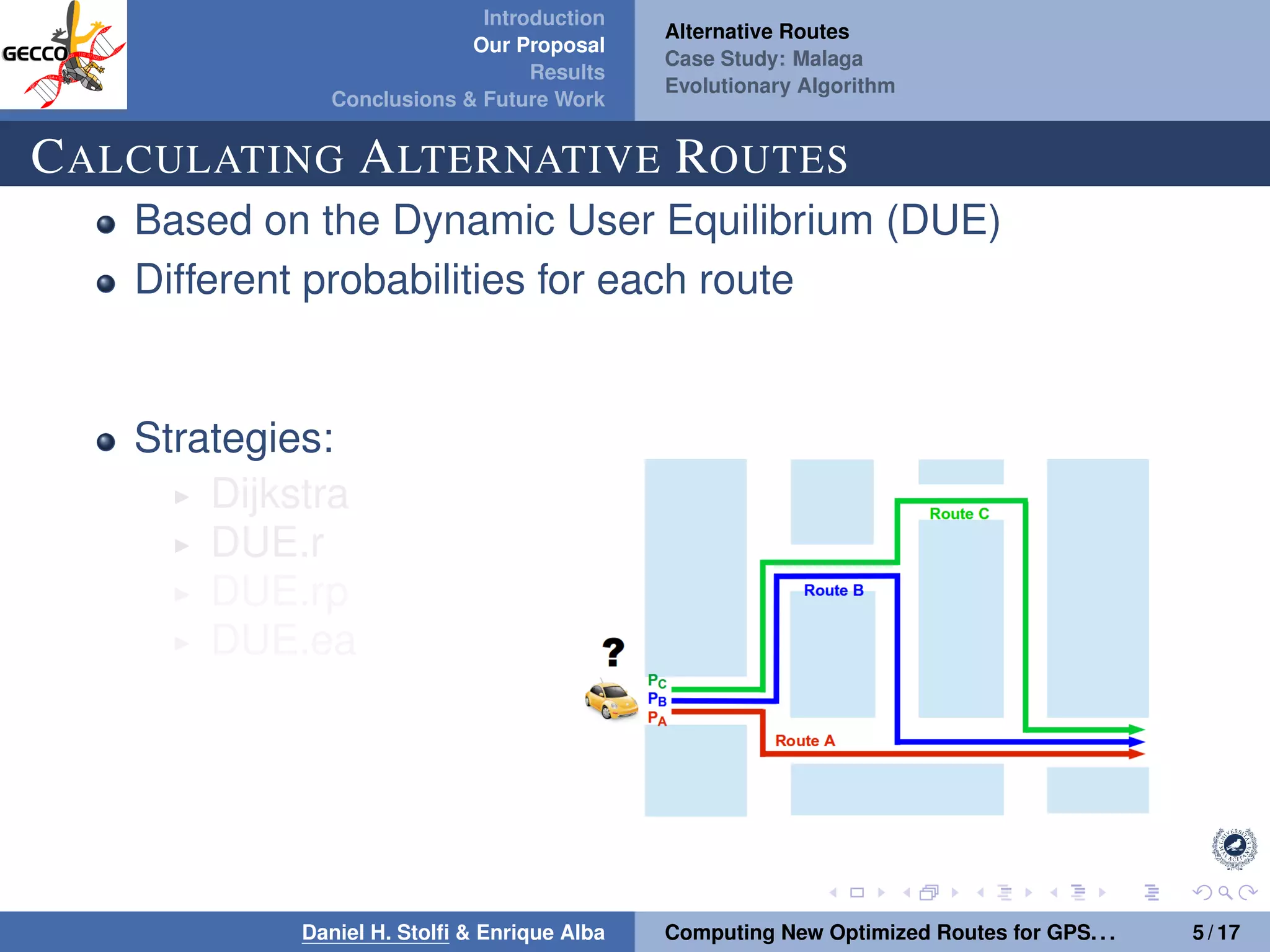
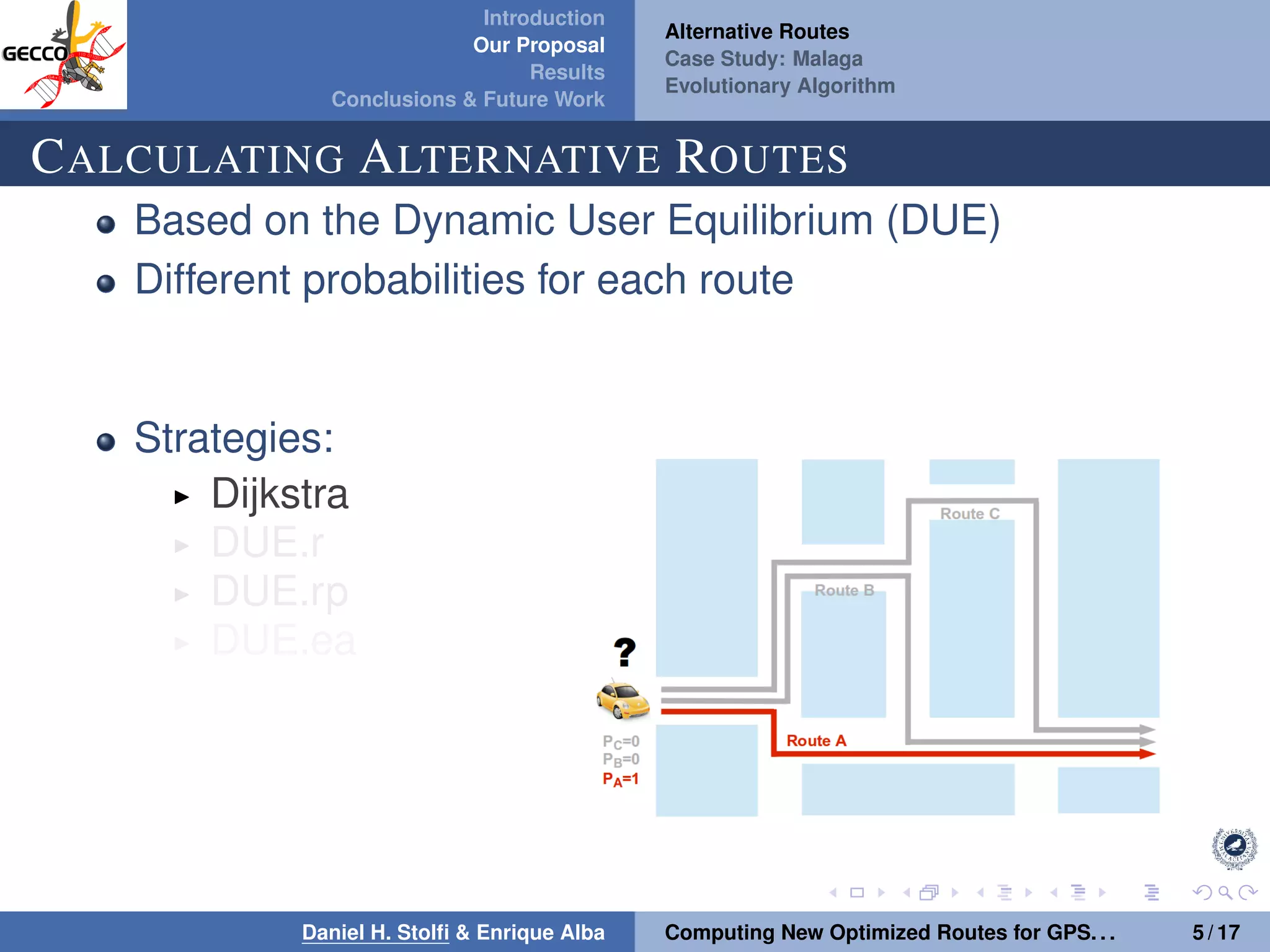
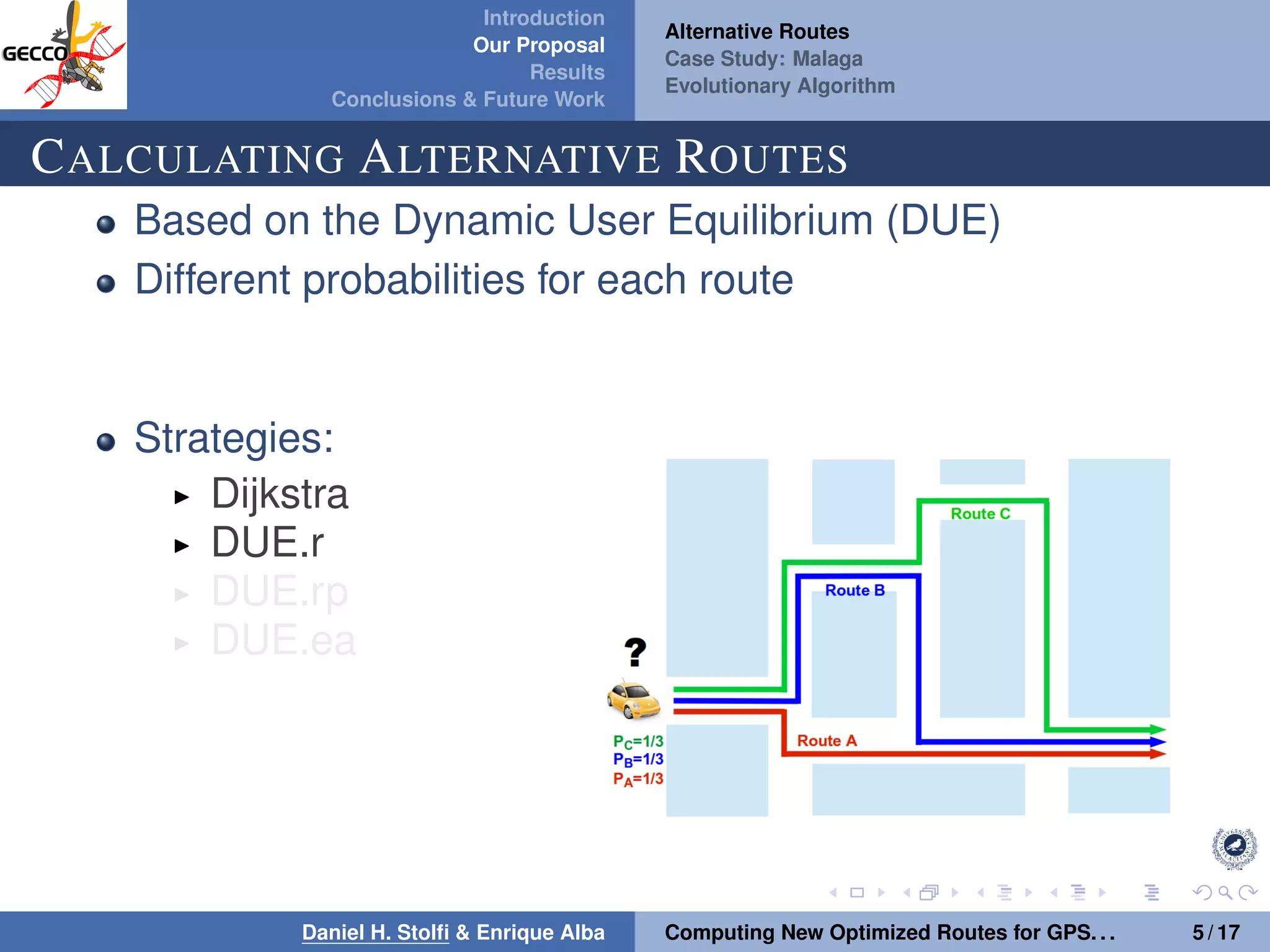
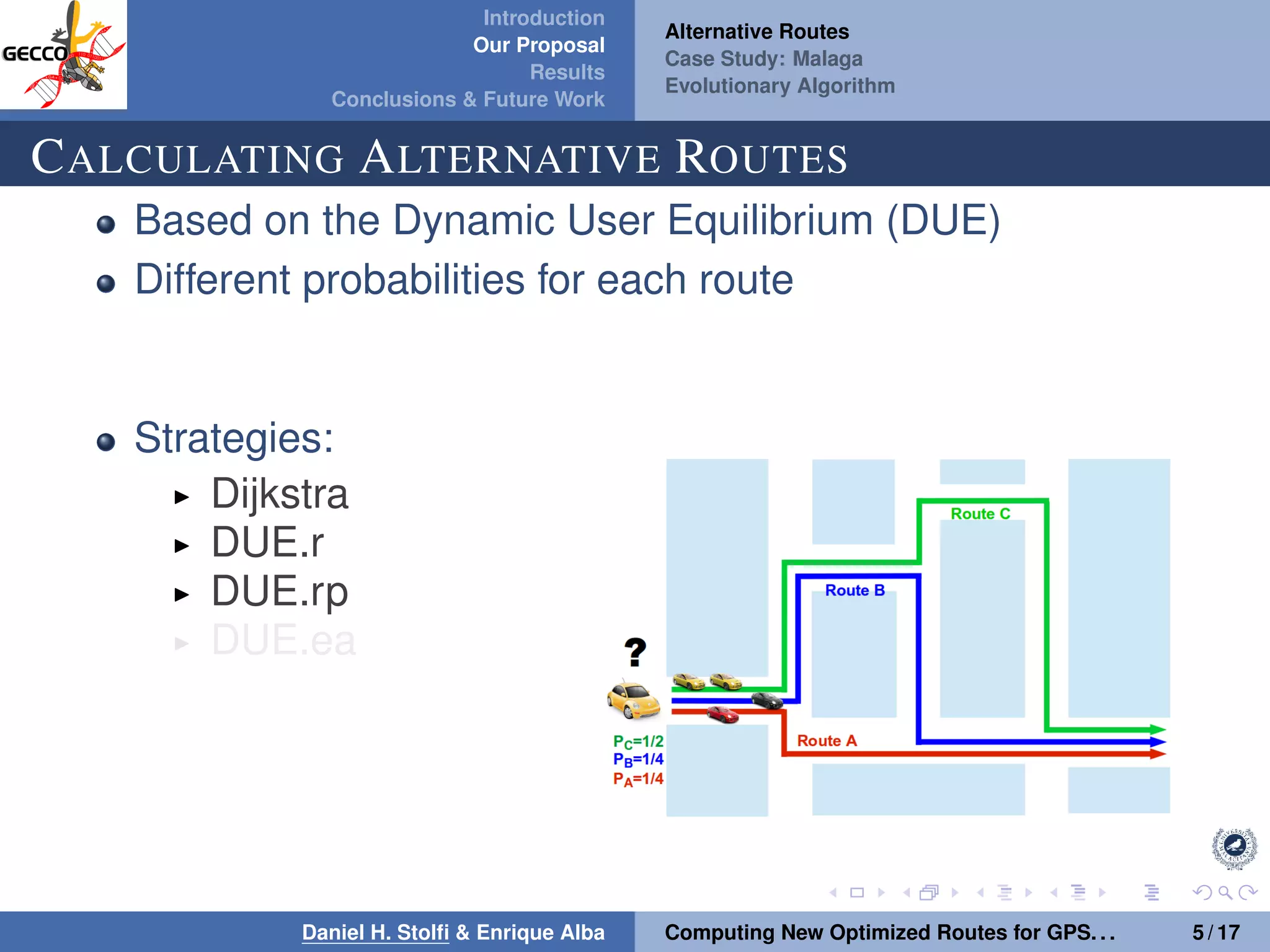
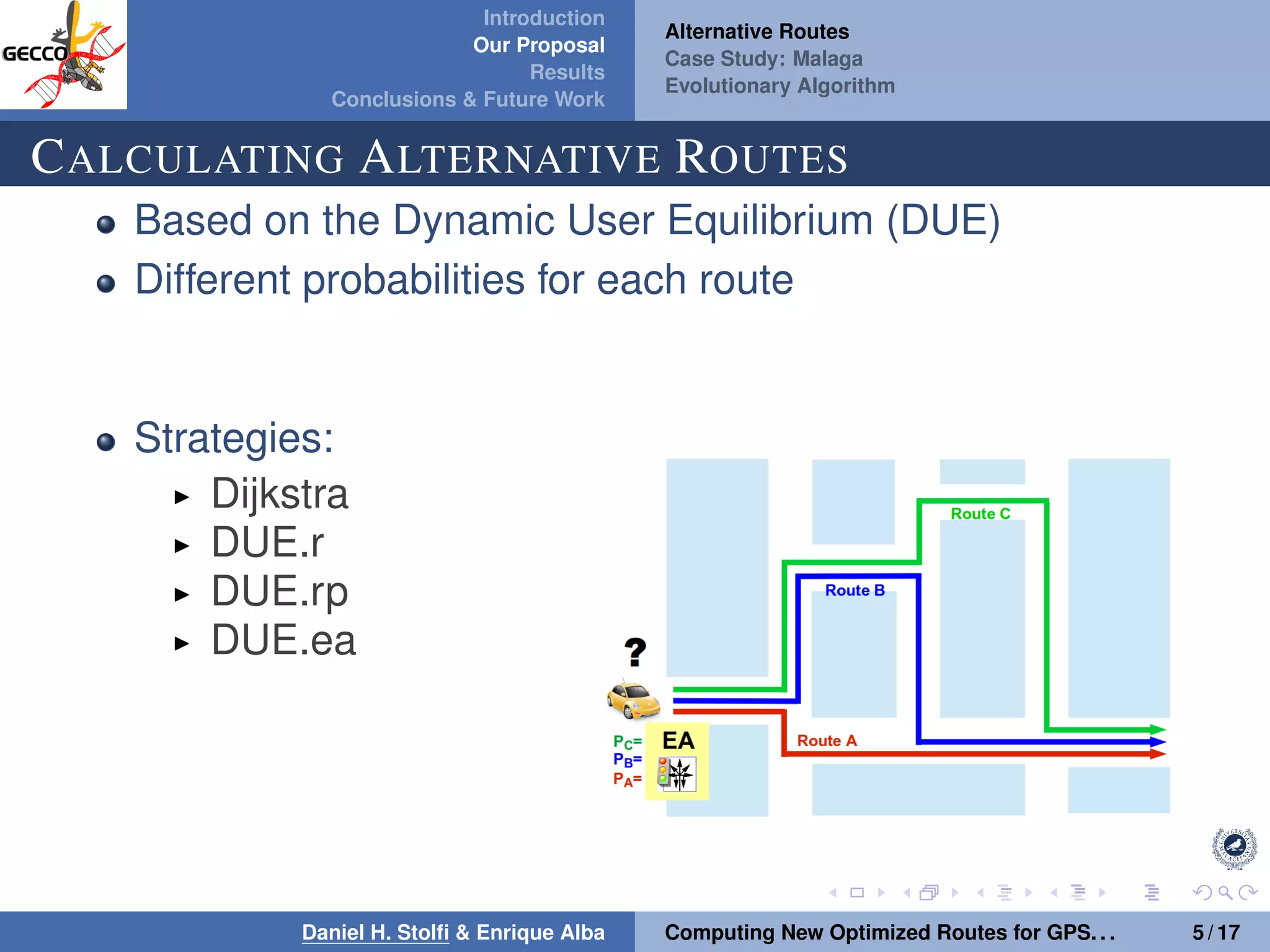
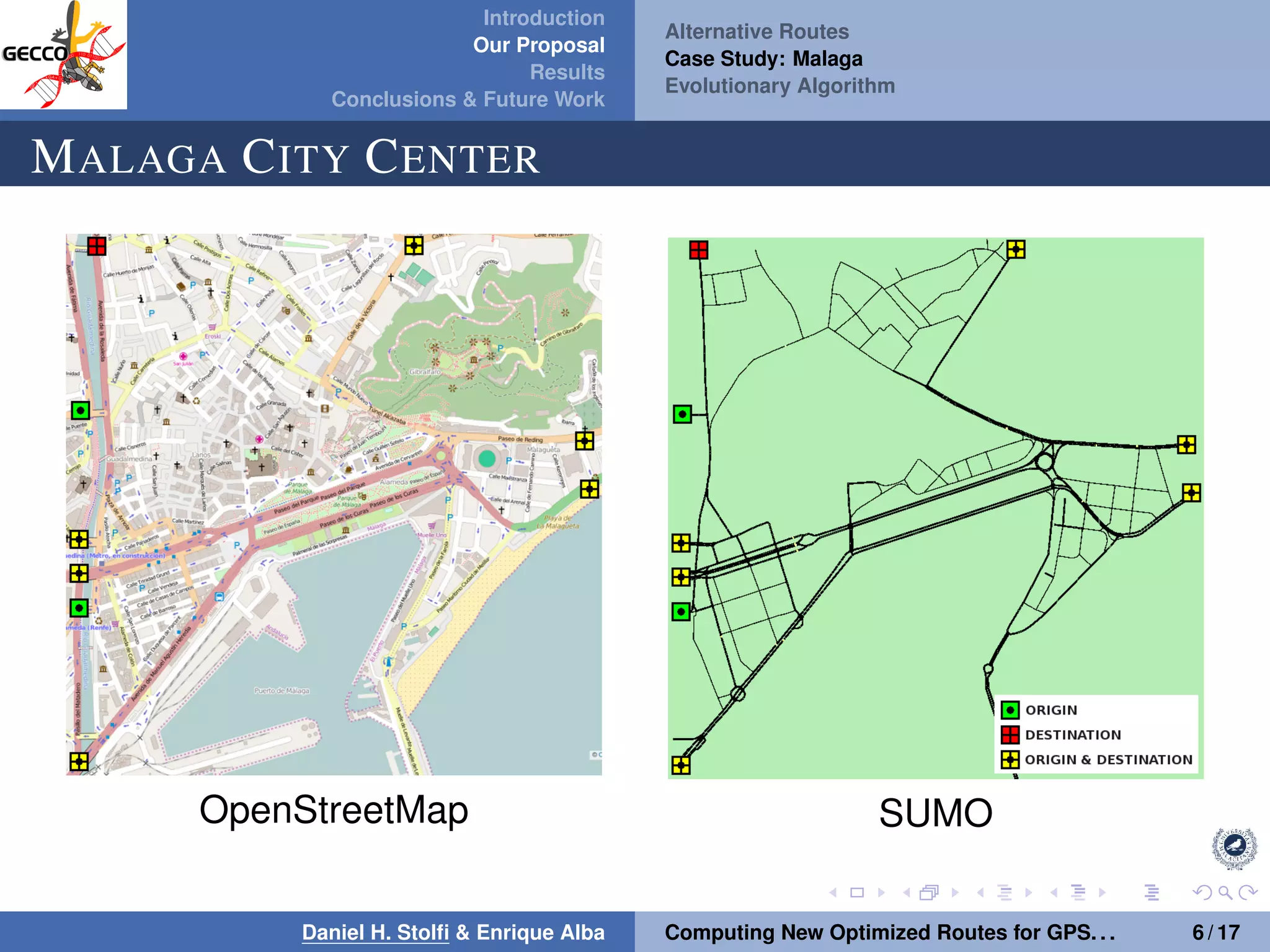
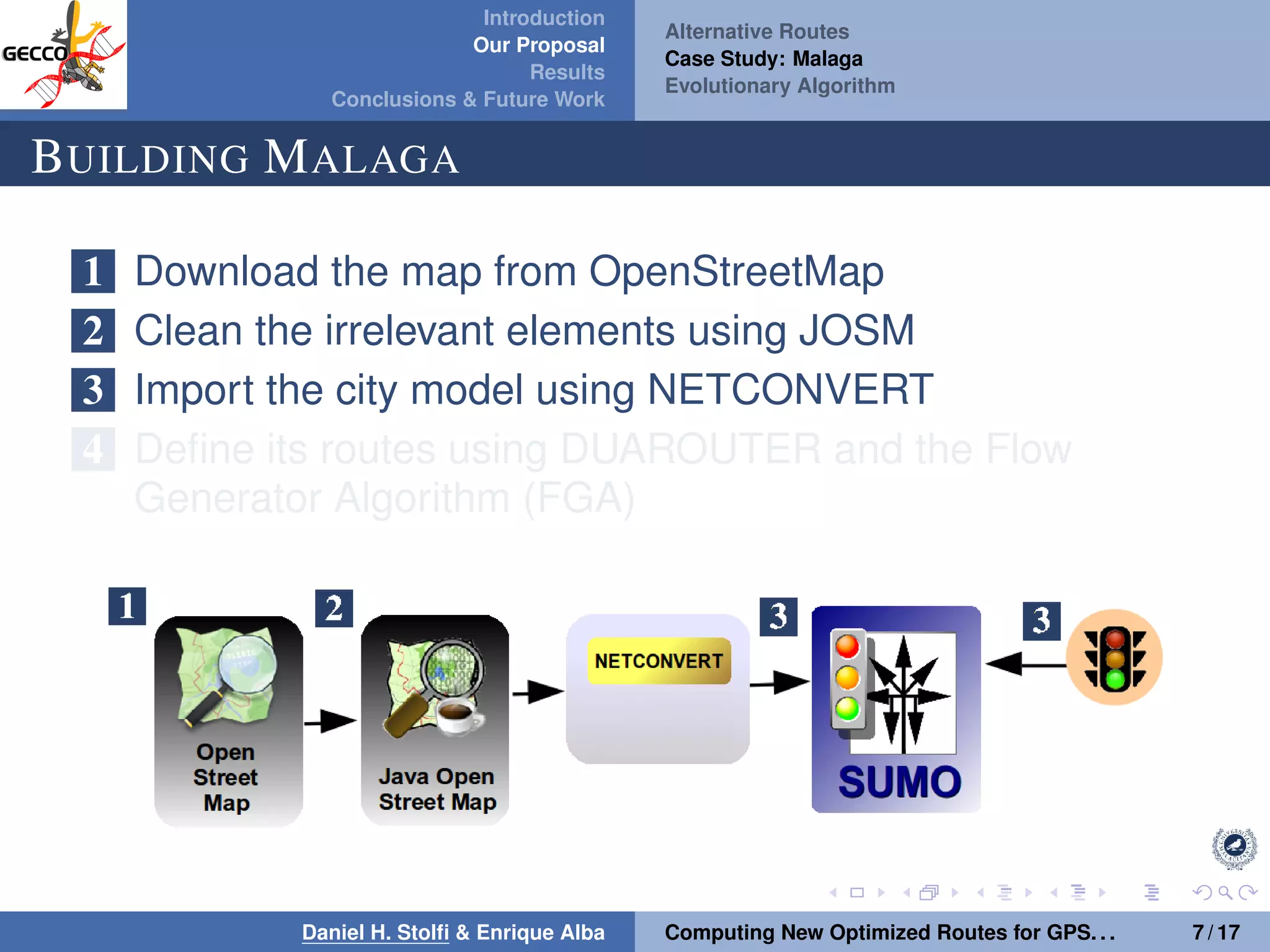
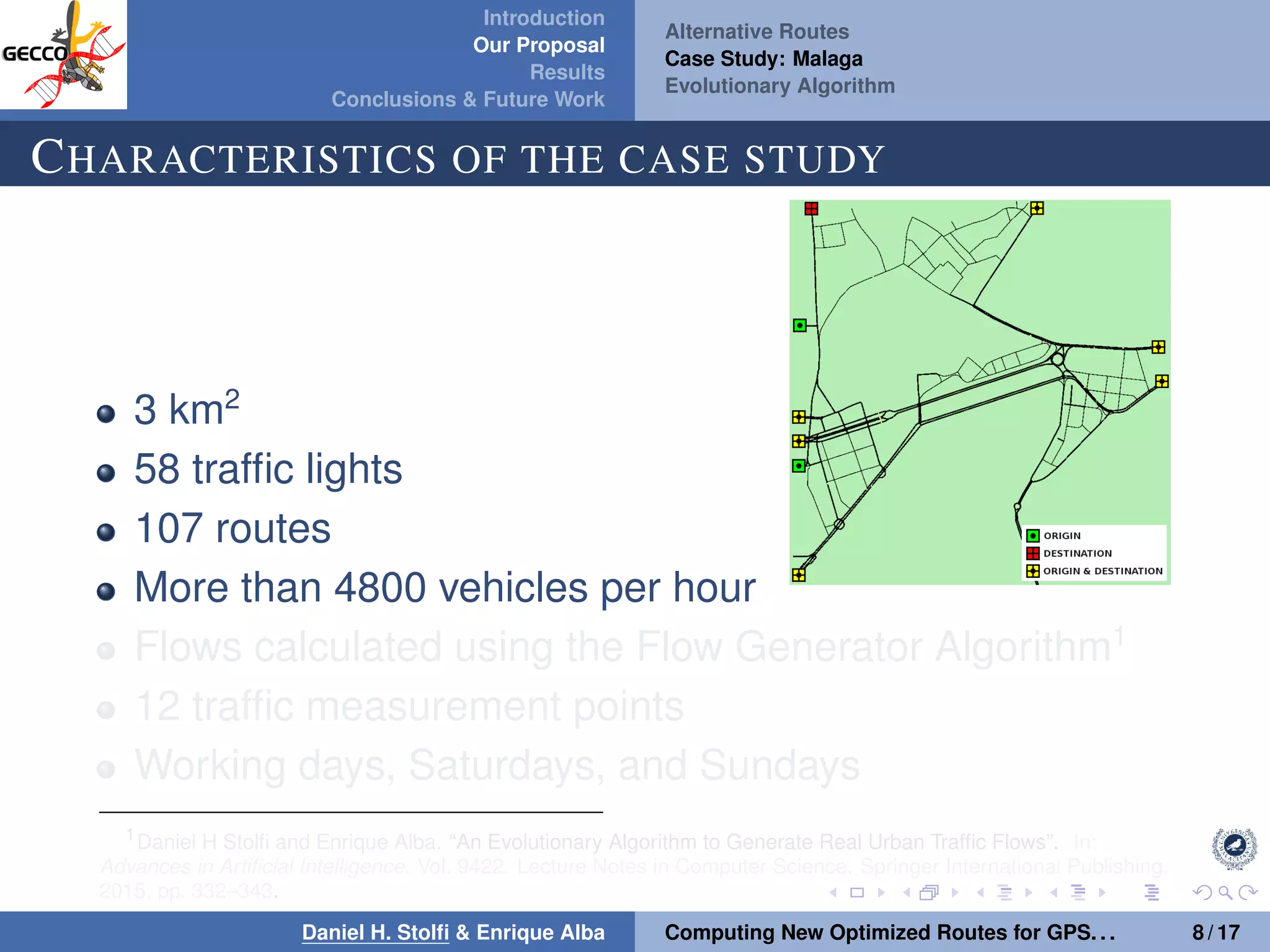
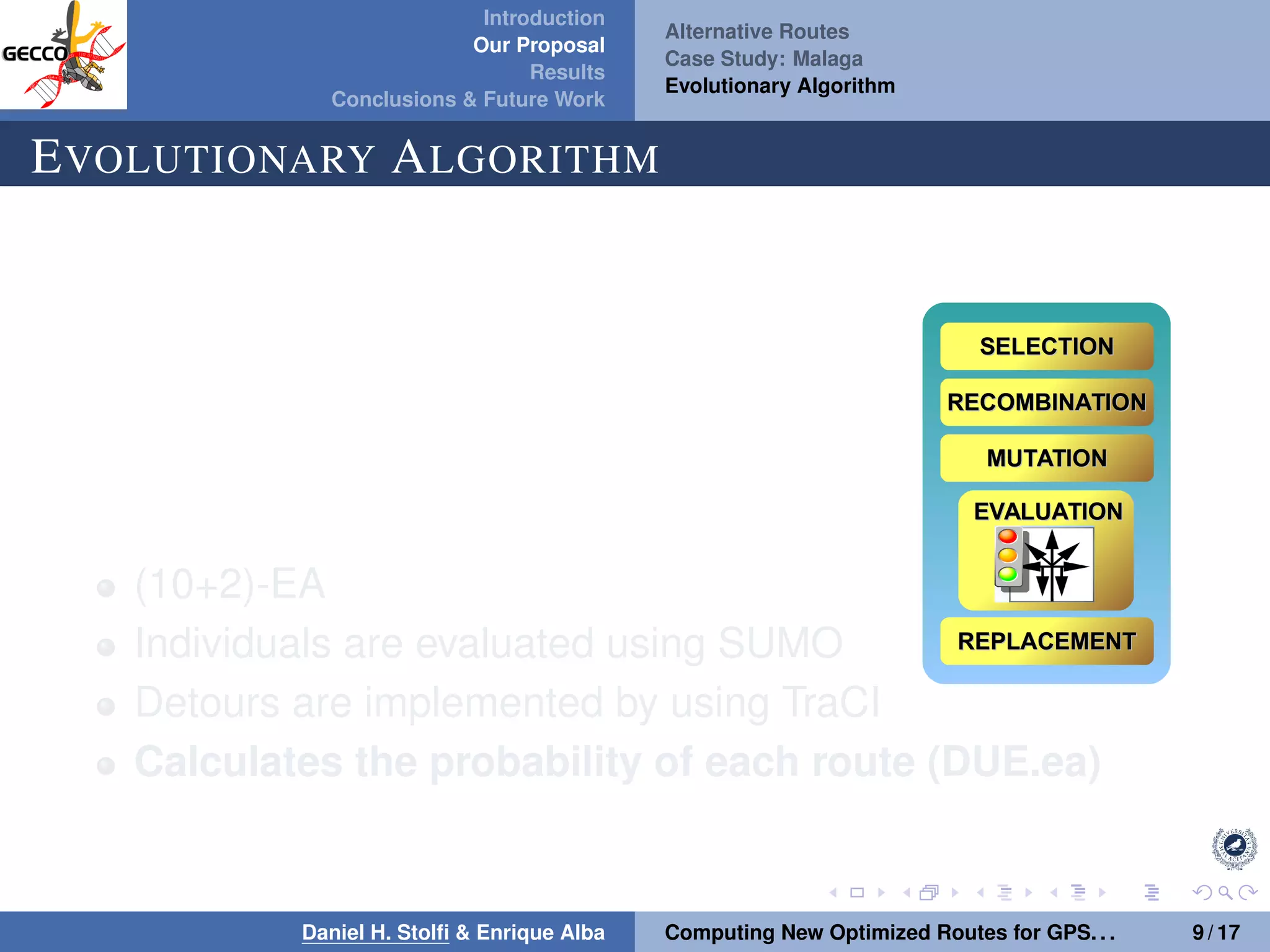
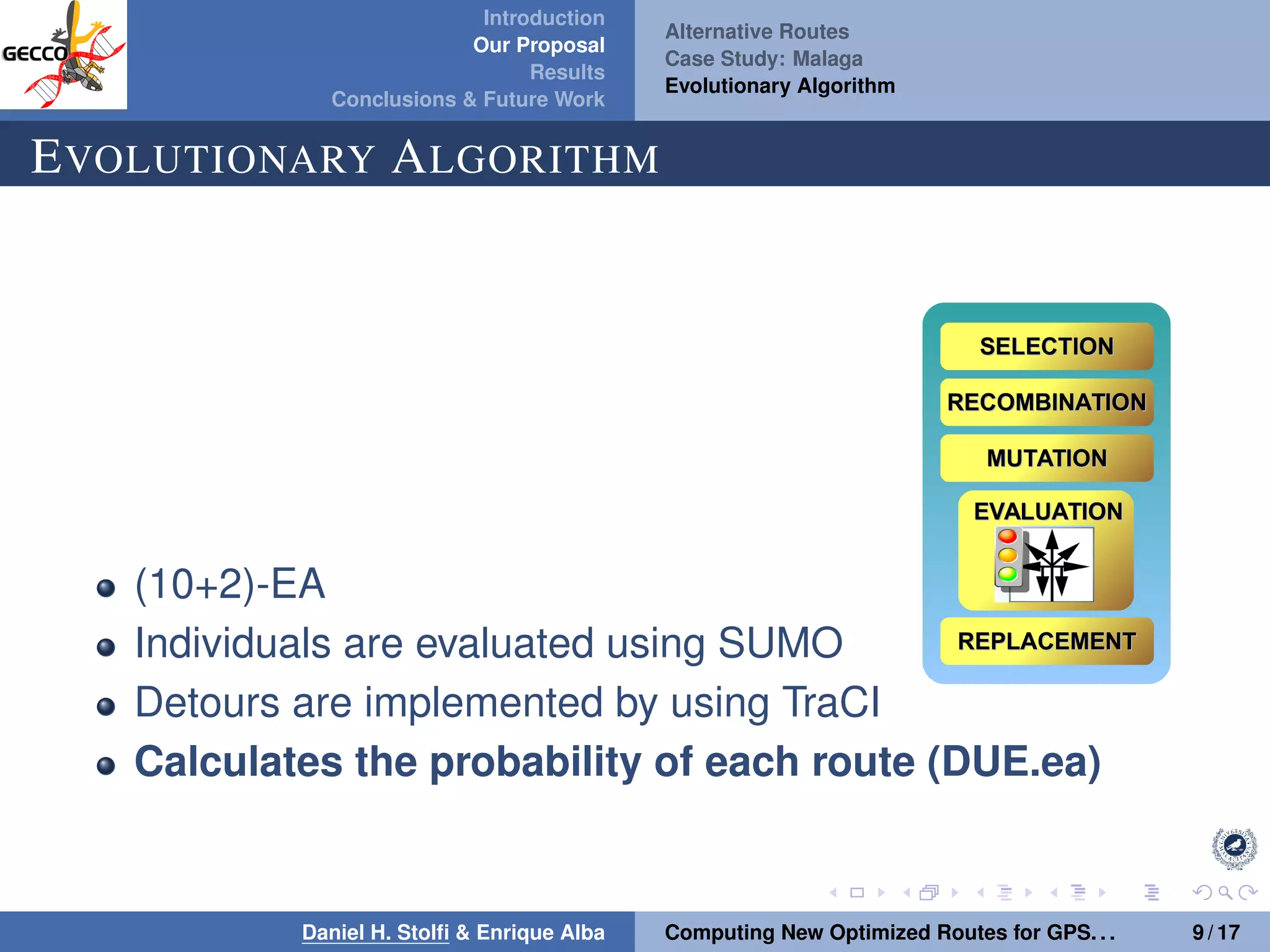
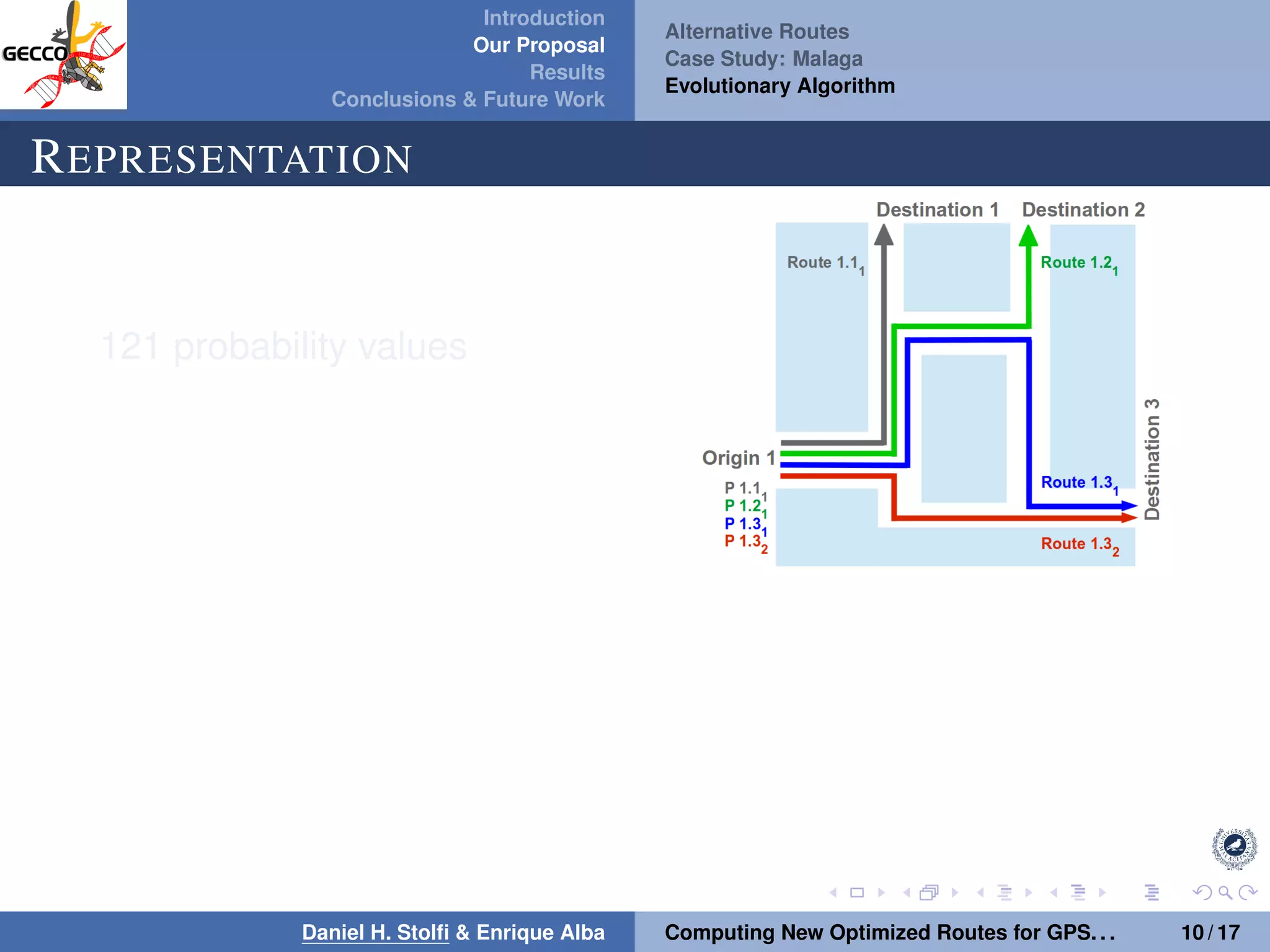
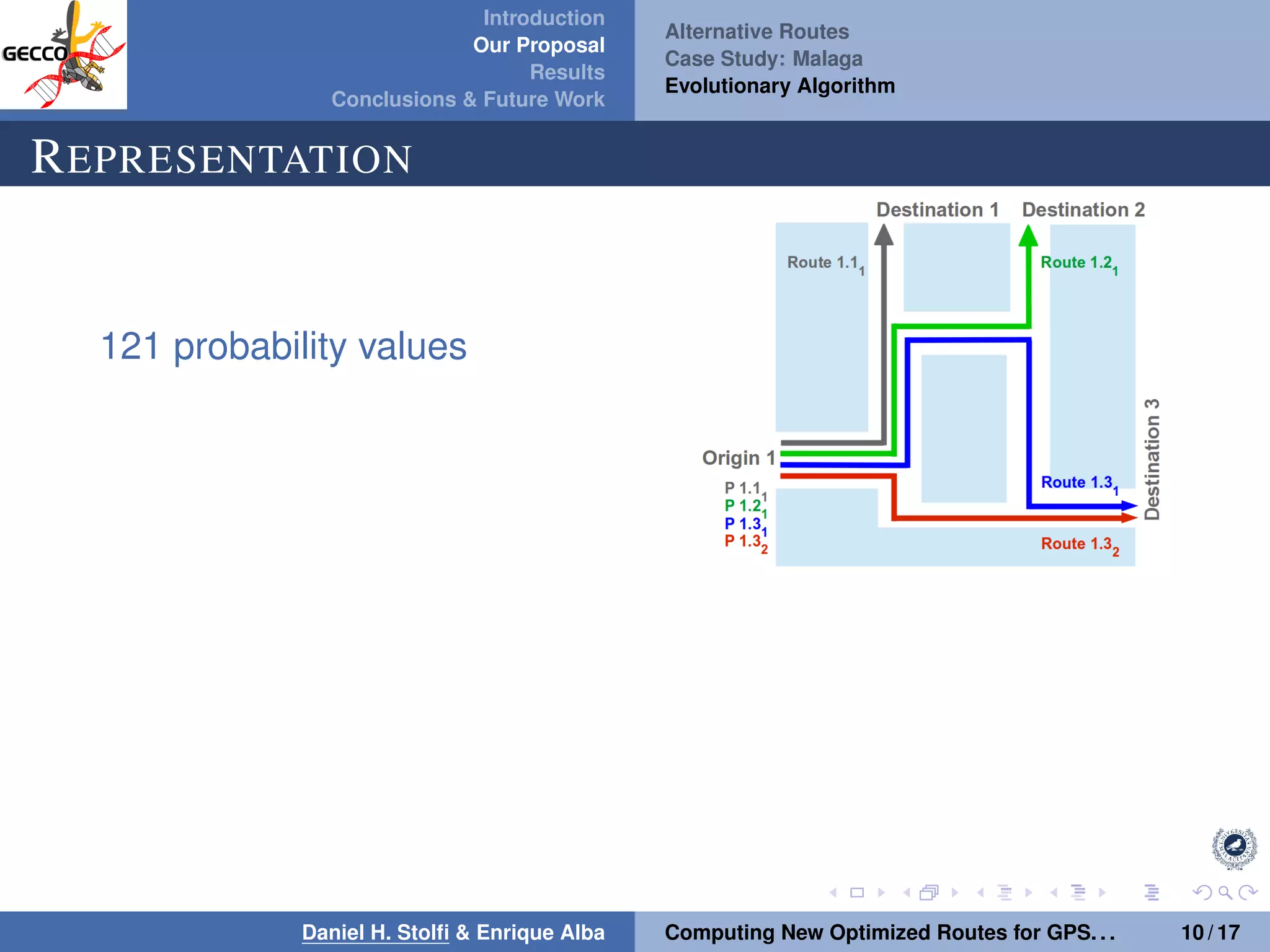
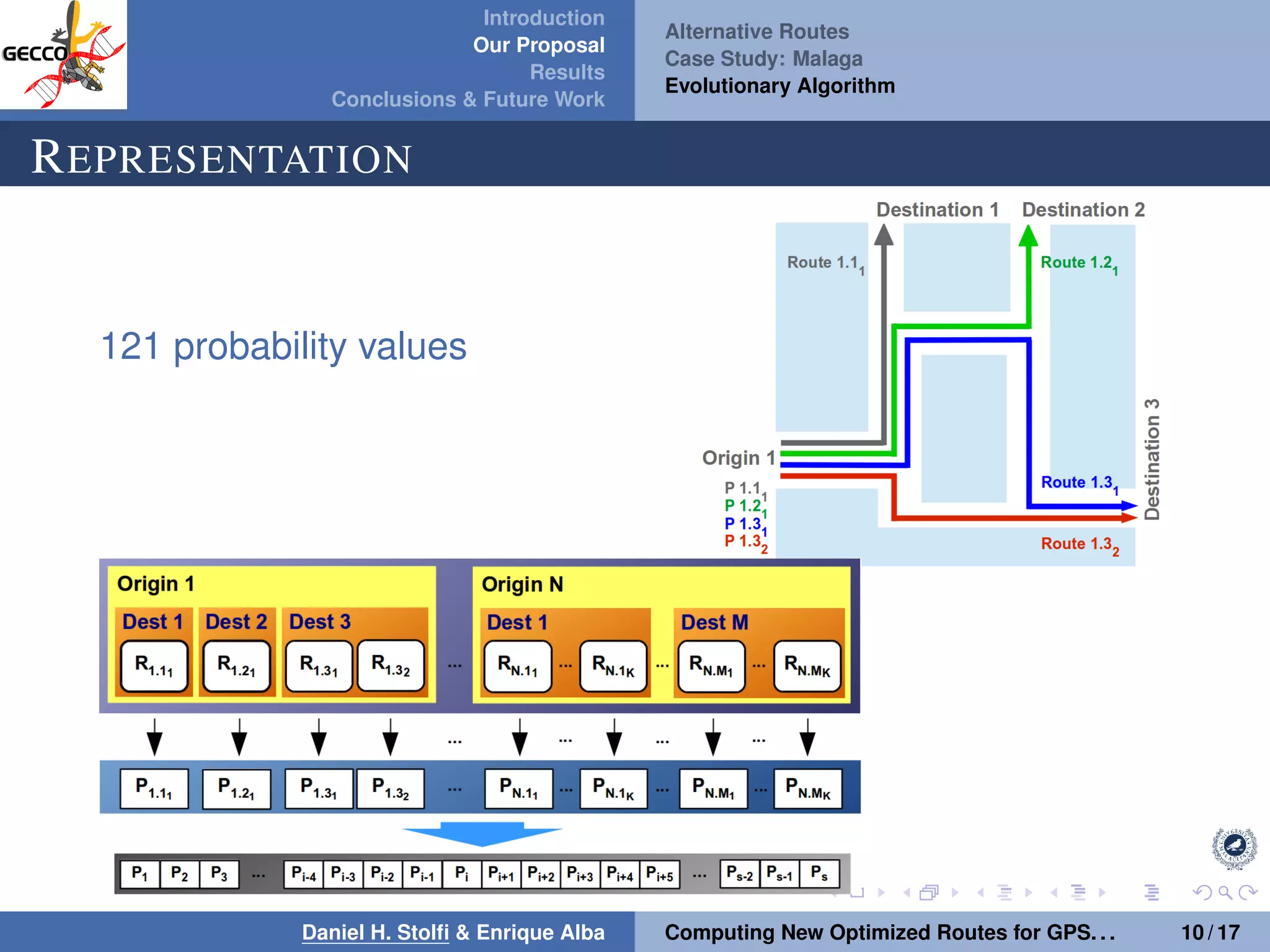
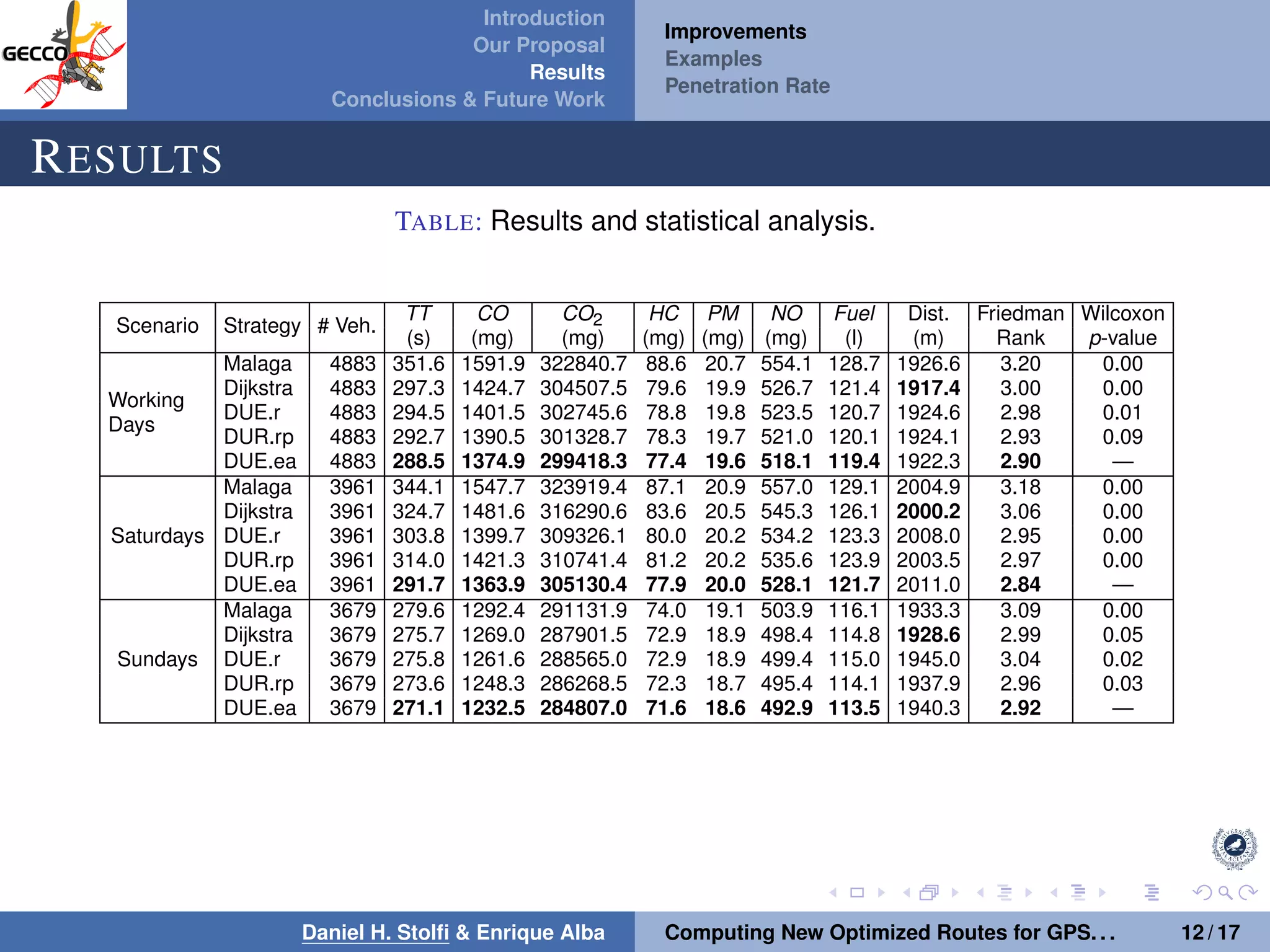
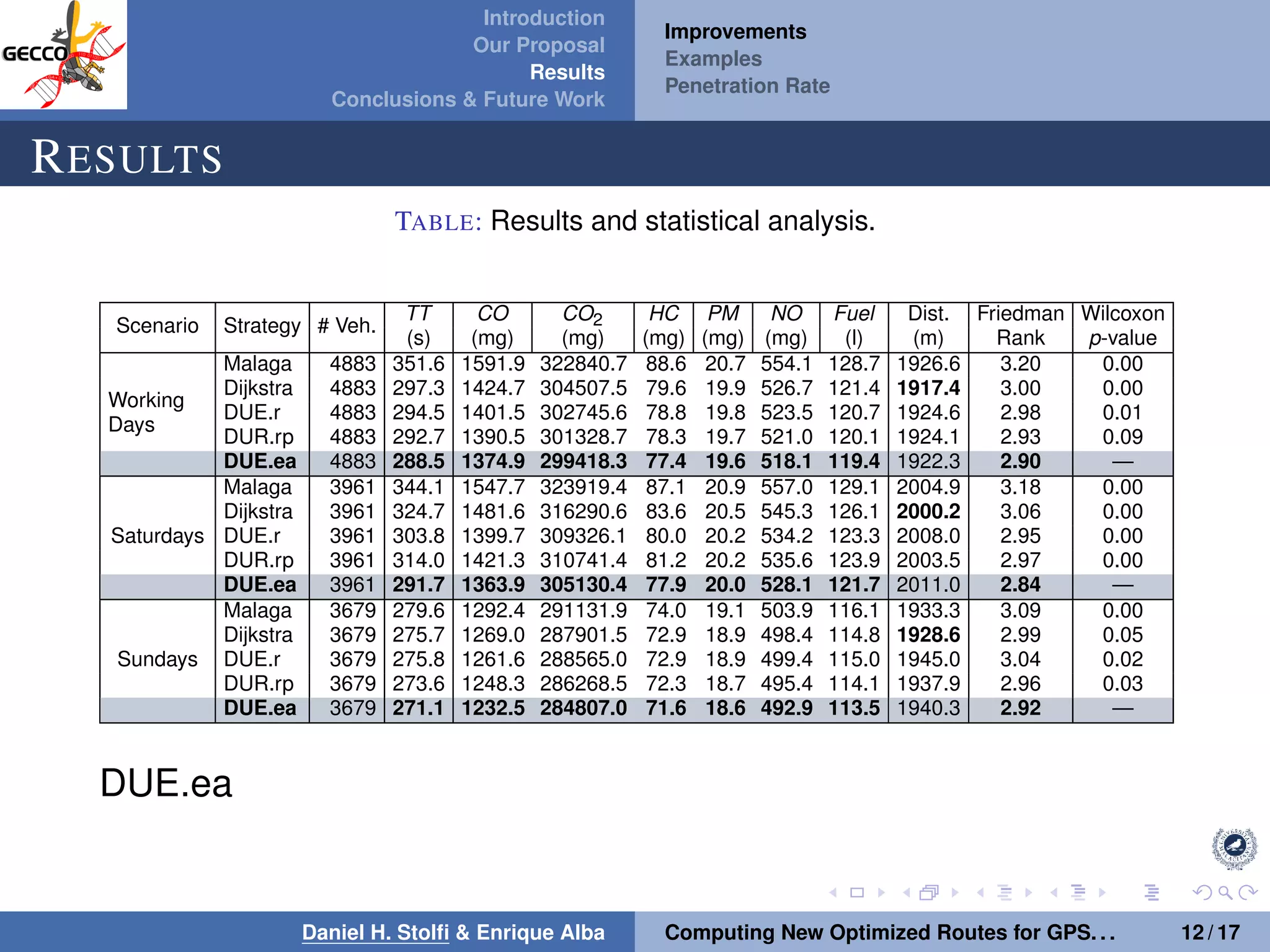
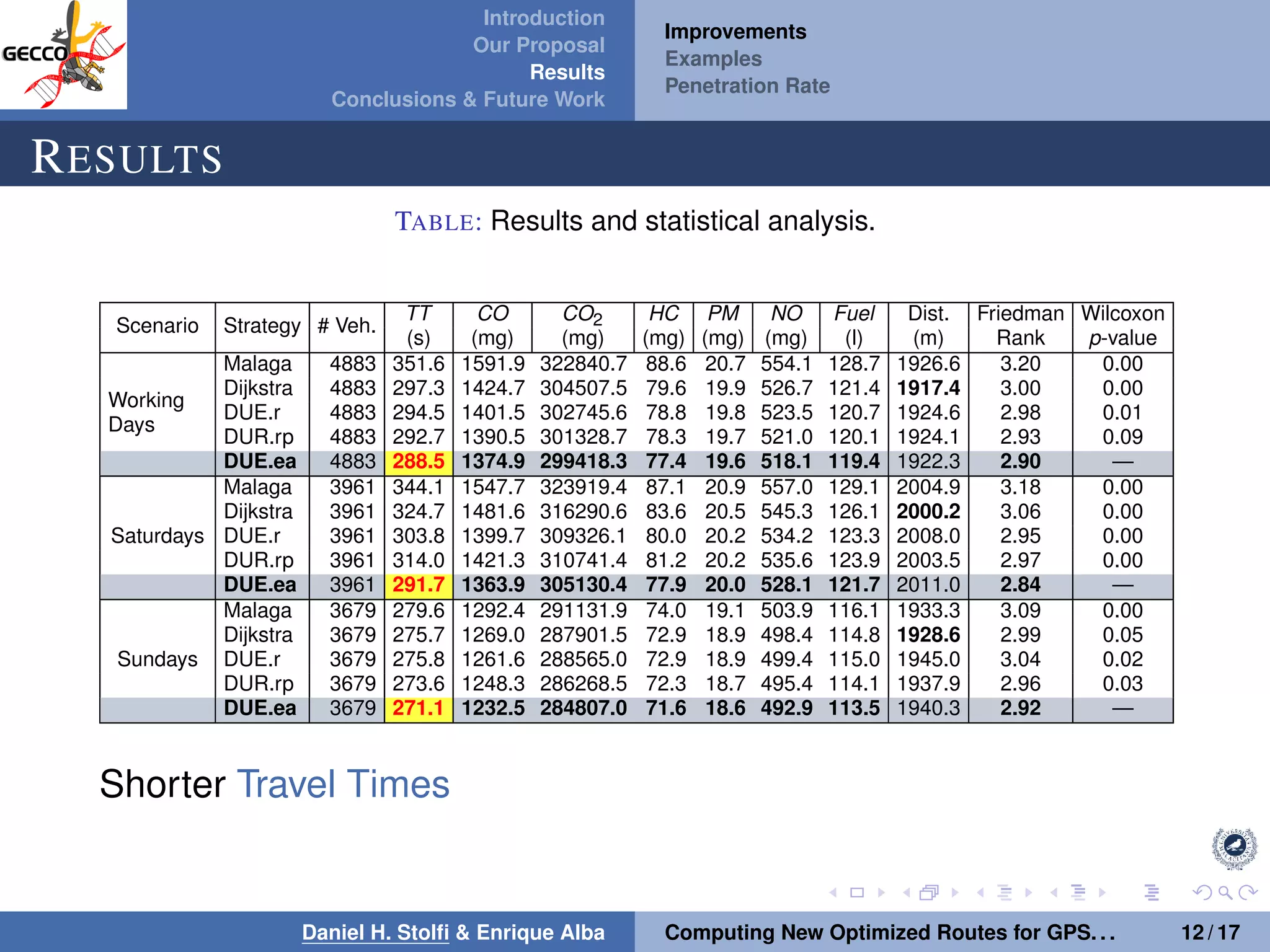
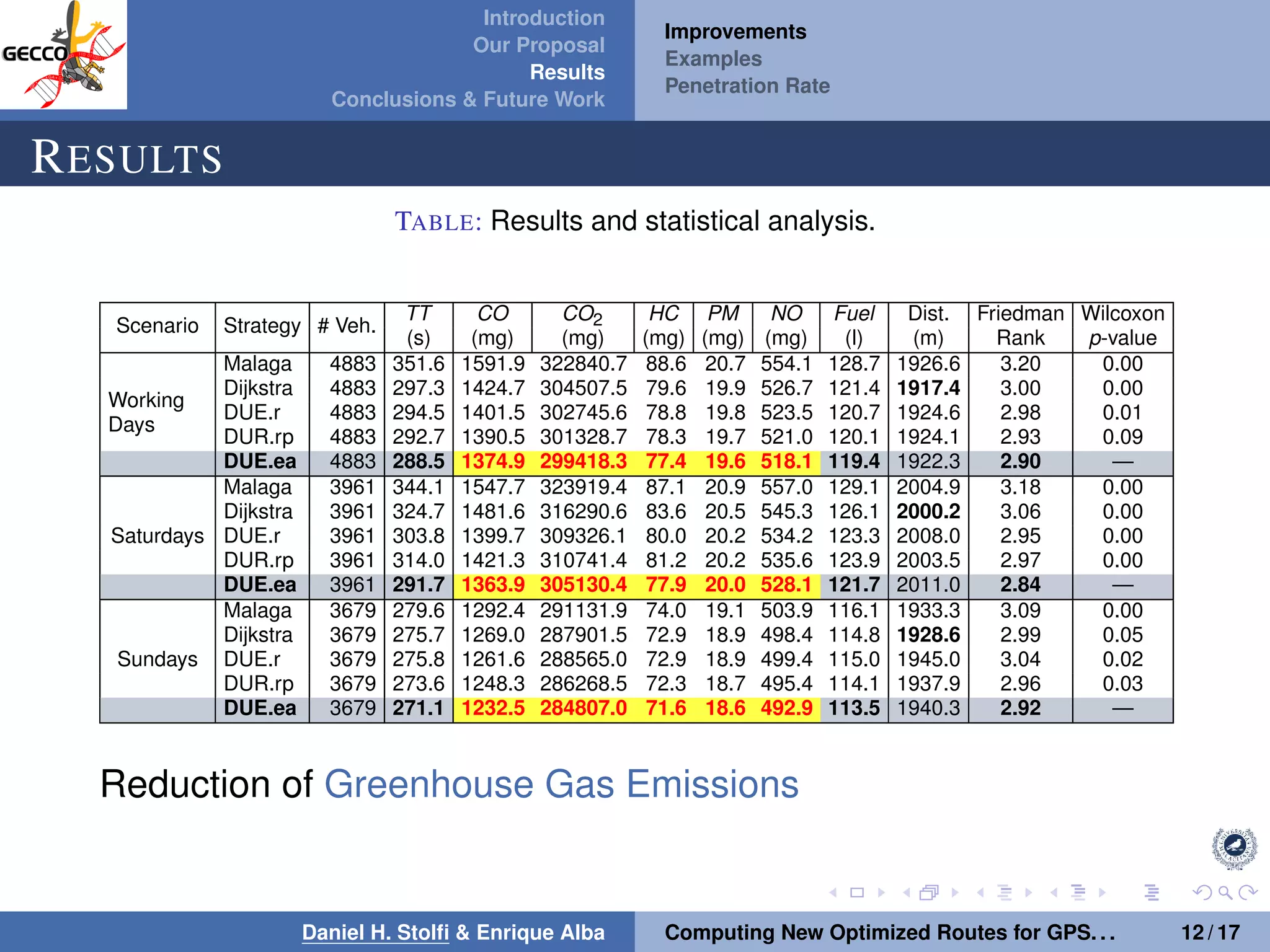
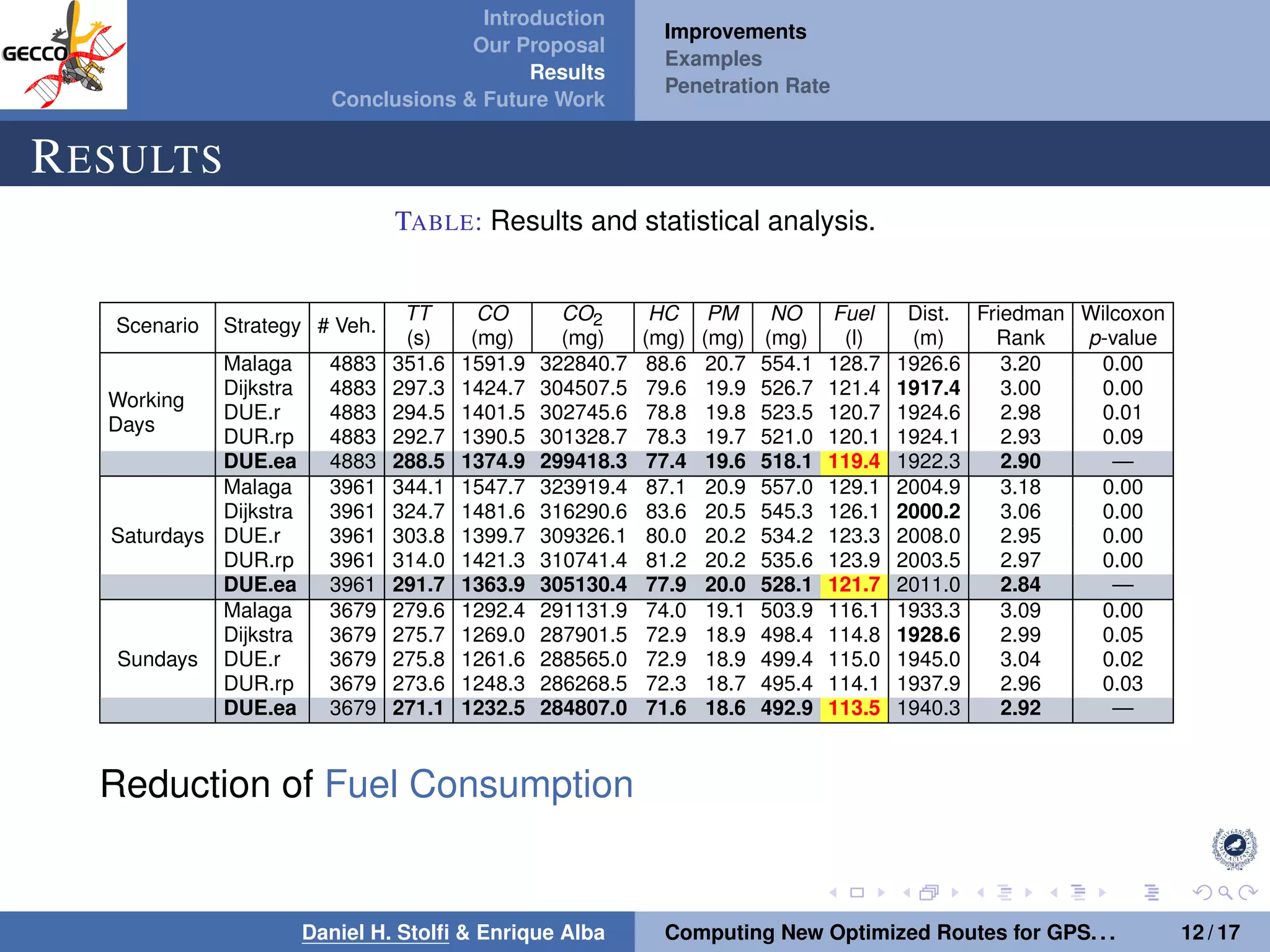
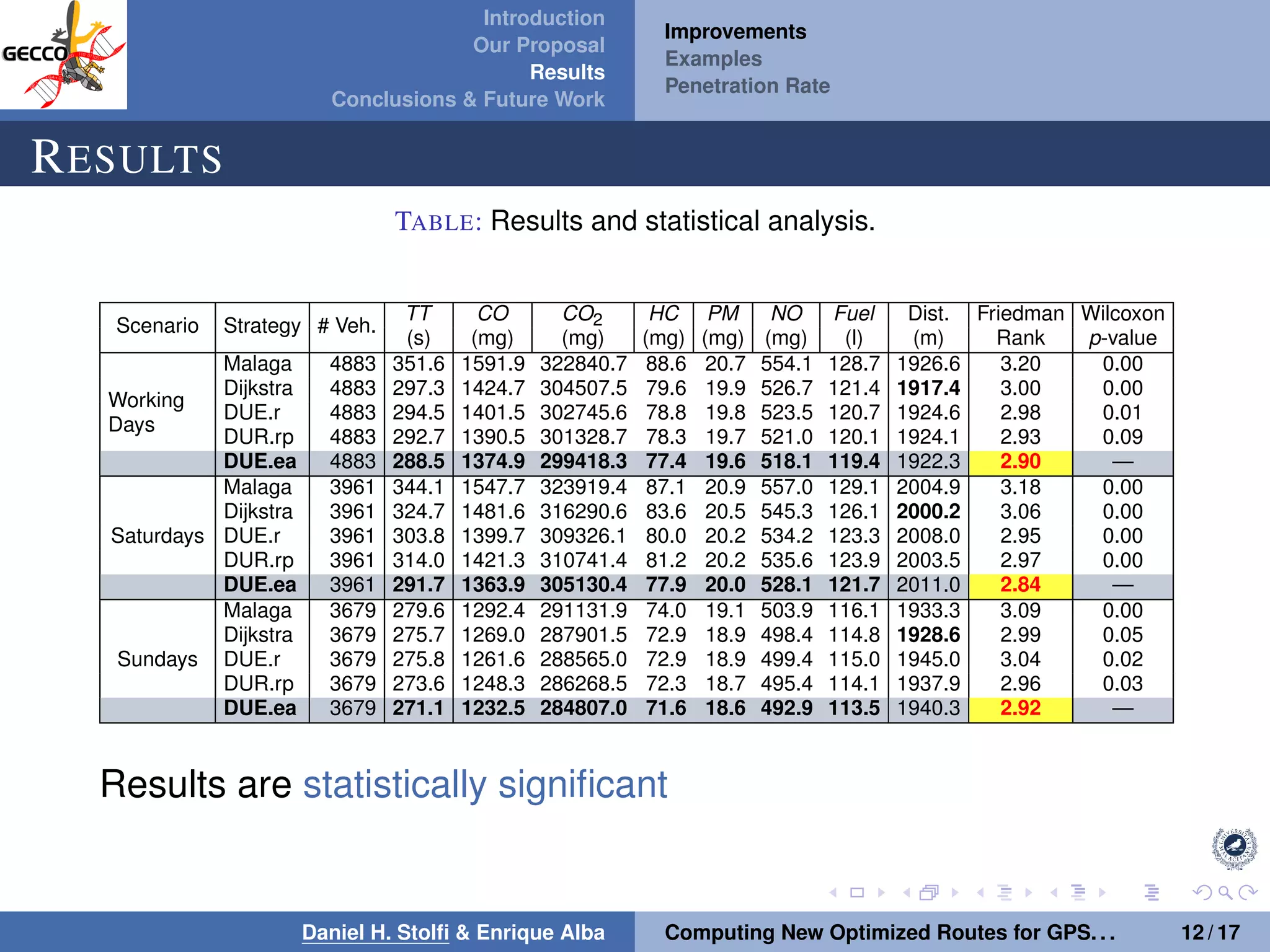
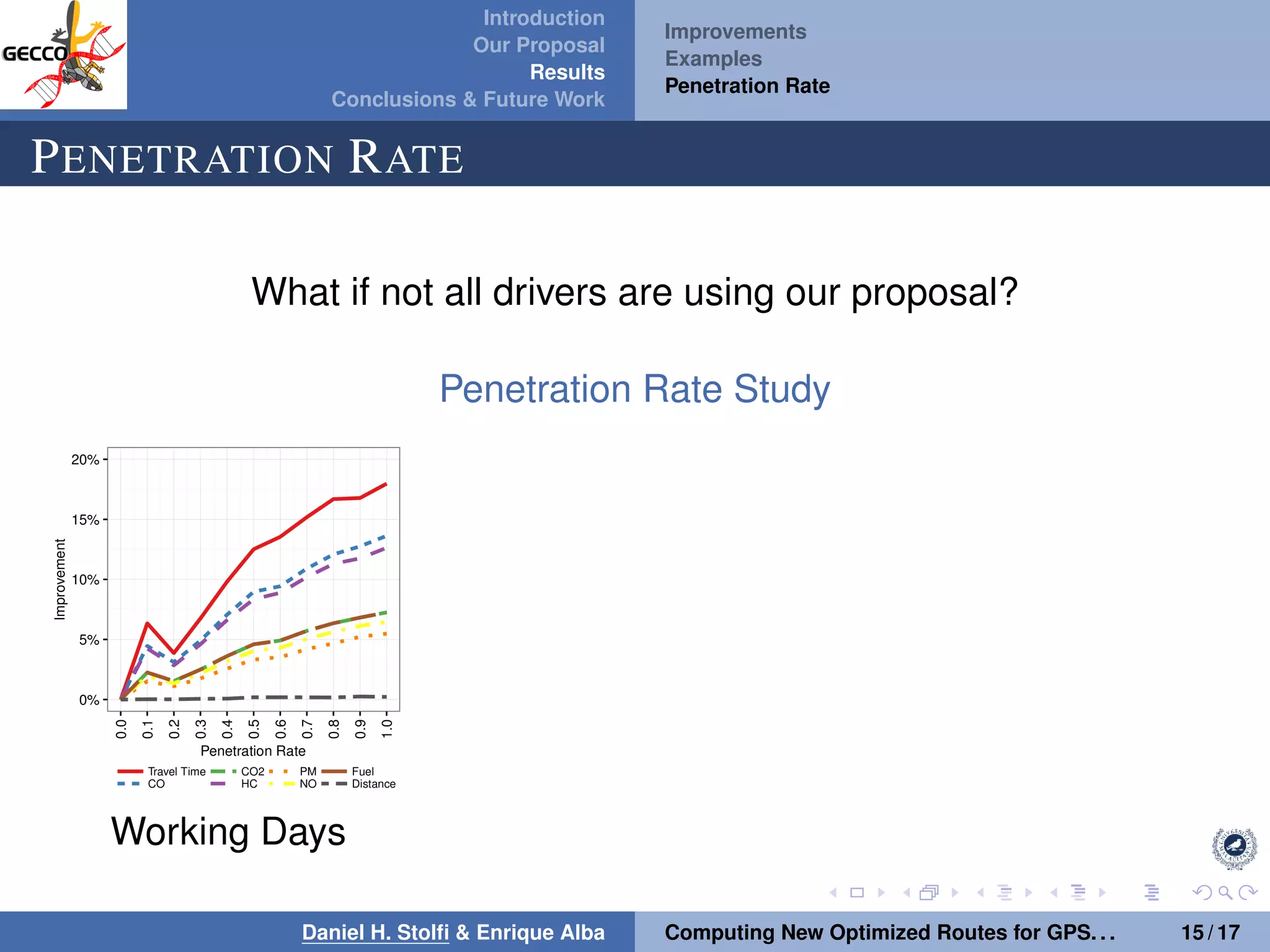
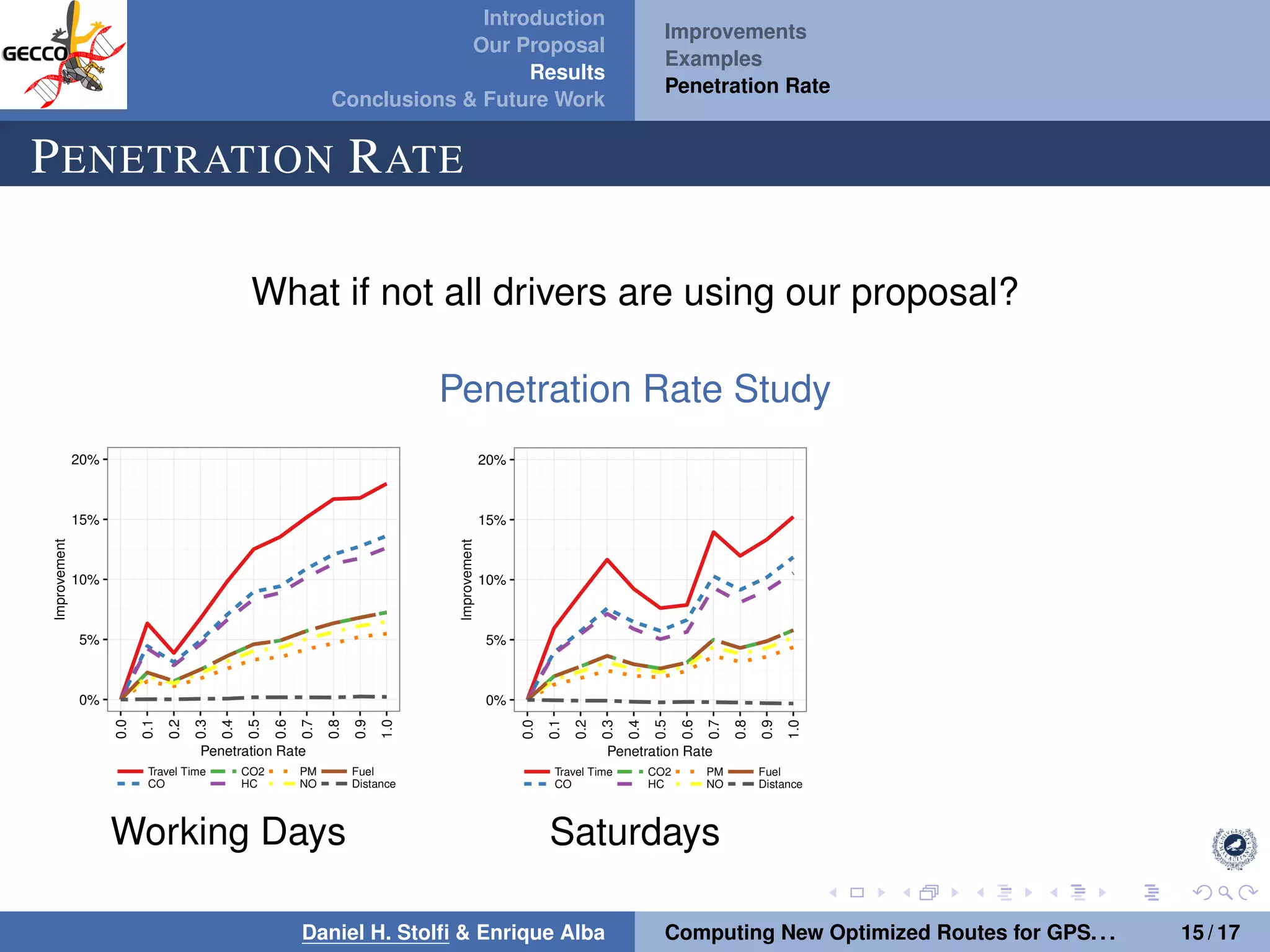
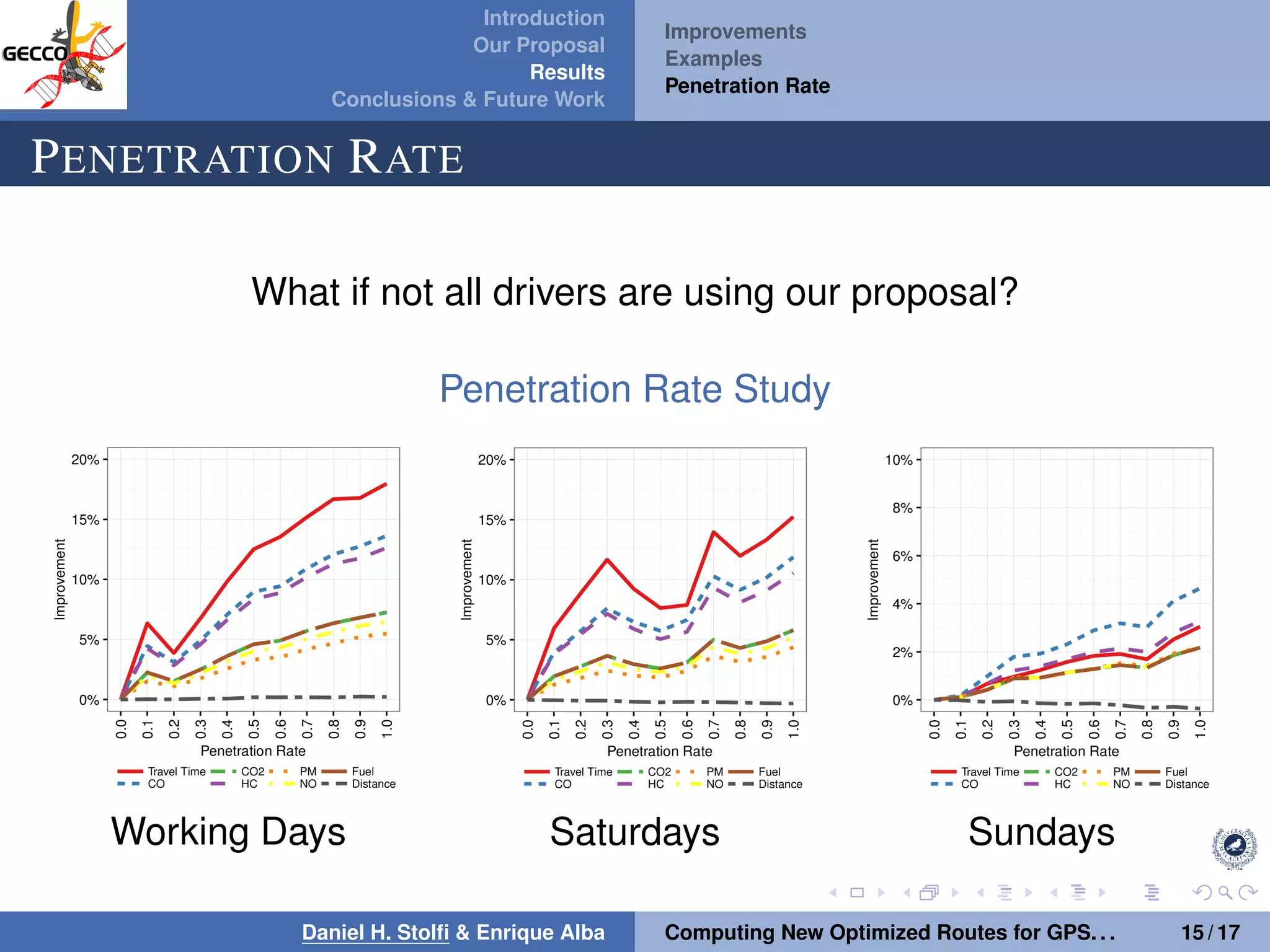
The document discusses a proposal by Daniel H. Stolfi and Enrique Alba for computing optimized routes for GPS navigators using evolutionary algorithms, addressing the growing traffic jams and environmental concerns in urban areas. It emphasizes the importance of alternative routes to reduce travel times, greenhouse gas emissions, and improve overall quality of life. The study specifically examines a case in Malaga, detailing the methodology, results, and future implications of the proposed solutions.