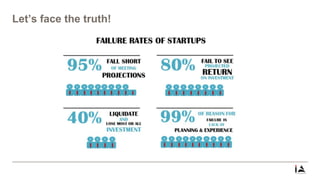
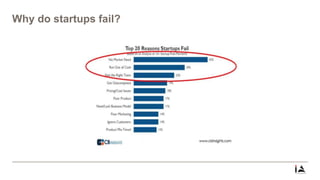
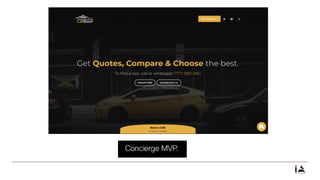
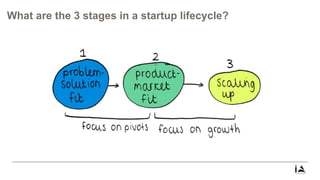
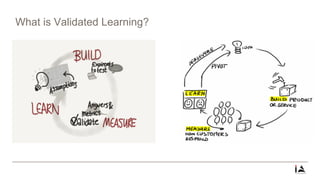
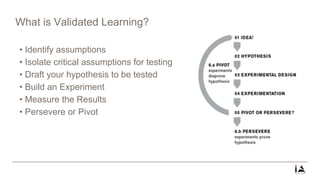
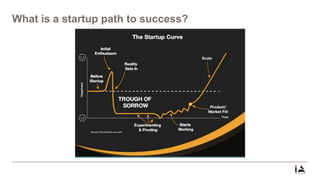
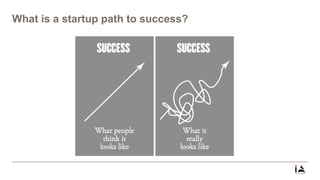
This document provides an overview of lean startup methodology. It discusses key concepts like minimum viable products (MVPs), hypotheses, experiments, pivoting, and validated learning. The document is presented as part of a talk on lean startup that covers: [1] defining lean, startups, and lean startup; [2] case studies; [3] risks and stages of a startup lifecycle; [4] MVPs and assumptions; [5] experiments and pivoting; [6] validated learning; [7] myths about lean startup; and [8] how to succeed as a startup.