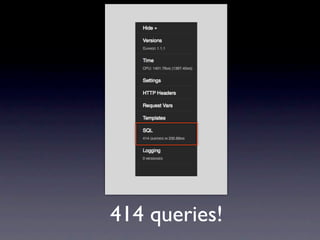
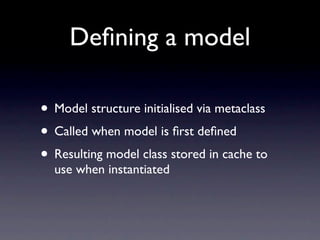
The document discusses advanced techniques for optimizing Django's Object-Relational Mapping (ORM), focusing on model definitions, relationships, and how to reduce query counts. It covers strategies such as utilizing caching, implementing more efficient queries with methods like select_related, and addressing common pitfalls like repeated database queries. The author emphasizes the importance of understanding query sources, applying optimizations, and profiling application performance.









![Querysets
• Model=manager returns a queryset:
foos Foo.objects.all()
• Queryset is an ordered list of instances
of a single model
• No database access yet
• Slice: foos[0]
• Iterate: {% for foo in foos %}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/europython-100722111505-phpapp01/85/Advanced-Django-ORM-techniques-13-320.jpg)






![Forwards relationship
>>> bar = Bar.objects.all()[0]
>>> bar.__dict__
{'id': 1, 'foo_id': 1, 'name': u'item1'}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/europython-100722111505-phpapp01/85/Advanced-Django-ORM-techniques-20-320.jpg)






![qs = Foo.objects.filter(criteria=whatever)
obj_dict = dict([(obj.id, obj)
for obj in qs])
objects = Bar.objects.filter(foo__in=qs)
relation_dict = {}
for obj in objects:
relation_dict.setdefault(
obj.foo_id, []).append(obj)
for id, related in relation_dict.items():
obj_dict[id]._related = related](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/europython-100722111505-phpapp01/85/Advanced-Django-ORM-techniques-27-320.jpg)
![qs = Foo.objects.filter(criteria=whatever)
obj_dict = dict([(obj.id, obj)
for obj in qs])
objects = Bar.objects.filter(foo__in=qs)
relation_dict = {}
for obj in objects:
relation_dict.setdefault(
obj.foo_id, []).append(obj)
for id, related in relation_dict.items():
obj_dict[id]._related = related](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/europython-100722111505-phpapp01/85/Advanced-Django-ORM-techniques-28-320.jpg)
![qs = Foo.objects.filter(criteria=whatever)
obj_dict = dict([(obj.id, obj)
for obj in qs])
objects = Bar.objects.filter(foo__in=qs)
relation_dict = {}
for obj in objects:
relation_dict.setdefault(
obj.foo_id, []).append(obj)
for id, related in relation_dict.items():
obj_dict[id]._related = related](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/europython-100722111505-phpapp01/85/Advanced-Django-ORM-techniques-29-320.jpg)
![qs = Foo.objects.filter(criteria=whatever)
obj_dict = dict([(obj.id, obj)
for obj in qs])
objects = Bar.objects.filter(foo__in=qs)
relation_dict = {}
for obj in objects:
relation_dict.setdefault(
obj.foo_id, []).append(obj)
for id, related in relation_dict.items():
obj_dict[id]._related = related](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/europython-100722111505-phpapp01/85/Advanced-Django-ORM-techniques-30-320.jpg)
![qs = Foo.objects.filter(criteria=whatever)
obj_dict = dict([(obj.id, obj)
for obj in qs])
objects = Bar.objects.filter(foo__in=qs)
relation_dict = {}
for obj in objects:
relation_dict.setdefault(
obj.foo_id, []).append(obj)
for id, related in relation_dict.items():
obj_dict[id]._related = related](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/europython-100722111505-phpapp01/85/Advanced-Django-ORM-techniques-31-320.jpg)
![qs = Foo.objects.filter(criteria=whatever)
obj_dict = dict([(obj.id, obj)
for obj in qs])
objects = Bar.objects.filter(foo__in=qs)
relation_dict = {}
for obj in objects:
relation_dict.setdefault(
obj.foo_id, []).append(obj)
for id, related in relation_dict.items():
obj_dict[id]._related = related](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/europython-100722111505-phpapp01/85/Advanced-Django-ORM-techniques-32-320.jpg)
![Optimising backwards
[{'time': '0.000', 'sql': u'SELECT
"foobar_foo"."id", "foobar_foo"."name" FROM
"foobar_foo"'},
{'time': '0.000', 'sql': u'SELECT
"foobar_bar"."id", "foobar_bar"."name",
"foobar_bar"."foo_id" FROM "foobar_bar"
WHERE "foobar_bar"."foo_id" IN (SELECT
U0."id" FROM "foobar_foo" U0)'}]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/europython-100722111505-phpapp01/85/Advanced-Django-ORM-techniques-33-320.jpg)


![generics = {}
for item in queryset:
generics.setdefault(item.content_type_id,
set()).add(item.object_id)
content_types = ContentType.objects.in_bulk(
generics.keys())
relations = {}
for ct, fk_list in generics.items():
ct_model = content_types[ct].model_class()
relations[ct] = ct_model.objects.
in_bulk(list(fk_list))
for item in queryset:
setattr(item, '_content_object_cache',
relations[content_type_id][item.object_id]
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/europython-100722111505-phpapp01/85/Advanced-Django-ORM-techniques-36-320.jpg)
![generics = {}
for item in queryset:
generics.setdefault(item.content_type_id,
set()).add(item.object_id)
content_types = ContentType.objects.in_bulk(
generics.keys())
relations = {}
for ct, fk_list in generics.items():
ct_model = content_types[ct].model_class()
relations[ct] = ct_model.objects.
in_bulk(list(fk_list))
for item in queryset:
setattr(item, '_content_object_cache',
relations[content_type_id][item.object_id]
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/europython-100722111505-phpapp01/85/Advanced-Django-ORM-techniques-37-320.jpg)
![generics = {}
for item in queryset:
generics.setdefault(item.content_type_id,
set()).add(item.object_id)
content_types = ContentType.objects.in_bulk(
generics.keys())
relations = {}
for ct, fk_list in generics.items():
ct_model = content_types[ct].model_class()
relations[ct] = ct_model.objects.
in_bulk(list(fk_list))
for item in queryset:
setattr(item, '_content_object_cache',
relations[content_type_id][item.object_id]
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/europython-100722111505-phpapp01/85/Advanced-Django-ORM-techniques-38-320.jpg)
![generics = {}
for item in queryset:
generics.setdefault(item.content_type_id,
set()).add(item.object_id)
content_types = ContentType.objects.in_bulk(
generics.keys())
relations = {}
for ct, fk_list in generics.items():
ct_model = content_types[ct].model_class()
relations[ct] = ct_model.objects.
in_bulk(list(fk_list))
for item in queryset:
setattr(item, '_content_object_cache',
relations[content_type_id][item.object_id]
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/europython-100722111505-phpapp01/85/Advanced-Django-ORM-techniques-39-320.jpg)
![generics = {}
for item in queryset:
generics.setdefault(item.content_type_id,
set()).add(item.object_id)
content_types = ContentType.objects.in_bulk(
generics.keys())
relations = {}
for ct, fk_list in generics.items():
ct_model = content_types[ct].model_class()
relations[ct] = ct_model.objects.
in_bulk(list(fk_list))
for item in queryset:
setattr(item, '_content_object_cache',
relations[content_type_id][item.object_id]
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/europython-100722111505-phpapp01/85/Advanced-Django-ORM-techniques-40-320.jpg)
![generics = {}
for item in queryset:
generics.setdefault(item.content_type_id,
set()).add(item.object_id)
content_types = ContentType.objects.in_bulk(
generics.keys())
relations = {}
for ct, fk_list in generics.items():
ct_model = content_types[ct].model_class()
relations[ct] = ct_model.objects.
in_bulk(list(fk_list))
for item in queryset:
setattr(item, '_content_object_cache',
relations[content_type_id][item.object_id]
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/europython-100722111505-phpapp01/85/Advanced-Django-ORM-techniques-41-320.jpg)
![generics = {}
for item in queryset:
generics.setdefault(item.content_type_id,
set()).add(item.object_id)
content_types = ContentType.objects.in_bulk(
generics.keys())
relations = {}
for ct, fk_list in generics.items():
ct_model = content_types[ct].model_class()
relations[ct] = ct_model.objects.
in_bulk(list(fk_list))
for item in queryset:
setattr(item, '_content_object_cache',
relations[content_type_id][item.object_id]
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/europython-100722111505-phpapp01/85/Advanced-Django-ORM-techniques-42-320.jpg)
![generics = {}
for item in queryset:
generics.setdefault(item.content_type_id,
set()).add(item.object_id)
content_types = ContentType.objects.in_bulk(
generics.keys())
relations = {}
for ct, fk_list in generics.items():
ct_model = content_types[ct].model_class()
relations[ct] = ct_model.objects.
in_bulk(list(fk_list))
for item in queryset:
setattr(item, '_content_object_cache',
relations[content_type_id][item.object_id]
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/europython-100722111505-phpapp01/85/Advanced-Django-ORM-techniques-43-320.jpg)
![generics = {}
for item in queryset:
generics.setdefault(item.content_type_id,
set()).add(item.object_id)
content_types = ContentType.objects.in_bulk(
generics.keys())
relations = {}
for ct, fk_list in generics.items():
ct_model = content_types[ct].model_class()
relations[ct] = ct_model.objects.
in_bulk(list(fk_list))
for item in queryset:
setattr(item, '_content_object_cache',
relations[content_type_id][item.object_id]
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/europython-100722111505-phpapp01/85/Advanced-Django-ORM-techniques-44-320.jpg)






