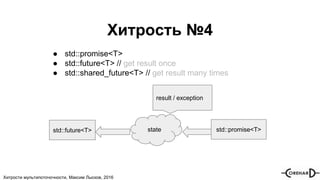
Документ касается множества аспектов мультипоточности в C++, включая использование std::packaged_task, std::future, std::promise, и различных типов мьютексов. Максим Лысков представляет хитрости и рекомендации по параллельному выполнению задач, синхронизации потоков и особенностям работы с памятью. Также рассмотрены различные методы и подходы для управления потоками и обеспечения безопасности операций между ними.




 {
return a * b;
});
std::future<int> result = task.get_future();
// any other code
task(2, 9);
std::cout << "task result: " << result.get() << 'n';](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/random-160619144517/85/slide-5-320.jpg)















![Хитрости мультипоточочности, Максим Лысков, 2016
Валидное выражение в С++
[](){}()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/random-160619144517/85/slide-22-320.jpg)

