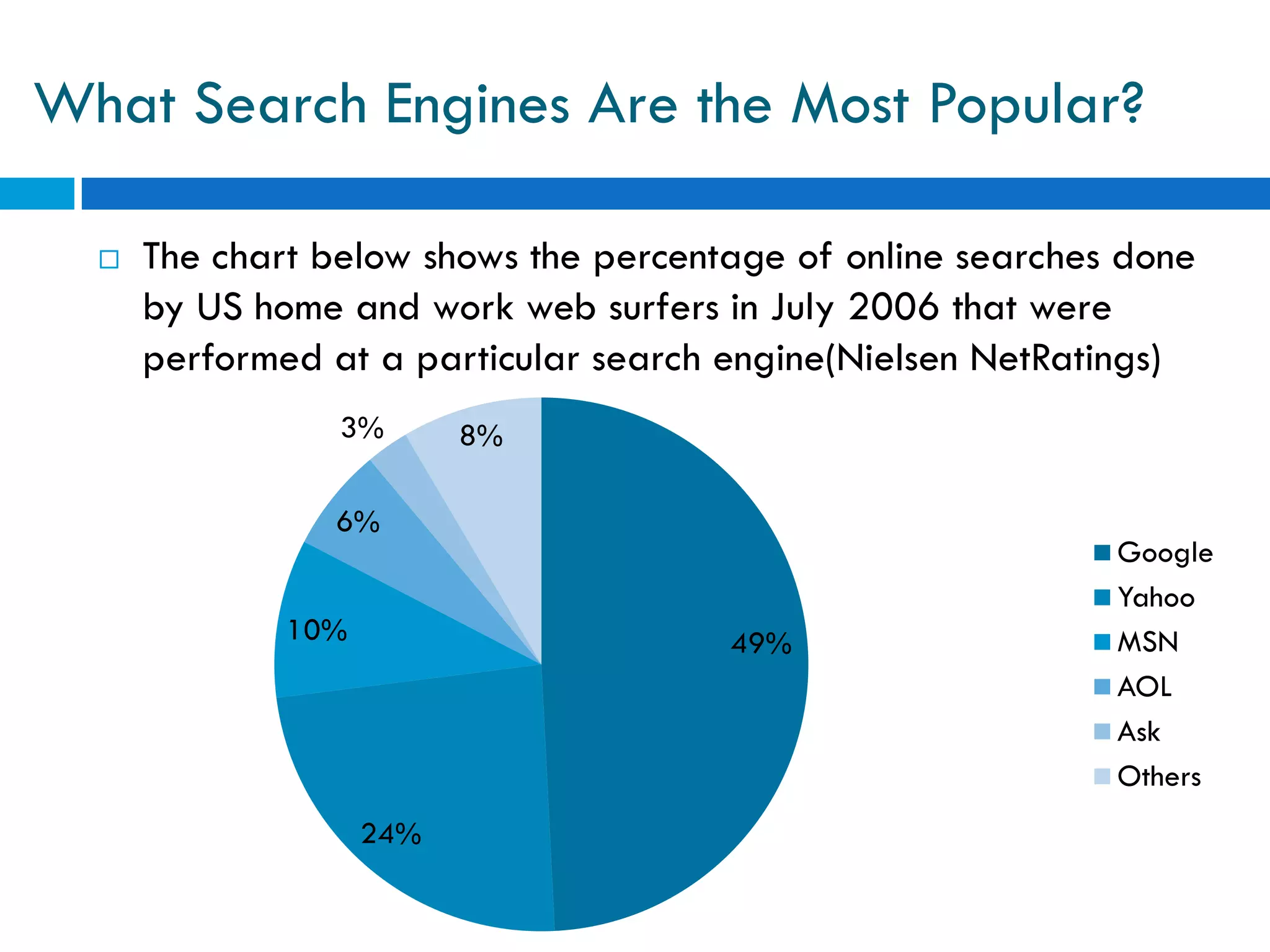
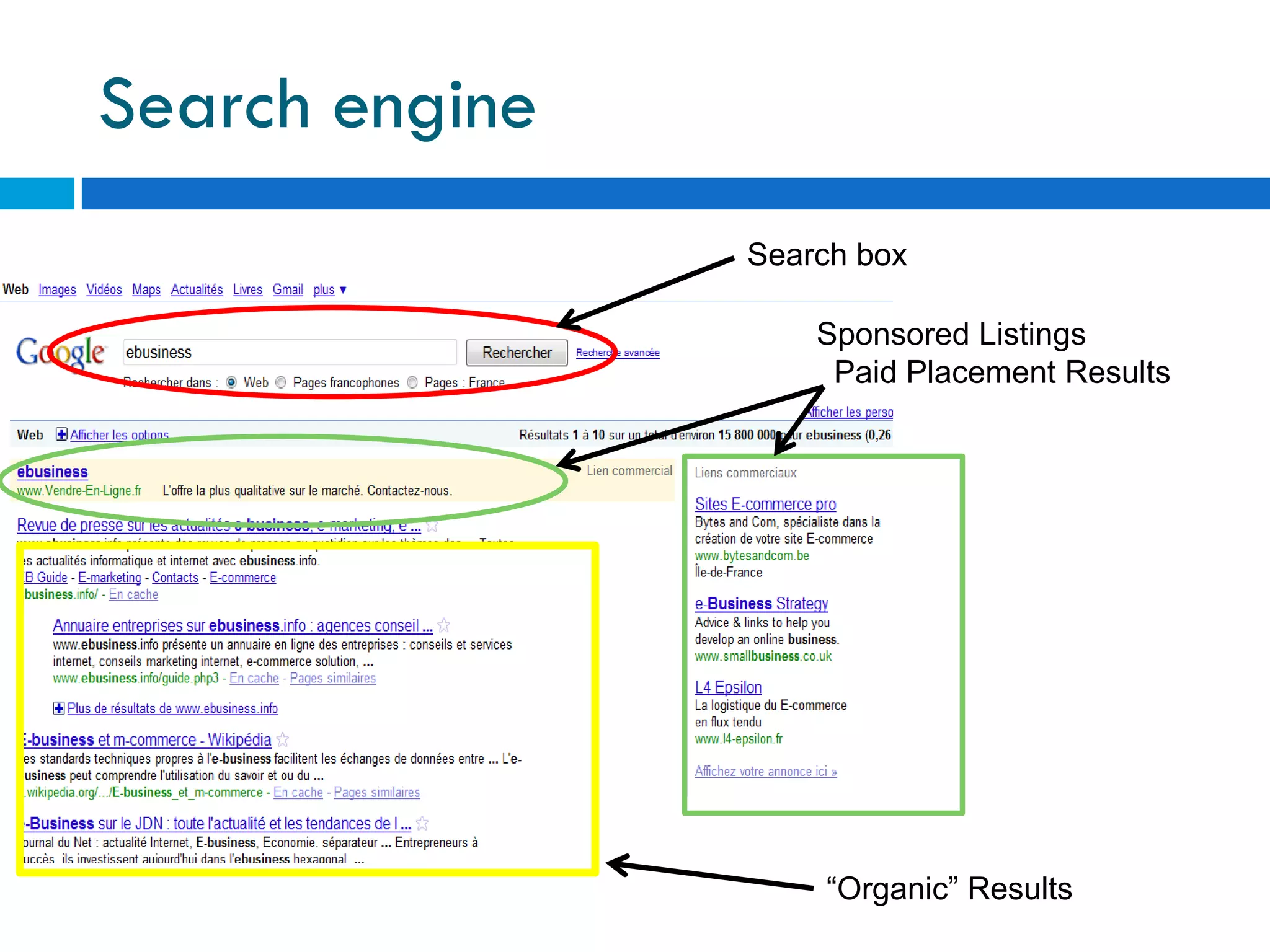
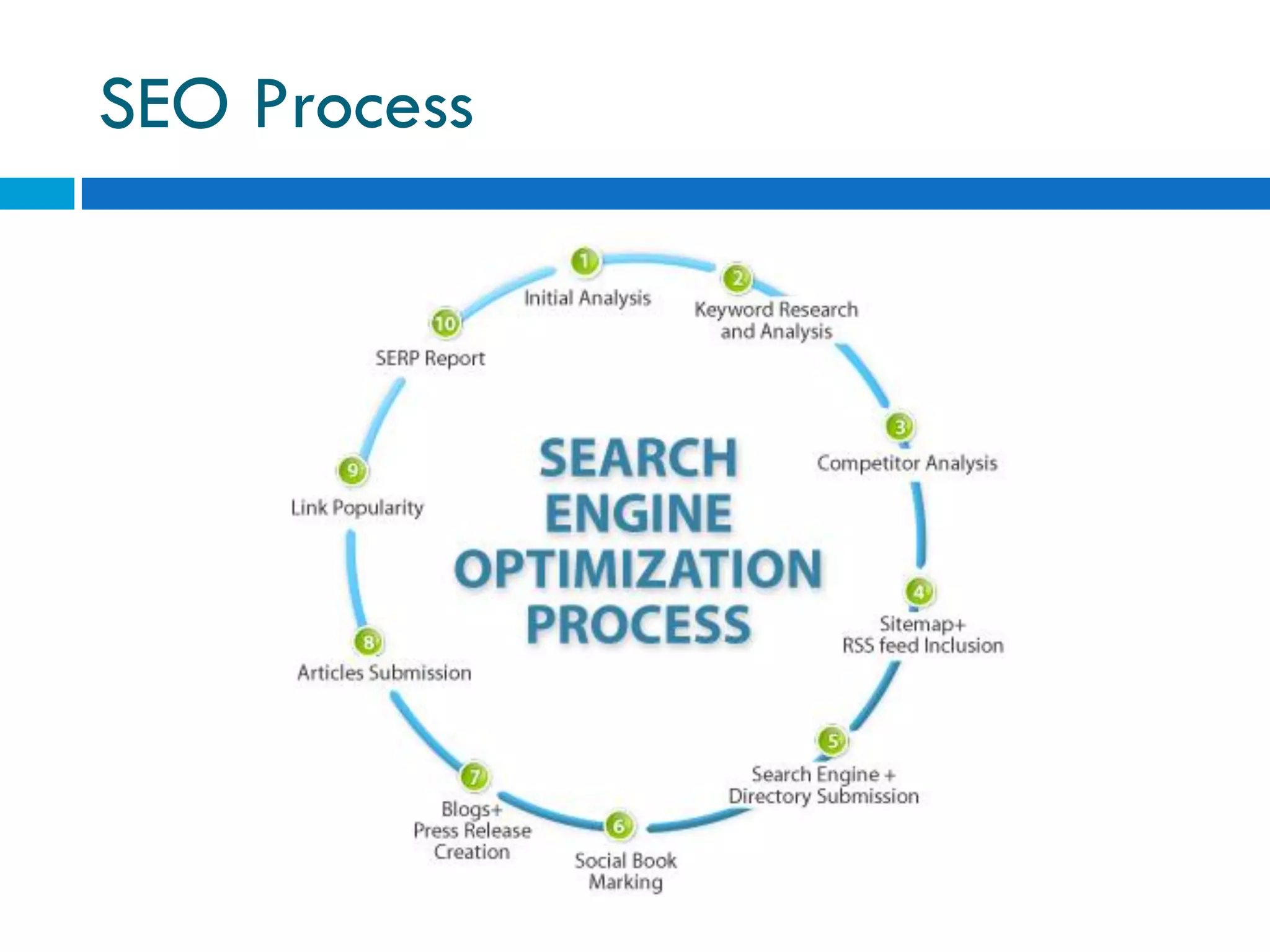
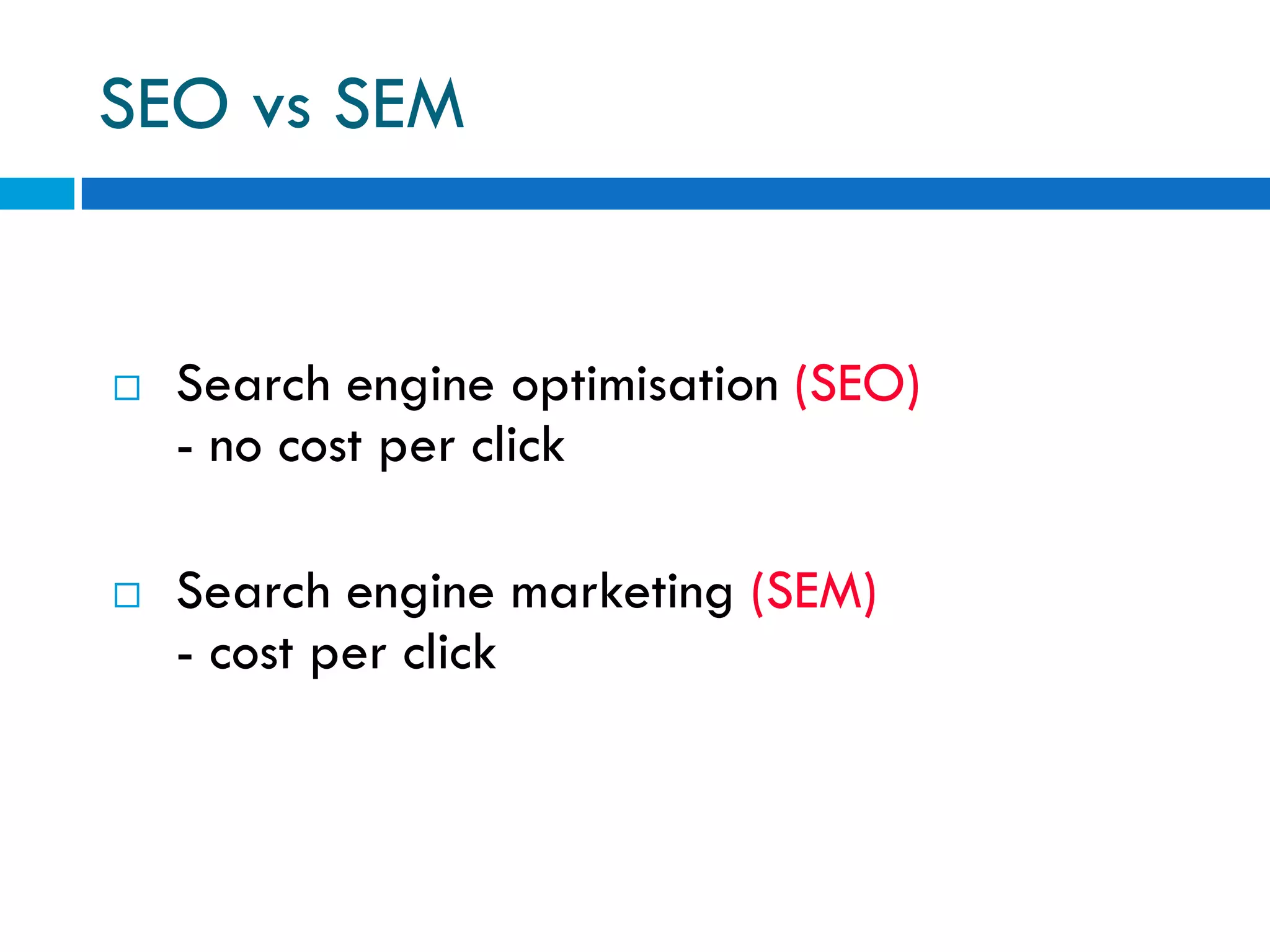
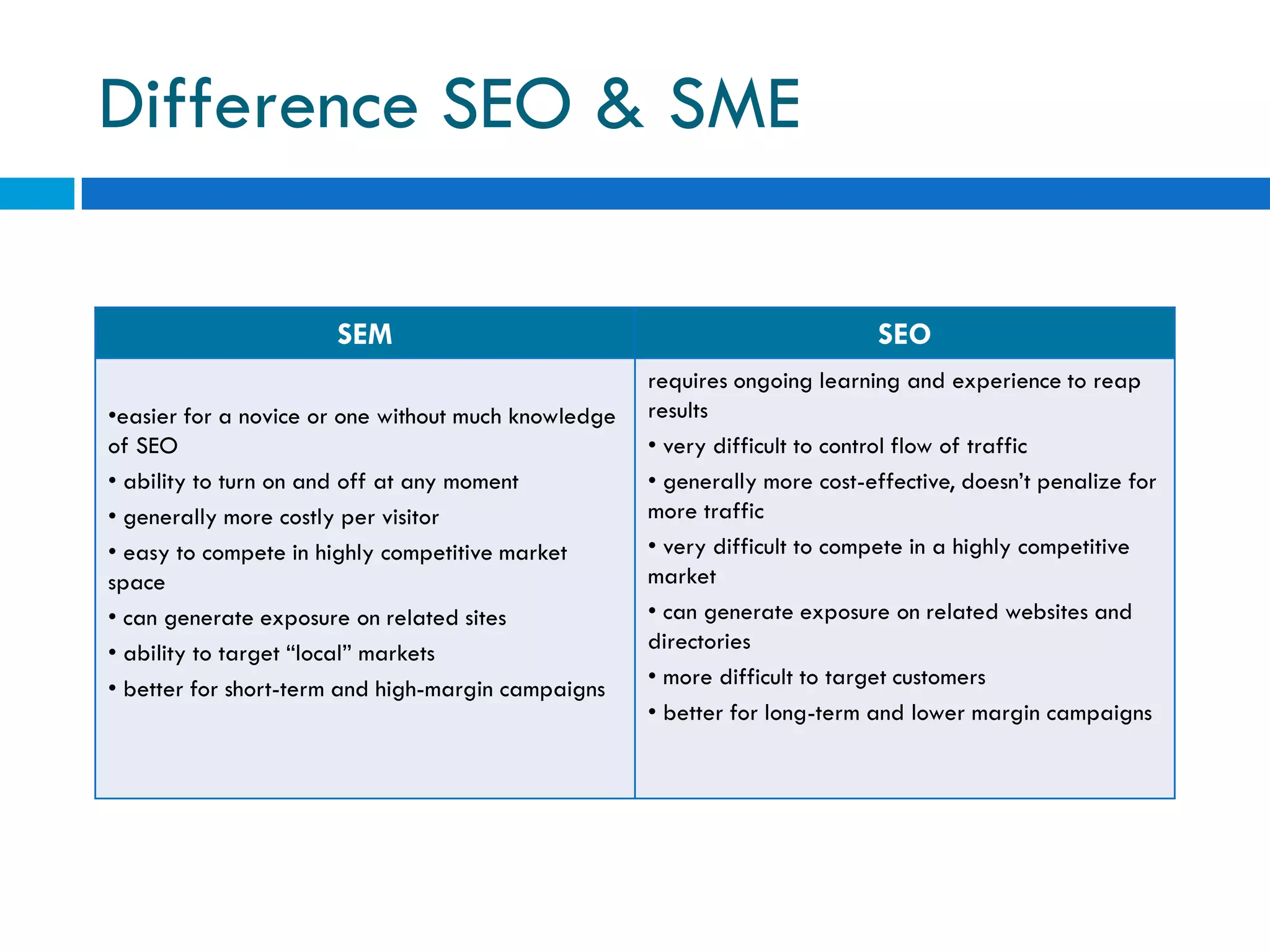
This document discusses various topics related to e-business, search engines, and online marketing. It defines search engines, search engine optimization (SEO), and search engine marketing (SEM). It explains that search engines aim to provide relevant results to users while generating revenue from advertising. Google is the most popular search engine, handling nearly half of all online searches. SEO refers to optimizing websites to achieve high search engine rankings for targeted keywords. SEM involves purchasing paid listings on search engines through programs like pay-per-click advertising. Location based services provide information to mobile users based on their geographical position.