Embed presentation
Download as DOCX, PPTX
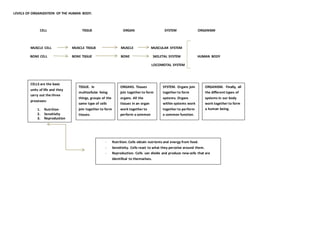
The document outlines the levels of organization in the human body from smallest to largest: cells, tissues, organs, systems, and organism. Cells are the basic unit of life and perform nutrition, sensitivity, and reproduction functions. Groups of the same cell type form tissues, tissues join to form organs, organs join to form systems, and all systems working together form the complete human organism.
