What is Payment Tokenization?
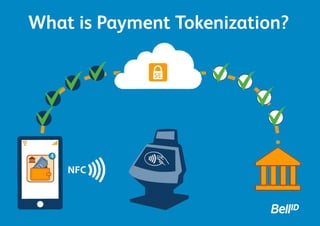
What is Payment Tokenization? Tokenization enables banks, acquirers and merchants to offer more secure (mobile) payment services. It is the process of replacing card data with alternate values. The original personal account number (PAN) is disconnected and replaced with a unique identifier called a payment token. The ‘mapping’ between the real PAN and the payment tokens is safely stored in the token vault. With tokenization the original PAN information is removed from environments where data can be vulnerable. Why tokenization? Tokenization heavily reduces payment fraud by removing confidential consumer credit card data from the network. The original data stays in the bank’s control. External systems have no access to this. Tokens are not based on cryptography and can therefore not be traced back to the original value. How does tokenization work? Step 1: A payment token is generated from the PAN for one time use within a specific domain such as a merchant’s website or channel. Tokens are sent to the token vault and stored in a PCI-compliant environment which does not allow merchants to store credit card numbers. Step 2: Tokens are loaded on the mobile device. Step 3: The NFC device makes a payment at a merchant’s NFC point-of-sales (POS) terminal. Step 4: The POS terminal sends the token to the acquiring bank, which sends it to the issuing bank through the payment network. Step 5: The issuer de-tokenizes the token to the real PAN and, if in order, approves the payment. Step 6: After authorization from the card issuer, the token is returned to the merchant’s POS terminal. Payment tokens perform like the original PAN for returns, sales reports, marketing analysis, recurring payments etc. 20. How can I issue tokens? In order to use tokenization, a bank or merchant should become a token service provider (TSP). A TSP manages the entire lifecycle of payment credentials including: 1. Tokenization: replaces the PAN with a payment token. 2. De-Tokenization: converts the token back to the PAN using the token vault. 3. Token vault: establishes and maintains the payment token to PAN mapping. 4. Domain management: improves protection by defining payment tokens for specific use. 5. Clearing and settlement: ad-hoc de-tokenization during clearing and settlement process. 6. Identification and verification: ensures the original PAN is legitimately used by the token requestor. Thinking of issuing payment tokens to e.g. secure mobile payments or secure your online sales channel? Bell ID can help: www.bellid.com – info@bellid.com Martin Cox – Global Head of Sales
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Similar to What is Payment Tokenization?
Similar to What is Payment Tokenization? (20)
Recently uploaded
Recently uploaded (6)
What is Payment Tokenization?
- 1. WHAT IS PAYMENT TOKENIZATION?
- 2. Tokenization enables banks, acquirers and merchants to offer more secure (mobile) payment services.
- 3. It is the process of replacing card numbers with alternate values.
- 4. The original personal account number (PAN) is disconnected and replaced with a unique identifier called a payment token.
- 5. The ‘mapping’ between the real PAN and the payment tokens is safely stored in the token vault.
- 6. With tokenization the original PAN information is removed from environments where data can be vulnerable.
- 8. 1. Tokenization heavily reduces the risk of payment fraud by removing confidential consumer credit card data from the payment network.
- 9. 2. The original card numbers stay in control of the bank. External systems do not have access to this information.
- 10. 3. Tokens are random numbers and arenotbasedoncryptography,hence they cannot be traced back to the original value.
- 11. How does tokenization work?
- 12. A token is generated from the PAN for one time use within a specific domain such as a merchant’s website or channel. Step 1:
- 13. Tokens are sent to the token vault and stored in a PCI-compliant environment.
- 14. Tokens are loaded on the mobile device as part of the virtual card profile. Step 2:
- 15. The NFC device makes a payment at a merchant’s contactless point-of-sale (POS) terminal using the token as the card number. Step 3:
- 16. The POS teminal sends the token to the acquiring bank, which sends it to the issuing bank through the payment network. Step 4:
- 17. The issuer de-tokenizes the token to the real PAN and, if matched, approves the payment. Step 5:
- 18. Response from the card issuer is returned to the POS terminal using the token as the card reference. Step 6:
- 19. Payment tokens act like the original PAN for returns, sales reports, marketing analysis and recurring payments.
- 20. How can I use tokens?
- 21. In order to use tokenization, a bank or merchant should become a token service provider (TSP).
- 22. A TSP manages the entire lifecycle of payment credentials including:
- 23. 1. Tokenization: Replaces the PAN with a payment token.
- 24. 2. De-Tokenization: Converts the token back to the PAN using the token vault.
- 25. 3. Token vault: Establishes and maintains the payment token to PAN mapping.
- 26. 4. Domain management: Improves protection by defining payment tokens for specific use.
- 27. 5. Identification and verification: Ensures the original PAN is legitimately used by the token requestor.
- 28. 6. Clearing and settlement: Ad-hoc de-tokenization during clearing and settlement process.
- 29. Thinking of issuing payment tokens to secure mobile payments or secure your online sales channel? Bell ID can help: www.bellid.com info@bellid.com
- 30. With over 20 years of expertise, Bell ID is considered the world’s leading provider of lifecycle management solutions for tokens (e.g. smart cards, mobile NFC phones) deployed in single and multi-application programmes. www.bellid.com Martin Cox Global Head of Sales m.cox@bellid.com