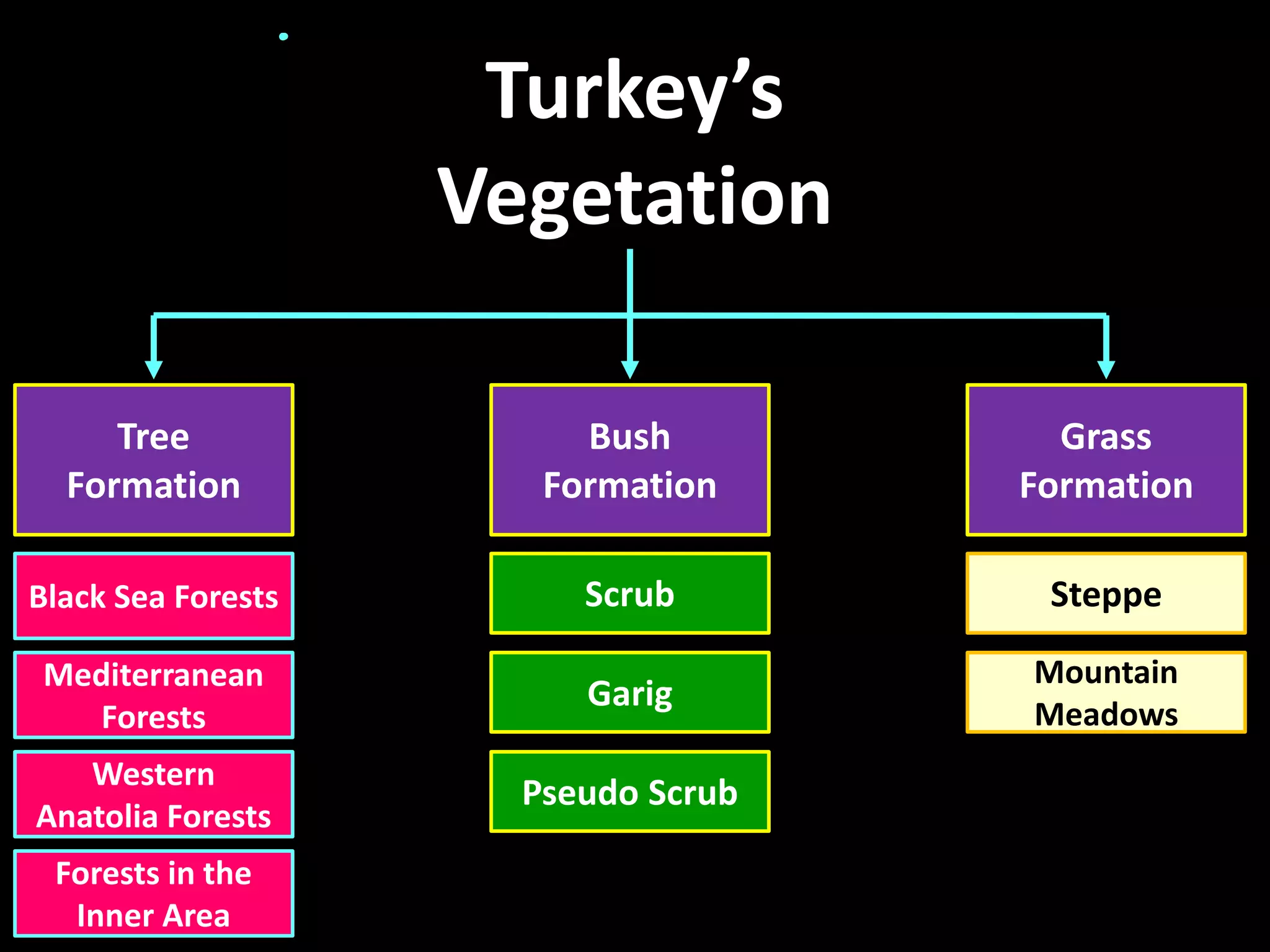
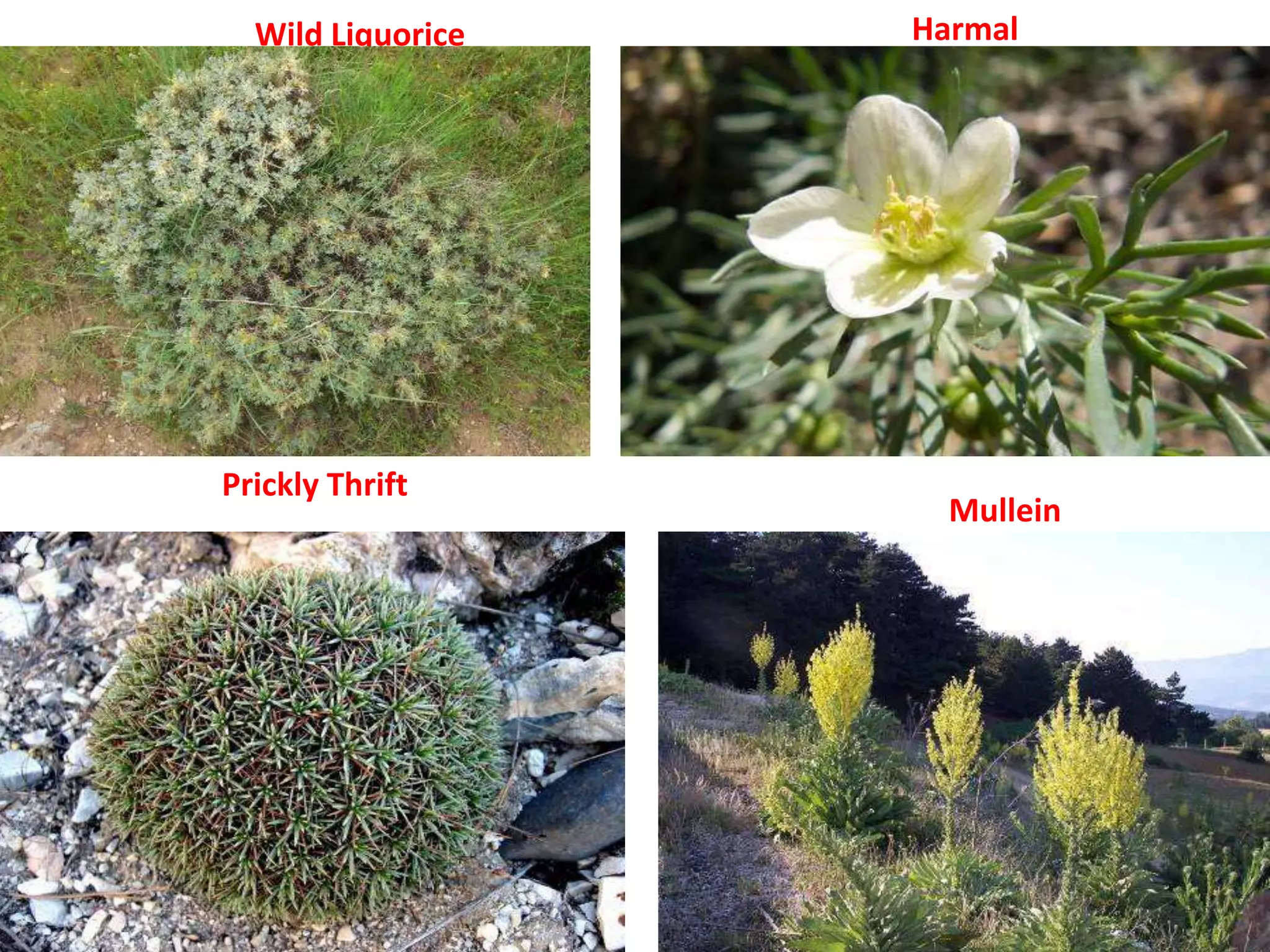
Turkey has a diverse variety of vegetation due to its varied climate, landforms, and human influence. Approximately 12,000 plant species have been identified in Turkey. The diversity of plant life is due to Turkey's location between different climate zones and its coastal position surrounded by seas. Some notable plant types found in Turkey include relict plants that have survived from earlier eras, and endemic plants that grow only in certain regions of Turkey. Forests make up 27.6% of Turkey's land and are divided into different zones based on location and dominant tree species. The most common tree types in Turkish forests are Calabrian pine, oak, larch, beech, and Scotch pine.