Fetal circulation & changes occurring at birth
- 1. Fetal Circulation & Changes occurring at birth Moderator:Dr.Anil Rawat
- 2. The Fetal Circulation… • differs from adult circulation in several ways • differences are attributable to the fundamental difference in the site of gas exchange – the placenta as compared to lungs in adults
- 3. Concepts • CVO • Fetal Hemoglobin
- 4. The concept of CVO • In the adult circulation, circulatory system is in series and there are no shunts, • the stroke volume of the RV should equal that of the LV and cardiac output can be defined in terms of the volume of blood ejected by one ventricle in 1 min. • In the fetus, as a result of intracardiac/extracardiac shunting, the stroke volume of the fetal LV is not equal to the stroke volume of the RV.
- 5. • The RV receives about 65% of the venous return and the LV about 35%. the situation is much more complex and cardiac output must be defined in different terms • The cardiac output of the fetus can only be spoken of in terms of the total output of both ventricles—the combined ventricular output (CVO). • 45% of the CVO is directed to the placental circulation with only 8% of CVO entering the pulmonary circulation.
- 6. Circulation at Materno Placental Level • placenta is anchored to the wall of the mother's uterus. • chorion acts as a barrier between the maternal and fetal circulation
- 7. • Maternal blood is delivered to the intervillous space of the chorionic plate, • bathes the chorionic villi that carry umbilical capillary beds, allowing fetal/maternal gas exchange • the deoxygenated blood returns via open ended venules
- 8. • the admixture of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, produces a po2 lower than usual • fetal hemoglobin in order to compensate for the relatively lower oxygen tension of the maternal blood supplying the chorion, must be able to bind oxygen with greater affinity
- 9. Feta Hb and Oxygen delivery in the fetus • Oxygen delivery is related to CVO and the oxygen content of blood. • Oxygen content of blood is determined by quantity of haemoglobin and its oxygen saturation. • The fetus has a high Hb concentration ,a high percentage of haemoglobin F (HbF), having lower content of 2,3-DPG, thus shifting the oxygen dissociation curve to the left.
- 10. • High CVO,high haemoglobin concentrations and the presence of HbF help to maintain oxygen delivery in the fetus despite the relatively low partial pressures of oxygen.
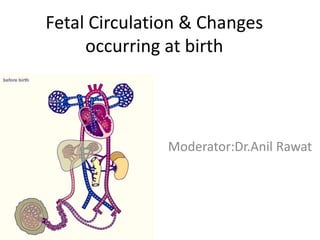
- 12. Course Of Flow
- 13. Course Of Flow • 50% of the umbilical venous blood is distributed to the left and right lobes of the liver, • the other half bypasses the liver through the ductus venosus • Portal venous blood is almost completely distributed to the right lobe of the liver;only 5–10% passes through the ductus venosus,none enters the left lobe of the liver.
- 14. • the left lobe of the liver receives exclusively well- oxygenated umbilical venous blood • the right lobe receives umbilical venous blood and most of portal venous blood
- 15. • The ductus venosus and left hepatic vein enter the inferior vena cava through a single orifice • blood from these veins is well oxygenated and streams in the posterior and left portion of the inferior vena cava in the direction of the foramen ovale to enter the left atrium
- 16. • The poorly oxygenated blood from the right hepatic vein joins blood returning from the distal inferior vena cava • these stream along the anterior and right portions of the inferior vena cava towards the tricuspid valve to enter the right ventricle.
- 17. • The inferior vena cava just below the diaphragm receives blood from four sources, all with different oxygen saturations, – umbilical vein – distal inferior vena cava – left and right hepatic veins • The blood flowing from these four veins does not mix completely but shows differential streaming.
- 18. • Blood returning to the heart through the superior vena cava has a PO2 of 12–15 mmHg and an oxygen saturation of 20–30%. • It is deflected by the tubercle of Lower in the right atrium in the direction of the tricuspid valve, and ~95% enters the right ventricle, whereas only ≤5% of superior vena caval blood passes across the foramen ovale into the left atrium.
- 19. • The preferential streaming of the venous blood results in blood of higher oxygen saturation in the left atrium than in the right ventricle and pulmonary artery • The blood entering the left atrium through the foramen ovale is joined by pulmonary venous blood.
- 20. • In the fetus,there is no gas exchange in the lung, the oxygen saturation of pulmonary venous blood (~50%) is slightly lower than pulmonary artery • pulmonary blood flow is low in the fetus and is considerably less than the volume of blood traversing the foramen ovale • oxygen saturation of mixed blood in the left atrium and left ventricle(65–70%) is only moderately lower than that of ductus venosus (80–90%).
- 21. Distribution Of Flow • The placenta receives the largest amount of combined right and left ventricular output (55%) and has the lowest vascular resistance in the fetus • The blood is oxygenated in the placenta, the oxygen saturation in the IVC (70%) is higher than that in the SVC (40%)
- 22. The highest partial pressure of oxygen (Po2) is found in the umbilical vein (32 mm Hg). SVC drains the upper part of the body, including the brain (15% of combined ventricular output), IVC drains the lower part of the body and the placenta (70% of combined ventricular output).
- 23. • the right ventricle ejects ~65% of combined ventricular output – This is twice of volume ejected by the left ventricle. • since pulmonary vascular resistance is high in the fetus,only ~12% of blood ejected into the pulmonary trunk is distributed to the lungs • remaining 88% of blood ejected by the right ventricle passes through the ductus arteriosus to the descending aorta.
- 24. • The left ventricle is filled by blood returning to the left atrium from the pulmonary veins and through the foramen ovale • of the 35% of combined ventricular output ejected by the left ventricle,~22% is distributed to the forelimbs, heart, head, and brain • only ~10% of CVO crosses the aortic isthmus to the descending aorta to join the blood traversing the ductus arteriosus from the pulmonary trunk.
- 25. • The descending aortic flow is ~67% of CVO • Umbilical placental circulation receives ~40% of CVO • lower trunk, hind limbs, and abdominal organs receive ~27% of CVO • low flow explains why the aortic isthmus is the narrowest part of the aorta in the term infant and why lesions that alter ascending aortic flow in utero affect the diameter of the aortic isthmus and transverse aortic arch.
- 27. Regulation of the circulation in the fetus • In the adult, the systemic and pulmonary circulations are separate. • The preload and afterload of the right and left ventricles are different, and their stroke volumes could differ. • The Frank–Starling mechanism adjusts the outputs of the two ventricles so that over a short period the ventricles eject similar volumes.
- 28. • reduction in venous return to right atrium decreases filling pressure and end-diastolic volume of RV, resulting in a decrease in stroke volume. • Pulmonary blood flow and venous return to the LA and LV are also reduced and the stroke volume decreases. • An increase in systemic arterial pressure decreases LV stroke volume; the end-diastolic volume increases so that, with the next beat, greater force is generated to increase the stroke volume.
- 29. • In fetus, the foramen ovale tends to equalize right and left atrial pressures throughout the cardiac cycle • The ductus arteriosus provides a large communication between the aorta and the pulmonary artery, resulting in almost identical pressures in the two vessels.
- 30. • Due to similar atrial /aortic/pulmonary arterial pressures, differences in stroke volumes of the left and right ventricles are the result of differences in afterload • The aortic isthmus, which is narrower than the ascending and descending aorta, functionally separates the upper and lower body circulations
- 31. Changes Occurring at Birth
- 32. • Conversion of the fetal to the adult circulation requires –eliminating the umbilical–placental circulation –Increase of pulmonary blood flow to a level necessary for adequate gas exchange –separation of the left and right sides of the heart by closure of fetal channels.
- 33. • The major events occurring at the time of birth include • separation of the placental circulation and establishment of rhythmic ventilation • Ventilation comprises two components: – physical expansion of the lungs with gas – elimination of fluid in the alveoli and increase in alveolar oxygen concentration associated with breathing air.
- 34. Changes ln patterns of blood flow • changes in circulation at the time of birth occur almost simultaneously. • the changes in the circulation after birth can be accounted for largely by the onset of rhythmic ventilation with air • removal of the placental circulation abolishes umbilical venous return
- 35. • The elimination of umbilical venous blood flow reduces inferior vena caval return • facilitates closure of the foramen ovale and causes a small decrease in right atrial pressure.
- 36. • Even without eliminating the placental circulation, ventilation increases pulmonary flow and results in foramen ovale closure • though the ductus arteriosus does not close completely immediately after birth, flow from the pulmonary trunk to the aorta is almost completely eliminated. • Hepatic blood flow is reduced within the first few hours after birth but increases after the portal blood flow is increased in association with feeding.
- 37. Changes in pulmonary circulation • During fetal life, pulmonary blood flow is low due to the high pulmonary vascular resistance. • related to both morphologic and functional features of pulmonary vessels. • Small pulmonary arteries have a thick medial layer composed predominantly of smooth muscle cells • These vessels are extremely reactive; they constrict markedly with hypoxia and dilate with an increase in PO2 • Endothelial factors, such as endothelium-derived relaxing factor and NO play an important role in regulating pulmonary vascular resistance.
- 38. • The reduction in pulmonary vascular resistance after birth is associated with rhythmic ventilation and oxygenation • A rise in PO2 is thought to increase endothelial release of nitric oxide,a potent vasodilator • vasoactive agents, such as endothelin, bradykinin & angiotensin also have a role
- 39. • Following the immediate fall in pulmonary vascular resistance following birth, morphologic changes in the pulmonary vessels result in a permanent fall in pulmonary vascular resistance. – most striking change is a decrease in the thickness of the smooth muscle layer in the small arteries. – results in a gradual further decrease in pulmonary vascular resistance and pulmonary arterial pressure within 2–3 weeks after birth
- 40. Closure of the ductus arteriosus • normally widely patent in the fetus,constricts after birth Functional closure of the DA occurs within 10 to 15 hours after birth by constriction of the medial smooth muscle in the ductus. Anatomic closure is completed by 2 to 3 weeks of age by permanent changes in the endothelium and subintimal layers of the ductus.
- 41. • current concept is that two factors are largely responsible for maintaining ductus patency inutero – – low oxygen tension of pulmonary arterial blood – effect of circulating prostaglandin(prostaglandin E2), which relaxes ductus arteriosus smooth muscle.
- 42. • Constriction of the ductus arteriosus occurs with increase in arterial PO2 associated with ventilation • a decrease in plasma prostaglandin E2 concentrations is an important mechanism • oxygen-sensitive potassium channels have been demonstrated to play an important role in the contraction of ductus arteriosus smooth muscle in response to increased oxygen levels • permanent closure of the ductus is achieved by fibrosis.
- 44. Clinical Significance • Persistence of any of the fetal shunts/physiology may lead to – Persistent Ductus Arteriosus – Patent Foramen Ovale/ASD – PPHN
- 45. Persistent Ductus Arteriosus • Occurs in 5-10% of all CHD • Persistent patency of ductus arteriosus between left PA and descending aorta • Ductus is usually cone shaped with small orifice to pulmonary artery
- 46. The responsiveness of the ductal smooth muscle to oxygen is related to the gestational age of the newborn; the ductal tissue of a premature infant responds less intensely to oxygen than that of a full-term infant. This decreased responsiveness of the immature ductus to oxygen is due to its decreased sensitivity to oxygen-induced contraction; it is not the result of a lack of smooth muscle development, as the immature ductus constricts well in response to acetylcholine. It may also be due to persistently high levels of PGE2 in preterm infants.
- 48. • Patients are usually asymptomatic when ductus is small • Large shunt PDA may cause CHF and consequently recurrent pneumonia • Pulmonary vascular obstructive disease may develop if large PDA with Pulmonary hypertension is left untreated
- 49. PFO/ASD • Failure of functional closure of foramen ovale causes formation of a small LR shunt • Common in newborn (75%) • ASD occurs as isolated anomaly with female preponderance
- 50. • Of 3 types – Secundum defect (most common,located in middle portion of atrial septum) – Primum defect(located in the anteroinferior atrial septum) – Sinus venosus defect(located in the posterosuperior atrial septum)
- 51. • Are usually asymptomatic • Spontaneous closure occurs in 40% patients in first 4 years of life • If large defect is untreated, CHF and Pulmonary HTN may develop in 2nd or 3rd decade of life
- 52. PPHN • 1 in 1500 live births • Characterized by persistence of pulmonary hypertension which causes varying degree of cyanosis from a RL shunt through PFO or PDA • Causes – Pulmonary vasoconstriction in presence of normally developed pulmonary vascular bed – Hypertrophy of pulmonary vascular smooth mucle – Developmentally abnormal pulmonary arterioles with decreased cross sectional area of pulmonary vasular bed
- 53. • Symptoms begin 6-12 hours after birth –Cyanosis –Retractions –Grunting –A gradient of 10% or more in oxygen saturation between preductal/postductal ABG s/o ductus arteriosus RL shunt –Cardiomegaly on CxR
- 54. Thank You
