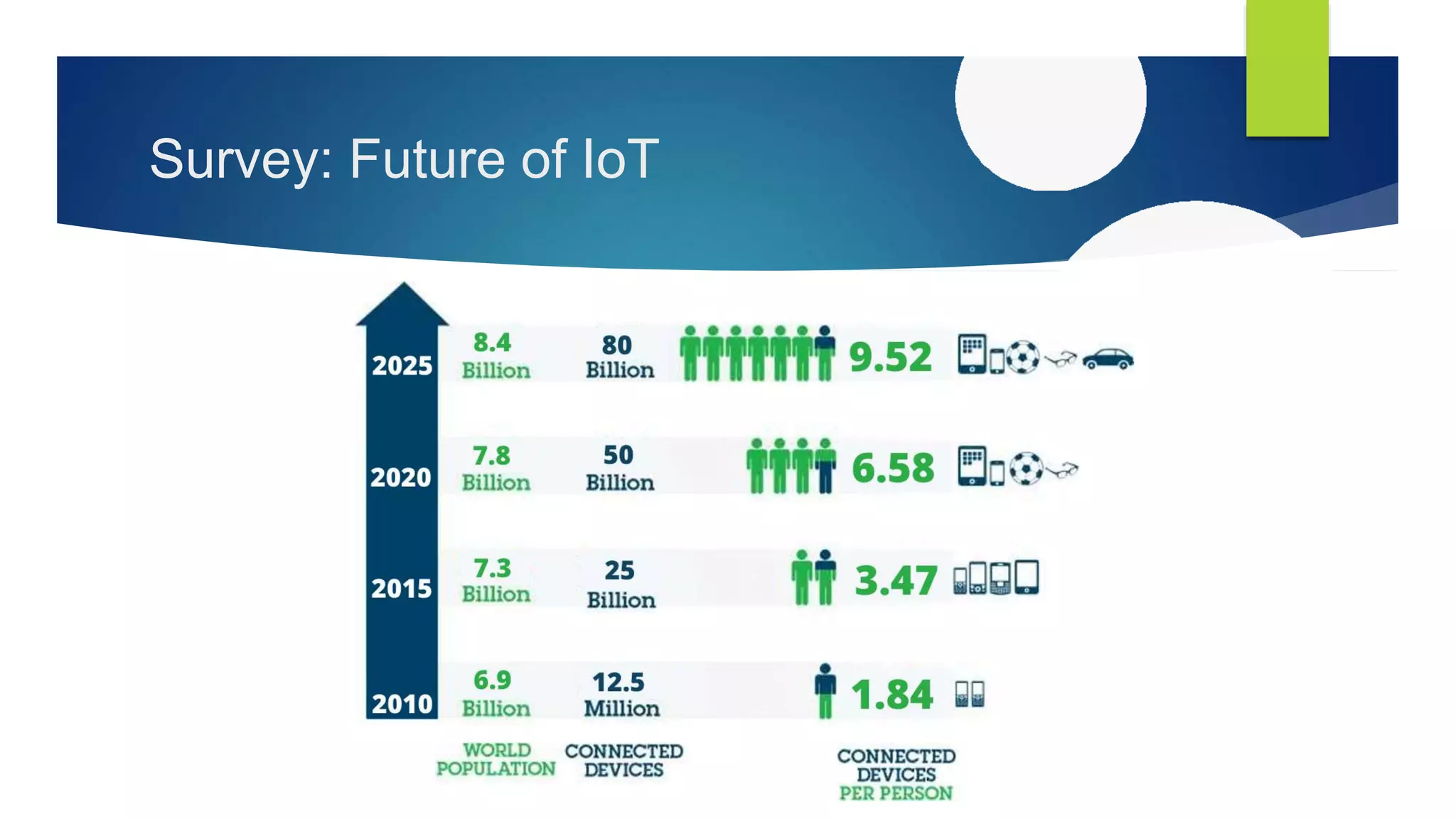
The Internet of Things (IoT) connects various objects and people with unique identifiers, enabling automatic data transfer over networks without human interaction, expanding applications from smart cities to agriculture. The document outlines the projected increase in connected devices and the potential for applications such as smart parking, environmental monitoring, and intelligent retail. It raises concerns about security, data privacy, and governmental surveillance in the evolving IoT landscape.