Hazardous Waste Incineration Guide
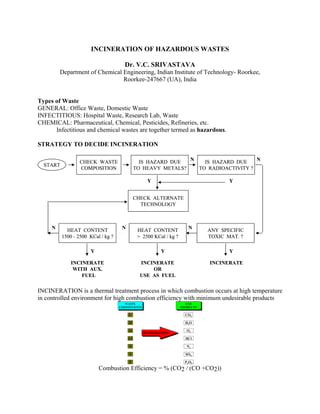
- 1. INCINERATION OF HAZARDOUS WASTES Dr. V.C. SRIVASTAVA Department of Chemical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology- Roorkee, Roorkee-247667 (UA), India Types of Waste GENERAL: Office Waste, Domestic Waste INFECTITIOUS: Hospital Waste, Research Lab, Waste CHEMICAL: Pharmaceutical, Chemical, Pesticides, Refineries, etc. Infectitious and chemical wastes are together termed as hazardous. STRATEGY TO DECIDE INCINERATION INCINERATION is a thermal treatment process in which combustion occurs at high temperature in controlled environment for high combustion efficiency with minimum undesirable products INCINERATIONINCINERATION WASTE CONSTITUENTS WASTE CONSTITUENTS C H O Cl N S P END PRODUCTS END PRODUCTS CO2 H2O O2 HCl N2 SOX P2O5 INCINERATIONINCINERATION WASTE CONSTITUENTS WASTE CONSTITUENTS C H O Cl N S P END PRODUCTS END PRODUCTS CO2 H2O O2 HCl N2 SOX P2O5 Combustion Efficiency = % (CO2 / (CO +CO2)) IS HAZARD DUE TO HEAVY METALS? START CHECK WASTE COMPOSITION IS HAZARD DUE TO RADIOACTIVITY ? Y CHECK ALTERNATE TECHNOLOGY ANY SPECIFIC TOXIC MAT. ? HEAT CONTENT > 2500 KCal / kg ? HEAT CONTENT 1500 - 2500 KCal / kg ? INCINERATEINCINERATE OR USE AS FUEL INCINERATE WITH AUX. FUEL N Y YYY N N N N IS HAZARD DUE TO HEAVY METALS? START CHECK WASTE COMPOSITION IS HAZARD DUE TO RADIOACTIVITY ? Y CHECK ALTERNATE TECHNOLOGY ANY SPECIFIC TOXIC MAT. ? HEAT CONTENT > 2500 KCal / kg ? HEAT CONTENT 1500 - 2500 KCal / kg ? INCINERATEINCINERATE OR USE AS FUEL INCINERATE WITH AUX. FUEL N Y YYY N N N N
- 2. INCINERATION SYSTEM WASTE PREPARATION WASTE PREPARATION WASTE FEEDING WASTE FEEDING INCINERATORINCINERATOR ACID GAS REMOVAL ACID GAS REMOVAL GAS COOLING GAS COOLING PARTICULATE REMOVAL PARTICULATE REMOVAL DEMISTER & STACK DEMISTER & STACK RESIDUE TREATMENT RESIDUE TREATMENT ASH DISPOSAL ASH DISPOSAL WASTE WASTE PREPARATION WASTE PREPARATION WASTE FEEDING WASTE FEEDING INCINERATORINCINERATOR ACID GAS REMOVAL ACID GAS REMOVAL GAS COOLING GAS COOLING PARTICULATE REMOVAL PARTICULATE REMOVAL DEMISTER & STACK DEMISTER & STACK RESIDUE TREATMENT RESIDUE TREATMENT ASH DISPOSAL ASH DISPOSAL WASTE WASTE HANDLING ACTIVITYACTIVITY METHODS / EQUIPMENTMETHODS / EQUIPMENT Preparation Conveying Feeding Screening /Shredding, Crushing, Blending, Heating, Baling, Evaporation Slat /Screw / Grab / Pneumatic Conveyors, Hoists, Pumps, Blowers Manual / Gravity /Ram / Screw Feeders, burners, Injectors, Sludge lances ACTIVITYACTIVITY METHODS / EQUIPMENTMETHODS / EQUIPMENT Preparation Conveying Feeding Screening /Shredding, Crushing, Blending, Heating, Baling, Evaporation Slat /Screw / Grab / Pneumatic Conveyors, Hoists, Pumps, Blowers Manual / Gravity /Ram / Screw Feeders, burners, Injectors, Sludge lances TECHNOLOGY DESCRIPTION High temperature hazardous waste incinerators are available in a number of configurations and principles. Typically a process for treatment involves heating to a temperature greater than 850°C or, if the chlorine content is above 1 %, greater than 1,100 °C, with a residence time greater than 2 seconds, under conditions that assure appropriate mixing and subsequent destruction.
- 3. Temperature & residence time: Combustion temperature and residence time needed for mixed hazardous wastes cannot be readily calculated and are often determined empirically. Some common solvents such as alcohols and toluene can easily be combusted at temperatures less than 1,000 o C and less than one second residence time, while other more complex organic halogens require more stringent conditions. UUSS EEPPAA TTooxxiicc SSuubbssttaanncceess CCoonnttrrooll AAcctt ((TTSSCCAA)) PPCCBB IInncciinneerraattiioonn CCrriitteerriiaa:: “...mmoorree ccoommpplleexx oorrggaanniicc hhaallooggeennss ssuucchh aass PPCCBB rreeqquuiirreess 11220000 OO CC aanndd 22 sseecc rreessiiddeennccee ttiimmee ”” EEUU DDiirreeccttiivvee 22000000//7766//EECC oonn IInncciinneerraattiioonn ooff WWaassttee rreegguullaatteess CCoo--iinncciinneerraattiioonn ooff HHaazzaarrddoouuss WWaassttee iinn CCeemmeenntt KKiillnnss:: ““......iiff mmoorree tthhaann 11 %% ooff hhaallooggeennaatteedd oorrggaanniicc ssuubbssttaanncceess,, eexxpprreesssseedd aass cchhlloorriinnee,, aarree iinncciinneerraatteedd,, tthhee tteemmppeerraattuurree hhaass ttoo bbee rraaiisseedd ttoo mmiinniimmuumm 11110000 °°CC dduurriinngg aatt lleeaasstt ttwwoo sseeccoonnddss””.. INFECTITIOUS WASTE INCINERATION Infectitious Waste: WWaassttee tthhaatt ccaann sspprreeaadd iinnffeeccttiioonn,, ggeenneerraatteess iinn hhoossppiittaallss && mmeeddiiccaall iinnssttiittuuttiioonnss,, rreesseeaarrcchh eessttaabblliisshhmmeennttss,, aanniimmaall//ssllaauugghhtteerr hhoouusseess.. FIXED HEARTH INCINERATOR Applicable For Wastes: Hospitals, Research Labs, Canteens, Hotels, Offices and banks, Automobile / White Goods Industries, Chemical industries, Workshops PRIMARY CHAMBER SECONDARY CHAMBER FEEDING DOOR DEASHING DOOR PRIMARY BURNER SEC. BURNER HEARTH TO GAS CLEANING PRIMARY CHAMBER SECONDARY CHAMBER FEEDING DOOR DEASHING DOOR PRIMARY BURNER SEC. BURNER HEARTH TO GAS CLEANING Two Stage Combustion •Primary Combustion: –Decomposition Of All Combustibles, –Gasification / Partial Combustion, –Burning Of Carbon •Secondary Combustion: –Complete Combustion Of All Unburnts And Partially Burnt In Gas Form, –Destruction Of Pathogens Temperature Control: Primary 800±50 O C & Secondary 1050 ±50 O C, Through Individual Burners In Both Chambers, Auto On/off Operation Of Burners For Fuel Efficiency Residence Time - 1 Sec @ 1050±50 C in Secondary Chamber, Through Adequate Sizing, Turbulence To Ensure Proper Mixing With Air Chimney Height: Min 30 Meters, To Ensure Low Ground Level Concentration
- 4. CHEMICAL WASTE INCINERATION CHEMICAL WASTE: By-product Gases And Vapors, Organic Liquid Streams, Aqueous Waste Containing Dissolved Organics And Salts, Distillation Bottom Tars, Organic Sludge And Semi-solids, Slurries And Sludge With High Moisture, Granular Solids, Filter Cakes SOURCES OF CHEMICAL WASTESOURCES OF CHEMICAL WASTE • Petrochemicals • Pharmaceuticals • Antibiotics, Bulk Drugs • Oil Refineries, Srus • Agro-chemicals, Pesticides • Dyes, Dye-intermediates • Organic Chemicals • Speciality Chemicals • Petrochemicals • Pharmaceuticals • Antibiotics, Bulk Drugs • Oil Refineries, Srus • Agro-chemicals, Pesticides • Dyes, Dye-intermediates • Organic Chemicals • Speciality Chemicals • Polymers, Plastics • Pulping Mills • Coke Ovens (By-product Recovery) • Coating, Printing, And Laminating • Automobiles (Paint Shop) • Polymers, Plastics • Pulping Mills • Coke Ovens (By-product Recovery) • Coating, Printing, And Laminating • Automobiles (Paint Shop) Industries Manufacturing And Handling Variety Of Chemicals Such As: CHEMICAL WASTE INCINERATORS STATIC: Liquid/Gaseous Injection, Fluid Bed Incinerator, Fixed Hearth NON – STATIC: Rotary Kiln LIQUID WASTE INCINERATORS APPLICATIONS Low melting distillation bottoms Organic liquid waste Waste Waters Gaseous Waste Chlorinated waste from PVC / ECH manufacturing High fluorine containing waste.
- 5. M. S. SHELL BURNER ASSEMBLY MANHOLE FLUE GAS OUTLET MANHOLE REFRACTORY INJECTOR M. S. SHELL BURNER ASSEMBLY MANHOLE FLUE GAS OUTLET MANHOLE REFRACTORY INJECTOR LIQUID WASTE INCINERATORS MERITS 1. No Secondary Combustion Chamber 2. Simple Construction 3. No Moving Parts 4. Suitable For Gaseous / Liquid Waste 5. Low Maintenance Required 6. Capable Of High Turndown. 7. Accepts Wide Range Of Liquid / Gaseous Waste. DEMERITS •For Only Atomizable Liquid Wastes. •Not Suitable For Slurries With Large Size Solids. FLUIDISED BED INCINERATORS APPLICATIONS Distillation Bottom Tars 2. Organic Liquid & Semi Solid Waste. 3. Sludge With High Moisture Content. 4. Organic Sludge. 5. Pharmaceutical Sludge 6. Aqueous Waste containing Sodium Sulfate & Sodium Carbonate & Recovery 7. Granular, Powdery waste
- 6. MERITS •Ability to handle heterogeneous waste. • High efficiency due to - Vigorous mixing in the bed - High retention time • Low NOx formation due to - Lower operating temperature & - Low excess air. • In bed neutralization possible for removing acid gases • Quick re-start due to heat stored in the bed. • Absence of moving parts hence low maintenance. • Flexibility to handle diverse fuels. DE-MERITS •Difficult To Remove Residual Materials From Bed. •Requires Elaborate Waste Preparation For Bulk Solids. •High Power Costs. •Incineration Temperature Limited To 800 Deg C. •Special Care For Feed Selection & Mixing Of Additives To Prevent Bed Damage. ROTARY KILN INCINERATORS •In Rotary kilns solid, sludge, containerized or pumpable waste is introduced at the upper end of the inclined drum. Temperatures in the kiln usually range between 850 and 1300ºC. The slow rotation of the drum allows a residence time of 30-90 minutes.
- 7. •The secondary combustion chamber following the kiln completes the oxidation of the combustion gases. Liquid wastes and/or auxiliary fuels may be injected here along with secondary air to maintain a minimum residence time of two seconds and temperatures in the range of 900-1300ºC, effectively destroying any remaining organic compounds. MERITS •Suitable For All Kinds Of Wastes. •Feed Capability For Drums & Bulk Containers. •Can Be Operated At High Temperatures. •Residence Time Adjusted By Varying Kiln Speed. •Waste Feeding - Without Much Preparation LIMITATIONS •Expensive For Low Feed Rates. •Subject To High Wear & Tear. •Relatively Low Thermal Efficiency. •Large Particulate Carry-over. •Air leakage possible without good sealing DEDICATED INCINERATORS DEDICATED INCINERATORS that handle a particular waste stream. An example of the latter might be a chemical manufacturing plant treating chlorinated wastes to recover HCl. Dedicated hazardous waste incinerators use a variety of incineration, pyrolysis, and plasma treatment techniques.
- 8. incinerator for treating liquid and gaseous chlorinated wastes at a chlorinated chemical manufacturing facility MMoonniittoorriinngg In addition to carbon monoxide, oxygen in the flue gas, air flows and temperatures, pressure drops, and pH in the flue gas can be routinely monitored at reasonable cost. While these measurements represent reasonably good surrogates for the potential for unintentional POPs formation and release, periodic measurement of PCDD/F’s in the flue gas will aid in ensuring that releases are minimized and the incinerator is operating properly. Maintaining Public Awareness and Communication •Successful incineration projects have been characterized by: holding regular meetings with concerned citizens; providing days for public visitation; posting release and operational data to the Internet; and displaying real time data on operations and releases at the facility site. General Combustion Techniques Ensure design of furnace is appropriately matched to characteristics of the waste to be processed. Maintain temperatures in the gas phase combustion zones in the optimal range for completing oxidation of the waste. Provide for sufficient residence time (e.g., 2 seconds) and turbulent mixing in the combustion chamber(s) to complete incineration. Pre-heat primary and secondary air to assist combustion. Use continuous rather than batch processing wherever possible to minimize start-up and shut- down releases. Establish systems to monitor critical combustion parameters including grate speed and temperature, pressure drop, and levels of CO, CO2, O2. Provide for control interventions to adjust waste feed, grate speed, and temperature, volume, and distribution of primary and secondary air. Install automatic auxiliary burners to maintain optimal temperatures in the combustion chamber(s). Hazardous Waste Incineration Techniques
- 9. •Rotary kilns are well demonstrated for the incineration of hazardous waste and can accept liquids and pastes as well as solids. ••Water-cooled kilns can be operated at higher temperatures and allow acceptance of wastes with higher energy values. ••Waste consistency (and combustion) can be improved by shredding drums and other packaged hazardous wastes. ••A feed equalization system e.g., screw conveyors that can crush and provide a constant amount of solid hazardous waste to the furnace, will ensure smooth feeding. Flue Gas Treatment The type and order of treatment processes applied to the flue gases once they leave the incineration chamber is important, both for optimal operation of the devices as well as for the overall cost effectiveness of the installation. Waste incineration parameters that affect the selection of techniques include: waste type, composition, and variability; type of combustion process; flue gas flow and temperature; and the need for, and availability of, wastewater treatment. Formation and Release of Unintentional POPs Emission testing has confirmed that composition of the waste, furnace design, temperatures in the post-combustion zone, and the types of air pollution control devices (APCD) used to remove pollutants from the flue gases are important factors in determining the extent of POPs formation and release. Depending on the combination of these factors, POPs releases can vary over several orders of magnitude per ton of waste incinerated. Average 6 - 7 Nm3 of flue gas per kg waste Specific collection/treatment for: Dust - staged filters Chlorine - neutralised by scrubbing with lime Sulphur - washing stage Dioxins - combustion control, activated carbon Examples of APCD’s relevant to the prevention or reduction of unintentional releases •Cyclones and multi-cyclones •Electrostatic precipitators – wet, dry, or condensation •Fabric filters – including catalytic bag filters •Static Bed Filters •Scrubbing systems - wet, spray dry, or ionization •Selective catalytic reduction (SCR) •Rapid Quenching Systems •Carbon Adsorption Wastewater from incineration Controls vary from country to country Quantity: •influenced by gas scrubbing technology chosen i.e. wet, semi-dry, dry
- 10. •Treatment: •in aerated lagoons / widely used / low cost / may not meet required standard •physico-chemical treatment may also be needed Best Environmental Practices for Waste Incineration Well-maintained facilities, well-trained operators, a well-informed public, and constant attention to the process are all important factors in minimizing the formation and release of the unintentional POPs from the incineration of waste. In addition, effective waste management strategies (e.g., waste minimization, source separation, and recycling), by altering the volume and character of the incoming waste, can also significantly impact releases. EEssttaabblliisshhiinngg QQuuaalliittyy RReeqquuiirreemmeennttss ffoorr WWaassttee FFeedd Facilities must be able to accurately predict the heating value and other attributes of the waste being combusted in order to ensure that the design parameters of the incinerator are being met. IInncciinneerraattoorr OOppeerraattiinngg aanndd MMaannaaggeemmeenntt PPrraaccttiicceess EEnnssuurriinngg GGoooodd CCoommbbuussttiioonn Optimal burn conditions involve: •mixing of fuel and air to minimize the existence of long-lived, fuel rich pockets of combustion products, ••attainment of sufficiently high temperatures in the presence of oxygen for the destruction of hydrocarbon species, and ••prevention of quench zones or low temperature pathways that will allow partially reacted fuel to exit the combustion chamber. Proper management of time, temperature, and turbulence as well as oxygen (air flow), by means of incinerator design and operation will help to ensure the above conditions. The recommended residence time of waste in the primary furnace is 2 seconds. Temperatures at or above 850°C are required for complete combustion in most technologies. Turbulence, through the mixing of fuel and air, helps prevent cold spots in the burn chamber and the buildup of carbon which can reduce combustion efficiency. Oxygen levels in the final combustion zone must be maintained above those necessary for complete oxidation. Residue Management Techniques •Unlike bottom ash, APCD residuals including fly ash and scrubber sludges may contain relatively high concentrations of heavy metals, organic pollutants (including PCDD/F), chlorides and sulfides. ••Mixing fly ash and FGT residues with bottom ash should be avoided since this will limit the subsequent use and disposal options for the bottom ash. ••Treatment techniques for these residues include: –Cement solidification. Residues are mixed with mineral and hydraulic binders and additives to reduce leaching potential. Product is landfilled. –Vitrification . Residues are heated in electrical melting or blast furnaces to immobilize pollutants of concern. Organics, including PCDD/F are typically destroyed in the process. –Catalytic treatment of fabric filter dusts under conditions of low temperatures and lack of oxygen; –The application of plasma or similar high temperature technologies.
- 11. –•Fly ash and scrubber sludges are normally disposed of in landfills set aside for this purpose. Some countries include ash content limits for PCDD/F in their incinerator standards. If the content exceeds the limit, the ash must be re-incinerated. CONTROLS AND SAFETIES •Temp. control for constant efficiency •Air control for adequate excess air •Pressure control for balance draft •pH control for scrubber performance •Interlocks for safe operation & shutdown Costs •Related to site-specific and country-specific factors •High level of sophistication & control = high construction costs •Air pollution control costs = 30-40% of total Scenario in Hazardous Waste Management in India •Major issues in India –30 million tons of waste generated apart from fly ash (2003 data) •8 million tons of hazardous waste •Key issues –Lack of secure landfills and Treatment, storage and disposal facility –Lack of incineration facilities –Lack of waste handling and management systems Hazardous waste disposal industry in the industry sector is worth about $200 million Utilization of wastes in cement plants •Waste utilisation in cement plants in India –Almost nil – except fly ash and gypsum •US/Japan and European Cement plants –Use 80% of waste as fuel –450 kg of waste is used as raw material for production of one ton of Cement production in Japan •Tremendous potential in India –Waste utilization technology –Waste processing equipment •Key requirement –Suitable legislation for waste processing in Cement industry Indian cement plants can absorb 14 million tons of hazardous waste /year CONCLUSIONS Hazardous waste incineration •Is in principle good strategy to treat hazardous waste in an environmentally sound way •are highly regulated
- 12. •need skilled personnel •require high operating and safety standards •require high capital investment•have medium to high operating costs