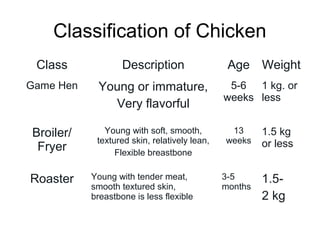
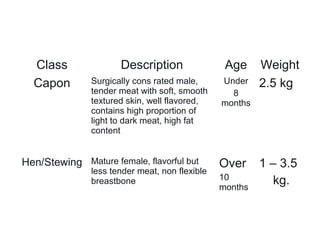
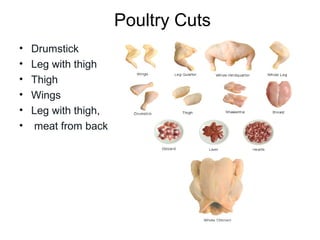
Poultry includes domesticated birds raised for meat like chicken, turkey, ducks, and more. It is generally inexpensive and versatile to cook using many methods. Poultry meat is classified by kind, class, style, and refrigeration state. The breast and wings are lighter in color than thighs and legs due to higher protein concentration. Poultry is similar to red meats with dark meat having more fat and connective tissue than white meat. Common market forms include live, whole, dressed, drawn, and ready-to-cook poultry as well as poultry parts. Chicken is further classified by class including broiler, roaster, capon, hen/stewing based on age,