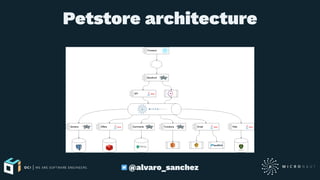
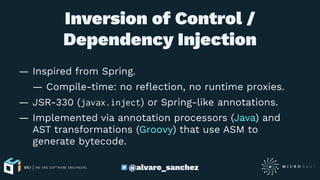
The document introduces Micronaut, a lightweight framework designed for building reactive microservices and cloud applications, emphasizing its compile-time dependency injection and performance efficiency. It covers features such as bean management, AOP, reactive programming, and serverless function support, alongside practical examples of HTTP clients and routing. The document also highlights the framework's minimal resource consumption compared to alternatives like Spring and Grails.



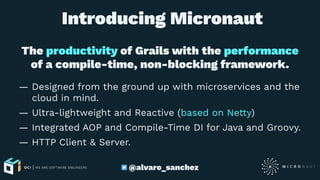





![Injectable types
— An Optional of a bean. If the bean doesn’t exist
empty() is injected. Alternatively, use @Nullable.
— An Iterable or subtype of Iterable (eg List, Collection
etc).
— A lazy Stream of beans.
— A native array of beans of a given type (Engine[]).
— A javax.inject.Provider if a circular dependency
requires it.
@alvaro_sanchez](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/micronaut-intro-greach2018-180317102941/85/Reactive-microservices-with-Micronaut-Greach-2018-13-320.jpg)









































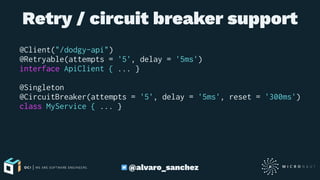
![Fallback support
@Validated
interface PetOperations<T extends Pet> {
@Get("/") Single<List<T>> list()
}
@Client(id = "pets", path = "/v1/pets")
interface PetClient extends PetOperations<Pet> {
@Get("/") Single<List<Pet>> findAll()
}
@Fallback
class PetClientFallback implements PetOperations<Pet> {
Single<List<Pet>> list() { Single.just([] as List<Pet>) }
}
@alvaro_sanchez](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/micronaut-intro-greach2018-180317102941/85/Reactive-microservices-with-Micronaut-Greach-2018-55-320.jpg)