Elimination system (urinary) 26 june 2015
- 2. OBJECTIVES 1. Describe factors that can alter urinary function 2. Discuss common problem of Urinary Elimination 3. Identify nursing intervention for common urinary problems
- 3. Bladder Quiz To test your knowledge, answer the following true or false questions. 1.The bladder of a healthy adult can hold up to 2 cups of urine comfortably for 2 to 5 hours. True / False True
- 4. 2. Holding urine in the bladder too long can lead to infections. True / False True Regular urination flushes away bacteria and helps keep the urinary tract sterile.
- 5. 3. Diabetes is one of the diseases that can affect the bladder True / False True Over time, diabetes can affect the nerves that control the bladder and intestinal tract. The bladder can become paralyzed and stop responding to signals that it is filling
- 6. 4. All kids are ready to start toilet training by 18 months. True / False False It's true that kids are bladders and digestive systems ready for toilet training at 18 months—But (understanding the urge to go to the bathroom, resisting distractions and remembering)are learnt at different pace.
- 7. 5. There are several types of urinary incontinence True / False True Urinary incontinence is only a general term used.
- 8. 6. Bladder control problems are common in older people True / False True With age, tissues in the urinary tract change, muscles weaken and nerves can be damaged.
- 9. 7. Urinating more than 8 or 10 times a day is normal. True / False False Urinating more than 8 times in 24 hours—or more than twice each night—can be a sign of an overactive bladder. This condition can affect people's self-esteem and confidence, sometimes making them afraid to be far from home,
- 10. 8. Healthcare team can't do much about an overactive bladder True / False False most problems can be improved with treatment. exercises to strengthen the pelvic muscles, lifestyle changes, medicines to calm the bladder's muscles and nerves, or devices to hold up the bladder could be helpful
- 11. 9. Prostate problems can affect bladder control in men True / False True Men with this problem may have a weak flow or have to urinate often during the day and night.
- 12. 10. Caffeine can affect the bladder True / False True Caffeinated drinks such as coffee, cola irritate the bladder and cause the bladder to fill quickly. This, in turn, can increase the urge to urinate and sometimes can lead to leaking. Medications, infection, being overweight, nerve damage, weak muscles and various health conditions can cause urine to leak as well
- 13. Result • Those who scored 10/10. welldone! • Those who scored 7-9/10. Great! • Those who scored 1-7/10. Good try! Pay attention to the class to get more knowledge about maintaining bladder function.
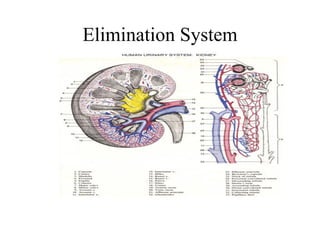
- 14. Urinary elimination system The act of bodily system consisting of the organs that eliminate urine which includes the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra.
- 15. Urination: Micturation, voiding and urination all refer to the process of emptying the urinary bladder. urine collects in the bladder until the pressure stimulates special sensory nerve ending in the bladder wall called stretch receptors.
- 16. FACTORS INFLUENCING URINARY ELIMINATION Growth & Development • Infants and children: urine appears light yellow, not concentrated. • Voluntary control of urine begins at 18–24 months of age and full control at 4–5 yrs. • After 50yrs: kidney shrinks • Elderly adults: increased frequency because of loss of muscle tone. Residual urine may increase leading to high risk of infection Psychosocial Factors • Privacy • Sufficient time • Appropriate position • Anxiety, stress
- 17. Fluid intake • Increase fluid intake • Fruits & vegetable • Caffeine increases urinary frequency Medications • Diuretics • Certain drugs changes color of urine Muscle tone • Regular exercise lead to strong muscle contraction and control of the external sphincter.
- 18. Pathological Conditions • Fever • Renal failure • Diabetes Mellitus • Calculus • Hypertrophy of prostate gland Surgical procedures • Anesthesia reduces output • Local trauma
- 19. ALTERED URINE PRODUCTION: • Polyuria or Diuresis-- 2500-4000mls/day (too much) increase intake— • Diuresis—more production, more excretion of urine • Polydipsia—intense thirst(associated with diuresis) • Oliguria--scant urine output-- less than 500 cc/day—in renal failure, nephrons not functioning. • Anuria—less than 100. • Complete kidney shutdown ,renal failure and urinary shutdown-- have the same meaning
- 20. ALTERED IN URINARY ELIMINATION: • Frequency. Void at frequent intervals due to cystitis ,stress pressure on bladder are some of the causes listed. • Nocturia/ Nycturia—increased frequency at night—Don’t give diuretics at night. Take by 5 p.m. • Urgency—Urgent need to void • Dysuria—Painful voiding, injury, infection, structural problems • Enuresis—involuntary passage of urination after age 4-5 years (primary and secondary) • Urinary Incontinence—urine overflows or dribbles Types: total, stress, urge, functional and reflex incontinence
- 21. Types of Urinary incontinence 1. Functional Urinary incontinence-Inability of usually continent person to reach toilet in time to avoid unintentional loss of urine. 2. Reflex Urinary Incontinence-Involuntary loss of urine at somewhat predictable intervals when a specific bladder volume is reached. 3. Stress Urinary Incontinence-Sudden leakage of urine occurring with activities that increase abdominal pressure, 4. Total Urinary Incontinence-Continuous and unpredictable passage of urine. 5. Urge Urinary Incontinence- lnvoluntary passage of urine occurring soon after a strong sense of urgency to void.
- 23. 37-23 Copyright 2004 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Common Alterations in Elimination • Urinary Elimination – Acute urinary incontinence – Chronic urinary incontinence
- 24. 37-24 Copyright 2004 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Common Alterations in Elimination Stress Urinary Incontinence (SUI) – Uncontrolled loss of urine caused by physical exertion in the absence of a detrusor muscle contraction – Associated with urethral hypermobility or intrinsic sphincter deficiency
- 25. 37-25 Copyright 2004 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Common Alterations in Elimination • Urgency and Urge Urinary Incontinence (overactive bladder syndrome) – Involuntary leakage accompanied by urge to void • Functional Urinary Incontinence – Altered mobility, manual dexterity – Ability to access toilet – Cognitive changes
- 26. 37-26 Copyright 2004 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Common Alterations in Elimination • Extraurethral Incontinence – Uncontrolled loss of urine that exists when the sphincter mechanism has been bypassed
- 27. • Retention—accumulation of urine in the bladder. Urine accumulates in bladder as much as 3000ml. Prolonged retention increases the possibility of UTI. On percussion a kettle drum (dull sound) can be heard • Hematuria--blood in urine • Residual—what’s left in the bladder after voiding • Calculi: - can occur in the kidney, bladder, or urethra. • Infections mean that disease producing bacteria are present in the urinary tract.. • Cyctitis :-is an inflammation of the bladder. Symptoms include frequent need to urinate, slow dribbling urination, burning during urination, pain, and blood in the urine.
- 28. Subjective data • Normal Pattern Identification – client description for alteration in urine output – Specific question regarding last voiding how many times per day Quantity of urine each time you void any night wakeup for micturation (be sensitive to the clients privacy and embarrassment) Assessment
- 29. Cont. • Risk Identification – Any previous problem related elimination i.e. renal calculi, UTI – How it was treated or resolved? – Any GU related previous surgery ? – Evaluate any other clinical problems? – Recent changes in daily routine (Increase activity, exercise, , fluid intake)? - Any significant changes in oral intake of beverages that contain alcohol or caffeine? – Medication that can effect on micturation such as diuretics ? – Assess motor or cognitive dysfunction ? – Visual impairment or communication impairment ?
- 30. Cont. Dysfunction Identification -Ask open ended questions – Have u notice any problem with voiding lately, is a good way to begin. – Do u have any pain or burning with urination? – Have u noticed any pink or radish color in your urine? – Do u feel you are able to empty your bladder completely every time you urinate? – Do u accidentally loose any urine when u cough and sneeze? – Do u have any difficulty in stopping and starting urine stream?
- 31. Cont.Objective Data • Assessment of urine • I/O, Bladder ultrasound • Physical Assessment – Inspection – Percussion – palpation • Diagnostic test and procedures – Collection of urine specimen • Random specimen • midstream specimen • 24 hr Specimen • Specimen from a catheter • Urine test • Blood test
- 32. Nursing Diagnosis Stress incontinence Self esteem disturbance Social Isolation Self care deficit: Toileting High risk for impaired skin integrity High risk for infection
- 33. Implementation Maintaining Normal Urinary Elimination Promoting fluid intake Maintaining normal voiding habits Assisting with toileting Managing Urinary Incontinence Continence training Pelvic muscle exercises Positive reinforcement Maintaining skin integrity Kegal exercises to strengthen muscles.
- 34. Wellness Teaching 1. Respond as soon as possible to the urge to void 2. Drink 8 to 10 glasses of water a day 3. After urination, females should wipe from the urinary meatus towards the anus 4. Maintain perineal-genital cleanliness 5. Avoid any harsh soap. 6. Avoid foods and fluids that contain excessive sodium which can lead to fluid retention 7. Empty the bladder completely at each voiding 8. Obtain medical assistance if burning accompanies voiding or if the urine changes color, clarity, odor or amount.