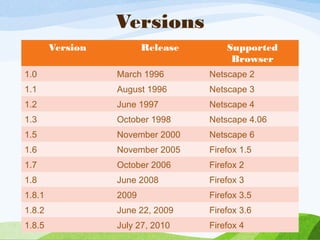
JavaScript is the programming language of the web that allows for dynamic and interactive effects on web pages. It was created in the 1990s by Netscape and Sun Microsystems and has evolved through several versions. JavaScript code runs directly in the browser and is used to add interactivity to HTML pages through elements like variables, arrays, and functions. Common applications of JavaScript include slideshows, dropdown menus, form validation, popups, and automatic page refreshes. Its advantages include client-side execution, ease of use, and speed, while developers must be careful of issues like case sensitivity and proper syntax.








![Arrays
var score = new Array(3);
score[0] = 35;
score[1] = 56;
score[2] = 10;
sum=score[0]+score[1]+score[2];
alert(sum) ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptvishal-170329160902/85/Javascript-Basics-10-320.jpg)





