This document provides an introduction to JavaScript, including:
- JavaScript is a client-side scripting language that makes web pages dynamic and interactive. It is supported by all major browsers.
- There are two types of scripting languages: client-side (like JavaScript) that execute in the browser, and server-side (like PHP) that execute on the server.
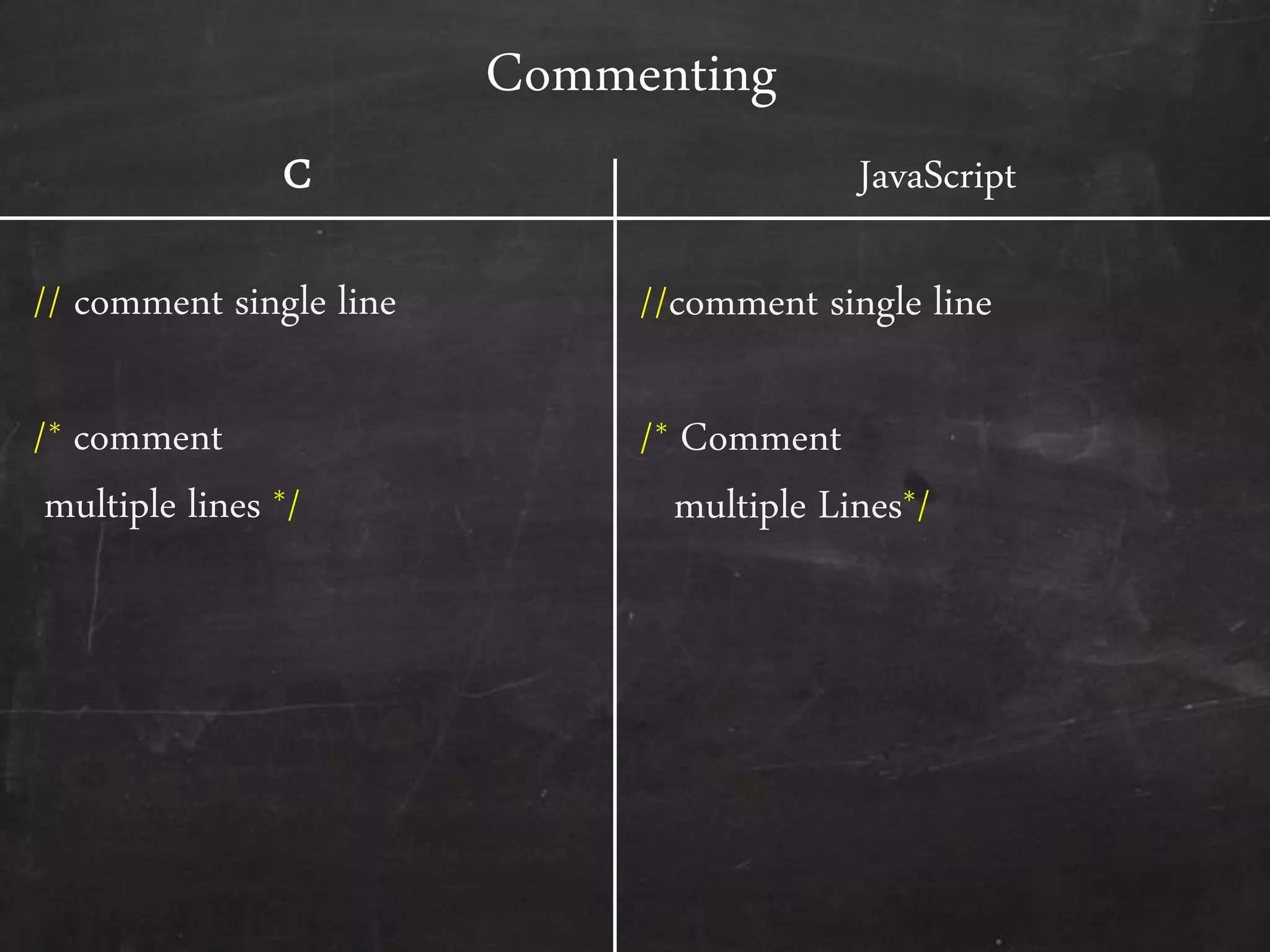
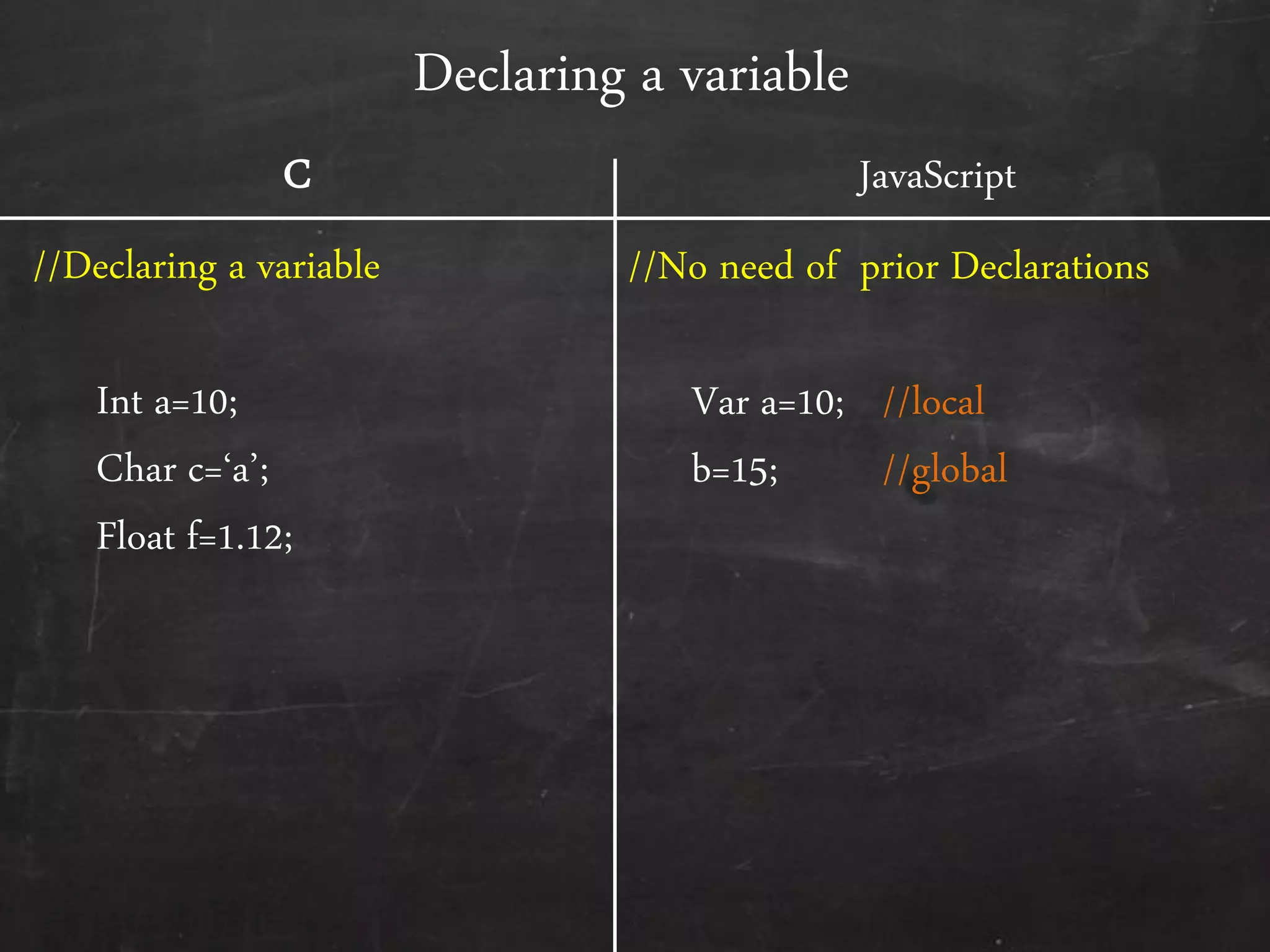
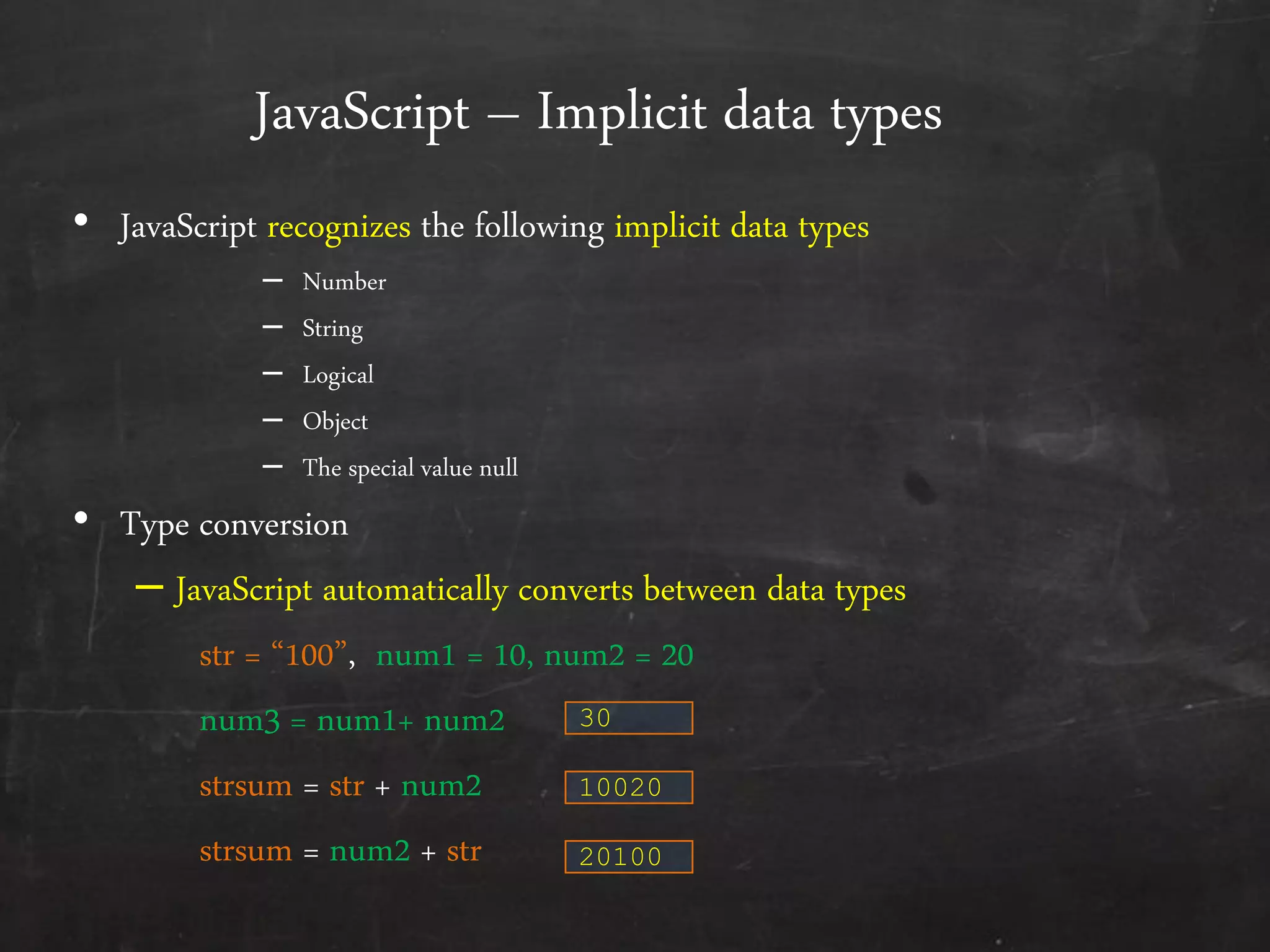
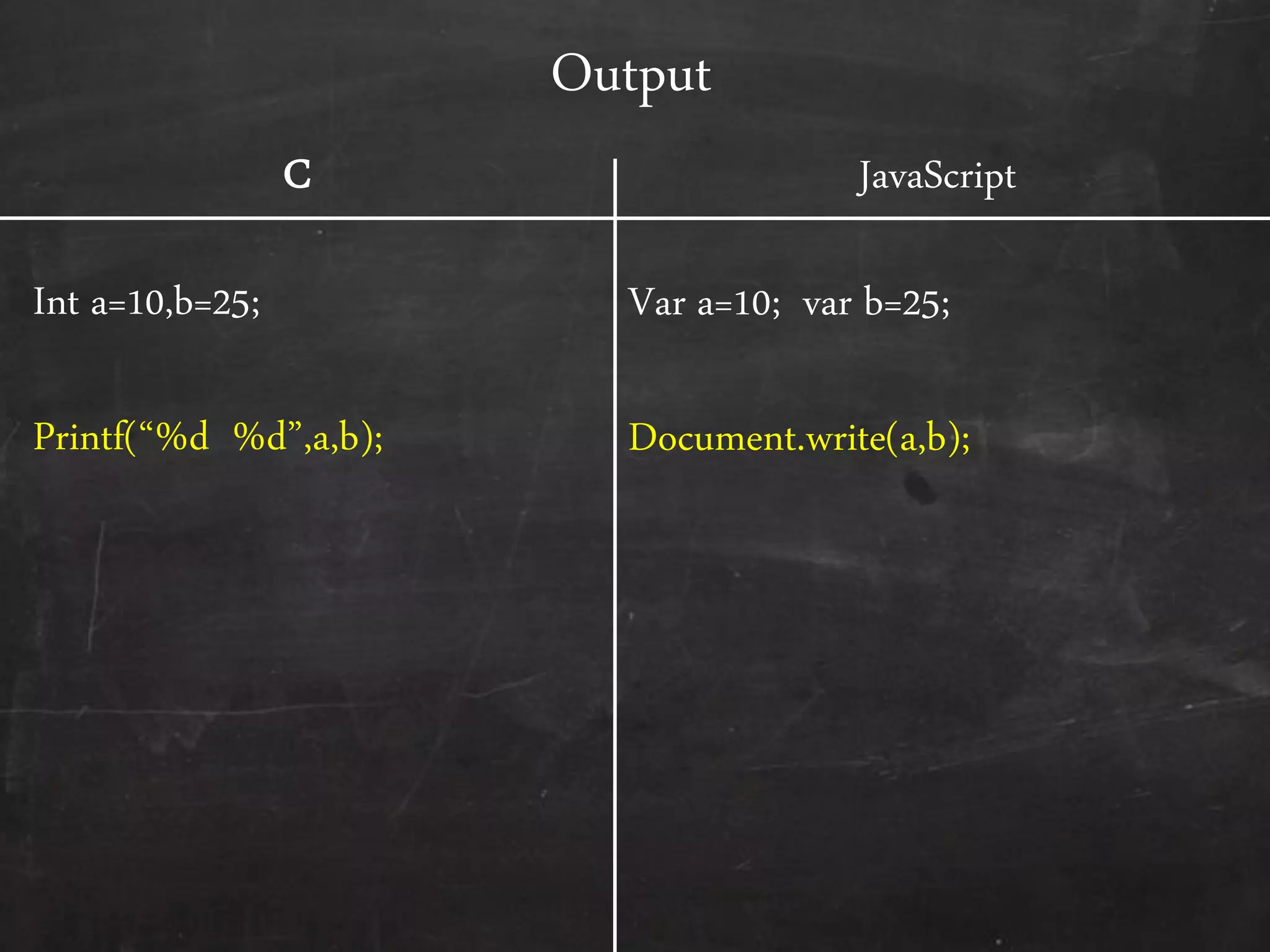
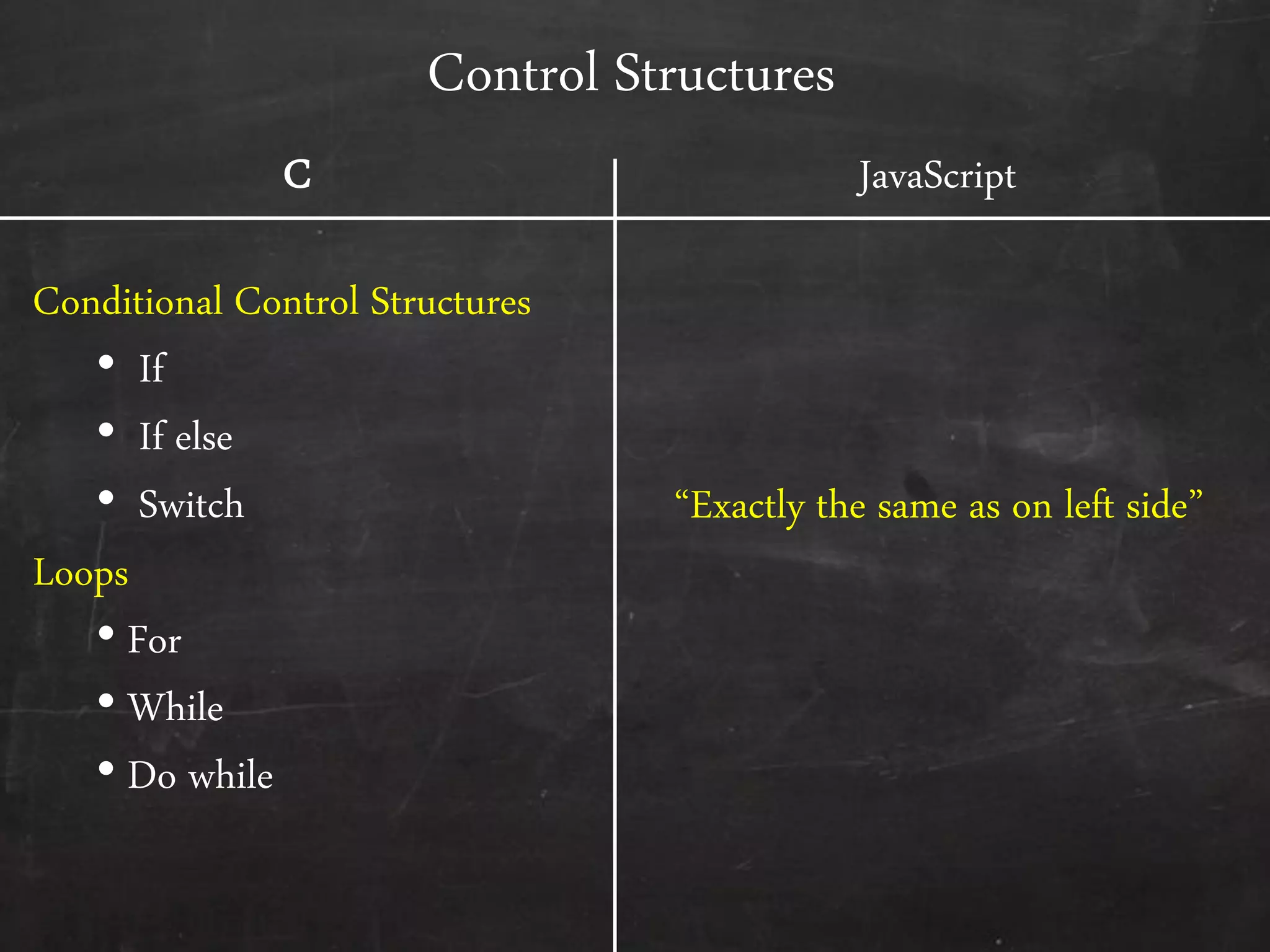
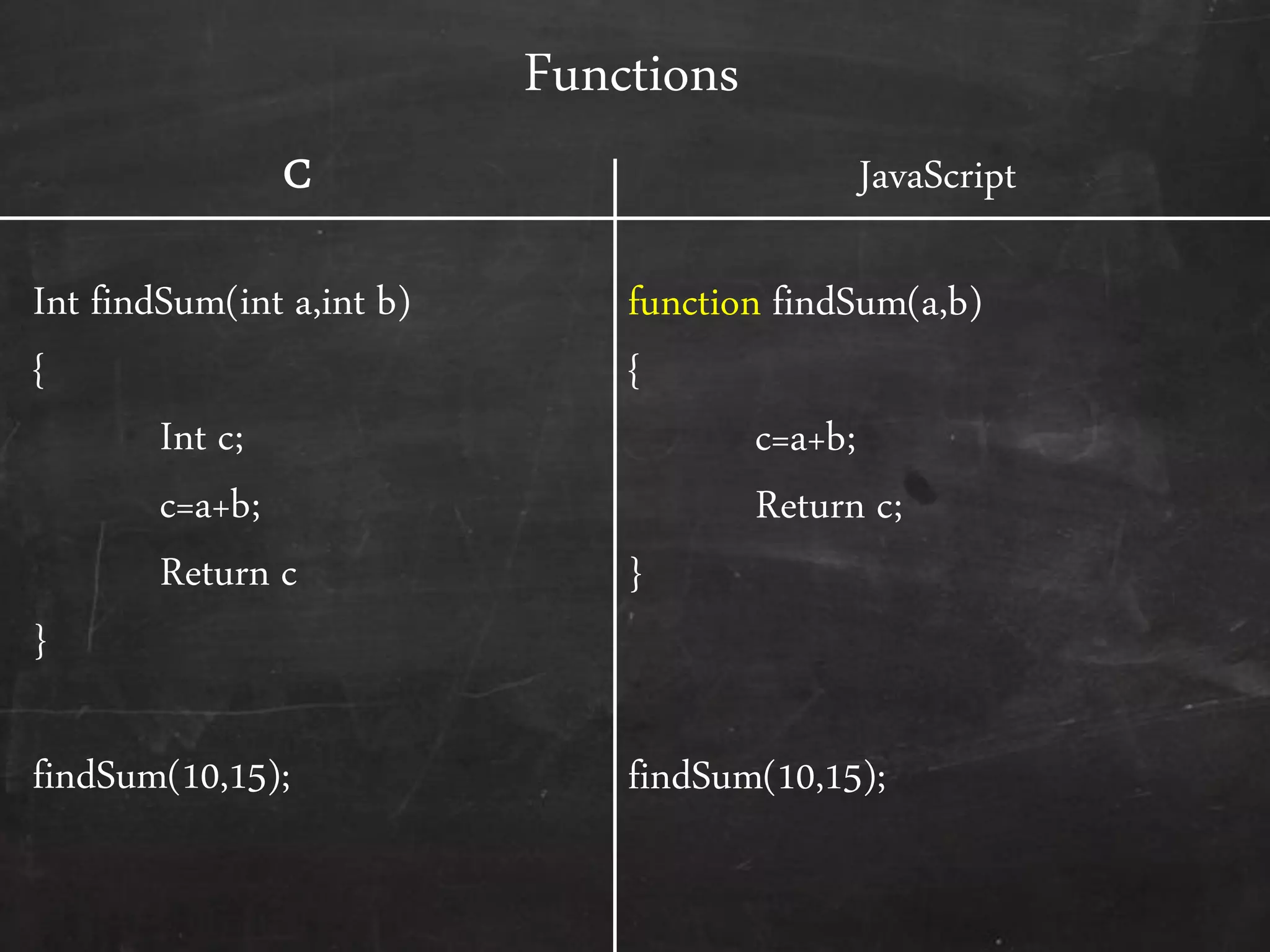
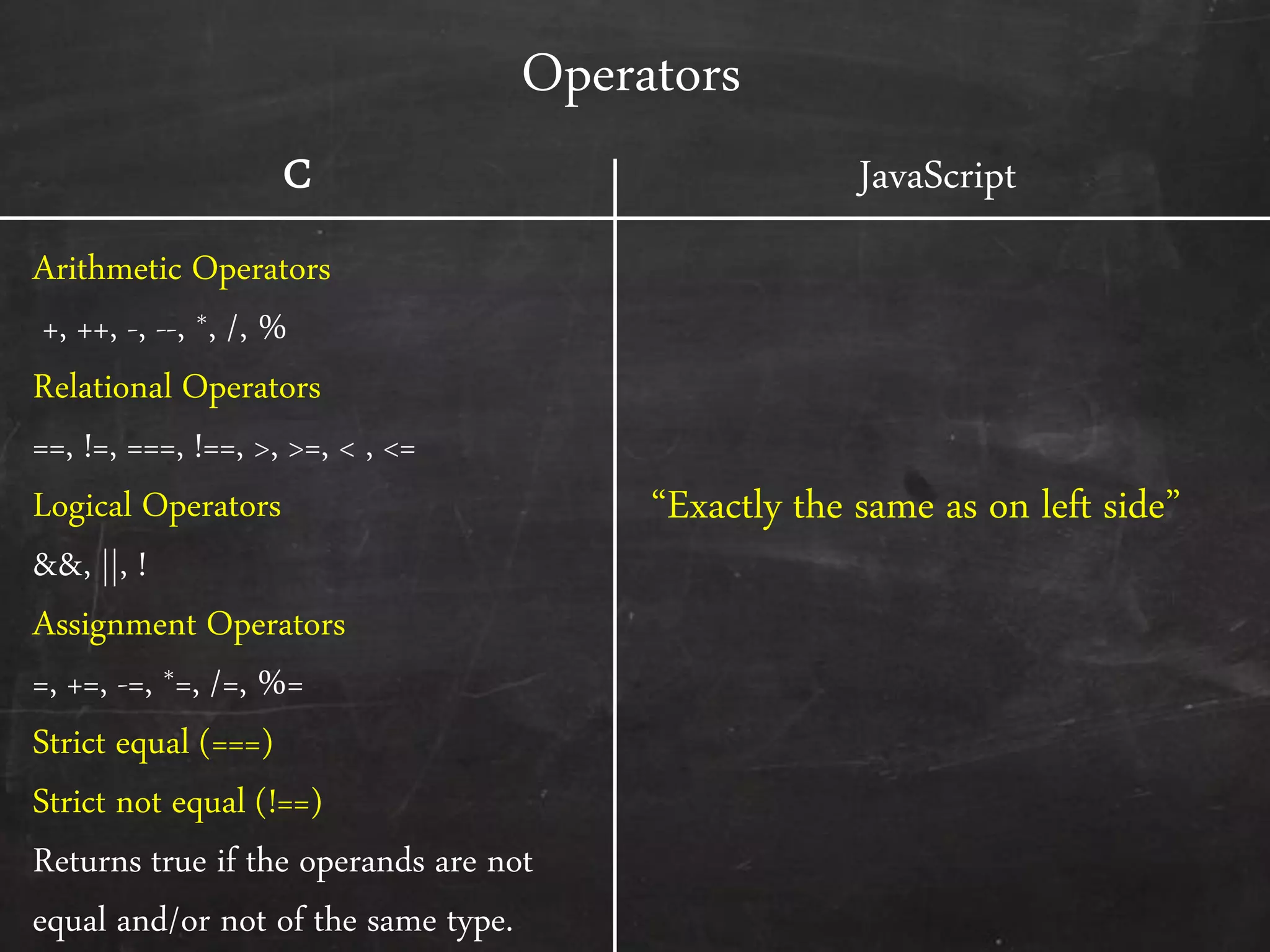
- The document outlines how to start programming in JavaScript using <script> tags, and covers JavaScript syntax including variables, data types, control structures, functions, operators, and built-in methods like alert().









![Dialog boxes (Window Object methods)
• Alert dialog box - alert(message)
– Takes in a string argument and displays an alert box.
• Prompt dialog box - prompt(message,[inputDefault])
– Displays a message and a data entry field
• Confirm dialog box - confirm(message )
– Serves as a technique for confirming user actions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascript-140329030011-phpapp02/75/Javascript-17-2048.jpg)


