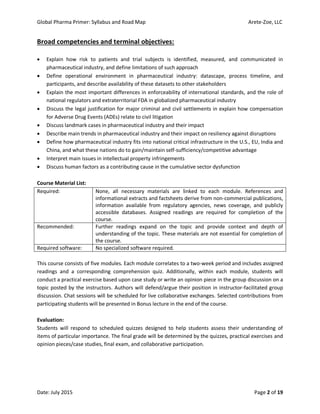
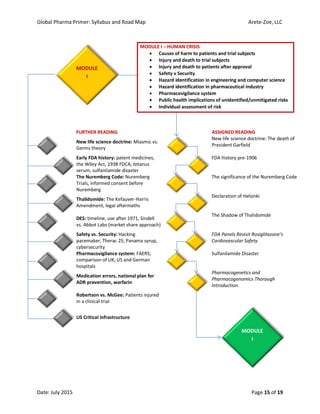
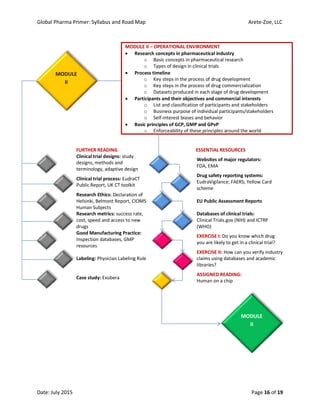
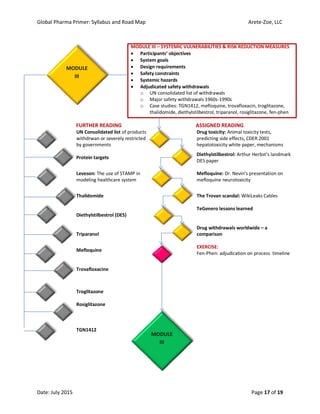
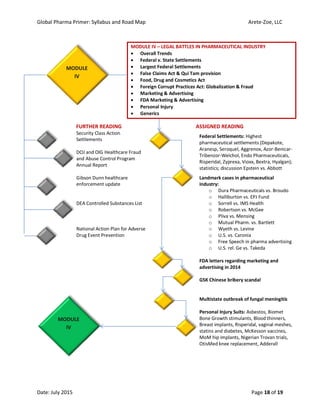
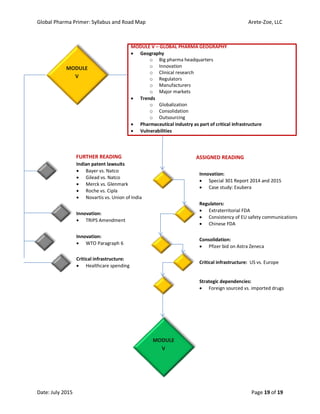
The document outlines the syllabus for the 'Global Pharma Primer' course, which lasts 10 weeks and covers critical aspects of the pharmaceutical industry, including drug development, regulatory policies, and public health implications. It includes broad competencies, specific learning objectives for each module, and evaluation methods such as quizzes and practical exercises. The course aims to enhance understanding of systemic vulnerabilities and risk communication in the pharmaceutical sector.