Dic Dr Umashankar
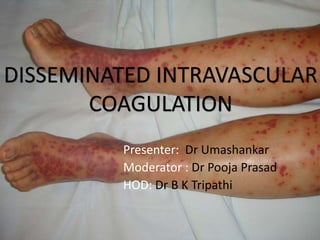
- 1. Presenter: Dr Umashankar Moderator : Dr Pooja Prasad HOD: Dr B K Tripathi DISSEMINATED INTRAVASCULAR COAGULATION
- 2. Objectives • Physiology of hemostasis • Understanding the pathophysiology of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) • Laboratory tests and diagnostic scoring • Treatment
- 3. Hemostasis 3 Major systems involved • Vessel wall – Endothelium – Extracellular matrix/ BM (type 4 collagen + other proteins) • Platelets • Coagulation cascade – Coagulation factors (proteins) • Active and inactive forms (zymogens)
- 4. Endothelial cells • ANTI- THROMBOTICS •PGI 2 •NO •ADP •Heparin like molecule •t-PA •Thrombomodulin •Protein C & S PRO-THROMBOTIC •vWF •Tissue factor •PAI
- 10. DIC-Definition ‘Acquired syndrome characterized by the intravascular activation of coagulation without a specific localization and arising from different causes. It can originate from and cause damage to the microvasculature, which if sufficiently severe, can produce organ dysfunction’. Taylor FBJ, Toh CH, Hoots WK, et al: Towards de nition, clinical and laboratory criteria, and a scoring system for disseminated intravascular coagulation. Thromb Haemost 86:1327, 2001.
- 11. • Sepsis • Trauma and tissue injury • Vascular disorders • Obstetrical complications • Cancer • Liver disorders • Immunological disorders • Drugs • Envenomation Causes of DIC
- 12. Pathophysiology
- 13. Tissue Factor–Factor VII(a) Pathway • Induced by cytokines, CRP, and advanced glycosylation end products. • Inducible TF monocytes and macrophages DIC associated with sepsis, cancer, or coronary disease • Cytokines - TNF-α, and IL-1 vascular endothelial cells • IL-6 is the dominant mediator of TF expression by mononuclear cells
- 14. The Intrinsic Pathway • Negatively charged substances- phospholipids, polyphosphates, and GAG • Meningococcal septicemia negative correlation with factor XII levels increased consumption • Does not directly contribute to DIC play important roles in propagating it by proinflammatory mechanisms related to vascular permeability, and enhancement of fibrinolysis
- 15. Cross-Talk Among Coagulation Proteases Results in Proinflammatory Effects • Interact with specific cell receptors and trigger proinflammatory mediators • Factor Xa – increases the production of monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1), IL-6, and IL-8 and upregulates adhesion proteins that tether neutrophils to the cell surface important driver of coagulation in DIC. • Thrombin induces the release of IL-8 and IL-6 from endothelial cells, fibroblasts and mononuclear cells.
- 16. Endogenous Anticoagulant Pathways in Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
- 17. • Fibrinolysis is activated initial activation of plasminogen activation, followed by marked impairment caused by the release of PAI-1 • PAI-1, the principal inhibitor of this system causing a net procoagulant situation. • Cytokine-mediated activation of vascular endothelial cells TNF-α and Il-1 causes t-PA and increased PAI-1 production. • Endotoxin and TNF-α stimulates PAI-1 production in the livers, kidneys, lungs, and adrenal glands . Fibrinolysis
- 19. Clinical Types of DIC Wada et al. Journal of Intensive Care 2014
- 20. Acute vs Chronic DIC • If activation occurs slowly – Thrombosis predominates • Trousseau’s syndrome, Kassabach Merit syndrome • Platelet levels are low along with raised levels of FDP and D-Dimer. • If reaction is rapid – Initially thrombosis followed by bleeding – most commonly seen form in clinical practice – It is a hematological emergency
- 21. Laboratory diagnosis • Platelet count • D-Dimer • PT • PTT • Fibrinogen • AT, Protein C, Protein S • PS for Schistocytes Kaneko T, Wada H. Diagnostic criteria and laboratory tests for disseminated intravascular coagulation. J Clin Exp Hematop. 2011;51(2):67-76
- 22. Platelet count • Typically, moderate-to-severe thrombocytopenia is present in DIC. • Thrombocytopenia is seen in as many as 98% of DIC patients, and the platelet count can dip below 50 × 109/L in 50%. • A trend toward decreasing platelet counts or a grossly reduced absolute platelet count is a sensitive (though not specific) indicator of DIC Kaneko T, Wada H. Diagnostic criteria and laboratory tests for disseminated intravascular coagulation. J Clin Exp Hematop. 2011;51(2):67-76
- 23. PT and aPTT • Prolonged in about 50–60% of cases • Mainly attributed due to Increased consumption of coagulation factors Impaired synthesis Abnormal liver function Vitamin K deficiency Loss of the coagulation proteins due to massive bleeding Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of disseminated intravascular coagulation. British Journal of Haematology0 2009; 145, 24–33
- 24. Fibrin degradation products and D- dimers • Measures fibrinolytic activity • Assays of FDPs do not discriminate between degradation products of cross-linked fibrin and fibrinogen degradation, which limits their specificity • New assays aimed at the detection of neo-antigens on degraded cross linked fibrin D-dimer Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of disseminated intravascular coagulation. British Journal of Haematology0 2009; 145, 24–33
- 25. Contd.. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of disseminated intravascular coagulation. British Journal of Haematology0 2009; 145, 24–33 Causes of elevated FDP and D-Dimers Acute coronary syndrome CVA Peripheral artery disease Malignancy Atrial fibrillation Congestive heart failure Pregnancy and puerperium preeclampsia Infections Acute venous thromboembolism Sickle cell disease
- 26. Soluble fibrin monomer (SF) • Offer theoretical advantages in DIC in reflecting thrombin action on fibrinogen. • As SF is only generated intravascularly, it should therefore not be influenced by extravascular fibrin formation as caused by local inflammation or trauma. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of disseminated intravascular coagulation. British Journal of Haematology0 2009; 145, 24–33
- 27. Fibrinogen • Useful tool for the diagnosis of DIC • Fibrinogen acts as an acute-phase reactant and despite ongoing consumption, plasma levels can remain well within the normal range for a long period of time. • Sequential measurements of fibrinogen might be more useful and provide diagnostic clues. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of disseminated intravascular coagulation. British Journal of Haematology0 2009; 145, 24–33
- 28. Blood film • Fragmented red blood cells rarely constitute >10% in DIC patients • When they are seen in increased numbers, other potential diagnoses thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) and other thrombotic microangiopathy Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of disseminated intravascular coagulation. British Journal of Haematology, 2009; 145, 24–33
- 29. Other markers of hemostasis • The natural anticoagulants antithrombin and protein C are often reduced in DIC • Purpura fulminans develops secondary to profound acquired deficiency of protein S. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of disseminated intravascular coagulation. British Journal of Haematology0 2009; 145, 24–33
- 30. Laboratory tests for DIC Abnormality in DIC type of DIC Other cause for the abnormality PT Prolongation NS, BL, MB Liver dysfunction, vitamin K deficiency FDP, D- dimer Elevation BL, NS, OF Venous thromboembolism, operation Fibrinogen Reduction BL, MB Liver dysfunction Platelet count Reduction OF, MB, BL, NS Bone marrow disorders, drugs Wada et al. Diagnosis and treatment of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) according to four DIC guidelines. Journal of Intensive Care 2014, 2:15 OF= Organ Failure; BL= Bleeding; MB= Massive bleeding; NS= Non Symptomatic
- 31. Laboratory tests for DIC Abnormality in DIC type of DIC Other cause for the abnormality TM Elevation OF Renal dysfunction, organ failure ADAM TS13 Reduction OF Liver dysfunction, thrombotic microangiopathy APTT Biphasic waveform OF Infection AT/PC Reduction OF, MB Liver dysfunction, capillary leak syndrome Wada et al. Journal of Intensive Care 2014, 2:15
- 32. Diagnostic criteria • The SCC/ISTH divided the state of DIC into overt DIC and non overt-DIC • The JMHW DIC diagnostic and ISTH overt-DIC diagnostic criteria are both applicable for Overt-DIC, while ISTH non-overt DIC diagnostic criteria and JAAM criteria for acute phase DIC apply to non-overt DIC. Kaneko T, Wada H. Diagnostic criteria and laboratory tests for disseminated intravascular coagulation. J Clin Exp Hematop. 2011;51(2):67-76
- 33. A comparision among the ISTH criteria, and JAAM DIC diagnostic criteria ISTH criteria JAAM criteria Underlying disease marker 0 points (essential) 0 points Clinical symptoms 0 points SIRS score ≥ 3 = 1 point Platelet counts 50 -100=1 point < 50= 2 points 80 -120 or > 30% reduction =1 point < 80 but > 50% reduction= 3 point Fibrin relates FDP, D dimer moderate increase = 2 points strong increase = 3 points FDP 10 - 25=1 point >25= 3 points Fibrinogen < 1g/L =1 point None PT prolonged PT 3- 6 s = 1 point > 6 s= 2 points PT ratio > 1.2 =1 point Diagnosis of DIC ≥ 5 points ≥ 4 points Kaneko T, Wada H. Diagnostic criteria and laboratory tests for disseminated intravascular coagulation. J Clin Exp Hematop. 2011;51(2):67-76
- 34. Thrombelastography (TEG) • A viscoelastic point of care hemostatic assay • Provides a graphic presentation of clot formation & lysis Johansson PI, et al. Scan J Trauma, Resus, & Emerg Med 2009; 17:45.
- 35. Hemostasis Monitoring with the TEG System • Rate of clot formation • Strength of clot • Stability of clot Hemostatic status Measures entire clotting process Measures: ∆Clot strength / time
- 36. TEG Method • whole blood incubated @ 37o C in a heated, kaolin-containing cup • Pin is suspended into cup and connected to a detector system (torsion wire) • Cup is oscillated continously • Fibrin forms between the cup and pin • Formation of fibrin results in transmitted rotation from the cup to the pin • Tracing is generated as a result of pin’s movement • Pattern & duration of different aspects of tracing provides information on the clotting and lysis process (after being collected in Citrate – if delay in running > 3 min)
- 37. TEG Tracing and Clotting Process Time (min) Initiation Platelet plug forms Fibrin strands form Clot grows Maximum clot forms Clot degradation takes over Clot dissolved Damage repaired Time
- 38. Graphical Representation Reaction time, first significant clot formation Achievement of certain clot firmness Maximum amplitude – maximum strength of clot Kinetics of clot development LY30 Percent lysis 30 minutes after MA
- 39. TEG Parameters: R Reaction time (4 – 8 min) FFP rVIIa PCC LMWH LMWH + ASA FFP + Platelets
- 40. TEG Parameters: K and angle () Rate of clot growth R Clot time IIa generation Fibrin formation Coagulation pathways R Clot time IIa generation Fibrin formation Coagulation pathways Parameter Hemostatic Activity Hemostatic Component Hypo- coagulable Hyper- coagulable R (min) R (min) R (min) R (min) K (min) (deg) K (min) (deg) K (min) (deg) K (min) (deg) Clot rate Fibrin mesh Fibrinplatelet Coag pathways platelets K Clot rate Fibrin mesh Fibrinplatelet Coag pathways platelets K Dysfunction 4-8 min : Angle (47 - 74°) K: Clot kinetics (0 - 4 min) FFP Cryoprecipitate
- 41. TEG Parameters: MA Maximum clot strength R Clot time IIa generation Fibrin formation Coagulation pathways R Clot time IIa generation Fibrin formation Coagulation pathways Parameter Hemostatic Activity Hemostatic Component Hypo- coagulable Hyper- coagulable R (min) R (min) R (min) R (min) K (min) (deg) K (min) (deg) K (min) (deg) K (min) (deg) MA MA MA MA Clot rate Fibrin X-linking Fibrinplatelet Coag pathways platelets K Clot rate Fibrin X-linking Fibrinplatelet Coag pathways platelets K Maximum clot strength Platelet – fibrin interactions Platelets (~80%) Fibrin (~20%) MA Maximum clot strength Platelet – fibrin interactions Platelets (~80%) Fibrin (~20%) MA Dysfunction Maximum amplitude (54 – 72 mm) Platelets ASA
- 42. TEG Parameters: LY30 Clot Breakdown R Clot time IIa generation Fibrin formation Coagulation pathways R Clot time IIa generation Fibrin formation Coagulation pathways Parameter Hemostatic Activity Hemostatic Component Hypo- coagulable Hyper- coagulable R (min) R (min) R (min) R (min) K (min) (deg) K (min) (deg) K (min) (deg) K (min) (deg) MA MA MA MA Clot stability Reduction in clot strength Fibrinolysis Clot stability Reduction in clot strength Fibrinolysis Clot rate Fibrin X-linking Fibrinplatelet Coag pathways platelets K Clot rate Fibrin X-linking Fibrinplatelet Coag pathways platelets K Maximum clot strength Platelet – fibrin(ogen) interactions Platelets (~80%) Fibrin(ogen (~20%) MA Maximum clot strength Platelet – fibrin(ogen) interactions Platelets (~80%) Fibrin(ogen (~20%) MA 30 min LY30 EPL 30 min LY30 EPL LY30 > 7.5% EPL > 15% N/A LY30 > 7.5% EPL > 15% N/A Dysfunction Lysis at 30 minutes (0 – 7.5%) TXA ACA
- 44. Treatment • The cornerstone of DIC treatment is the treatment of the underlying condition -- Administration of antibiotics or surgical drainage. • Some cases require additional supportive treatment, specifically aimed at the abnormality in the coagulation system. Wada H, Thachil Guidance for diagnosis and treatment of disseminated intravascular coagulation from harmonization of the recommendations from three guidelines. J Thromb Haemost 2013; 11: 761–7.
- 45. Platelets • The transfusion of platelets is recommended in DIC patients a) with active bleeding and a platelet count of <50 thousand b) high risk of bleeding and a platelet count of <20 thousand c) patients requiring an invasive procedure Wada H, Thachil Guidance for diagnosis and treatment of disseminated intravascular coagulation from harmonization of the recommendations from three guidelines. J Thromb Haemost 2013; 11: 761–7.
- 46. Role of FFP& Coagulation Factors • The administration of FFP may be useful in a) Patients with active bleeding with either prolonged PT/APTT (>1.5 times normal) b) decreased fibrinogen (<1.5 g /dL ). c) Patients requiring an invasive procedure • Dose : 15ml/kg • Disadvantage : volume overload can worsen pulmonary edema. Wada H, Thachil. J Thromb Haemost 2013; 11: 761–7.
- 47. Contd.. • The administration of fibrinogen concentrate or cryoprecipitate may be recommended in actively bleeding patients with persisting severe hypofibrinogenemia (<1.5 g /L ) despite FFP replacement • 4 units of FFP= 2 units of cryoprecipitate pools= 3g fibrinogen concentrate 1 g/L • Prothrombin complex concentrate (PCC) may be considered in actively bleeding patients if FFP transfusion is not possible. Wada H, Thachil Guidance for diagnosis and treatment of disseminated intravascular coagulation from harmonization of the recommendations from three guidelines. J Thromb Haemost 2013; 11: 761–7.
- 48. Anticoagulants • Heparin therapy in patients with DIC remains controversial. • Partly inhibit the activation of coagulation in DIC. • A large trial in patients with severe sepsis showed a slight benefit of low- dose heparin on 28-day mortality in patients with severe sepsis and no major safety concerns. • There is general consensus that administration of heparin is beneficial in some categories of DIC such as 1. metastatic carcinomas, 2. purpura fulminans, 3. aortic aneurysm 4. acute DIC when intensive blood component replacement fails to improve excessive bleeding 5. when thrombosis threatens to cause irreversible tissue injury (e.g., acute cortical necrosis of the kidney or digital gangrene).
- 49. Anticoagulants – Guidelines • Therapeutic doses of heparin should be considered in cases of DIC where thrombosis predominates • The use of low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) is preferred to the use of unfractionated heparin (UFH) in these cases • Prophylaxis for VTE with prophylactic doses of UFH or LMWH is recommended in critically ill, non-bleeding patients with DIC Wada H, Thachil Guidance for diagnosis and treatment of disseminated intravascular coagulation from harmonization of the recommendations from three guidelines. J Thromb Haemost 2013; 11: 761–7.
- 50. Fondaparinux • Prophylaxis of DVT after orthopedic surgeries • Little evidence in critically ill patients Gabexatane mesilate and Nafamostat • Synthetic protease inhibitor • Evaluated and used in Japan • mild anticoagulant and antifibrinolytic effects • used in patients with the bleeding, massive bleeding, and non-symptomatic types of DIC Wada H, Thachil Guidance for diagnosis and treatment of disseminated intravascular coagulation from harmonization of the recommendations from three guidelines. J Thromb Haemost 2013; 11: 761–7.
- 51. Anticoagulant factor concentrates Antithrombin The administration of AT may be considered in DIC patients Wada H, Thachil Guidance for diagnosis and treatment of disseminated intravascular coagulation from harmonization of the recommendations from three guidelines. J Thromb Haemost 2013; 11: 761–7.
- 52. Anticoagulant factor concentrates activated protein C
- 54. Thrombomodulin Guidelines- can be used in DIC
- 55. Antifibrinolytic treatment • In general, patients with DIC should not be treated with antifibrinolytic agents • Patients with DIC that is characterized by a primary hyperfibrinolytic state and who present with severe bleeding could be treated with lysine analogues, such as tranexamic acid (e.g. 1 g every 8 h) Wada H, Thachil Guidance for diagnosis and treatment of disseminated intravascular coagulation from harmonization of the recommendations from three guidelines. J Thromb Haemost 2013; 11: 761–7.
- 56. Summary • DIC is a not a disease itself but a outcome of varied etiology • Can be a varied spectrum from asymptomatic to massive bleeding type • Diagnosis should be made with high suspicion • Treatment should be individualized and tailor made