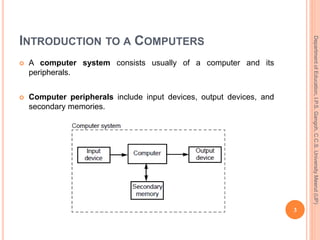
The document discusses the history and evolution of computers through five generations. The first generation used vacuum tubes and magnetic drums, were enormous in size, and relied on machine language. The second generation used transistors which made them smaller and more reliable. The third generation saw the development of integrated circuits which further miniaturized computers. The fourth generation is defined by the invention of microprocessors which placed all computer components on a single chip. The fifth generation still being developed aims to develop artificial intelligence capabilities.