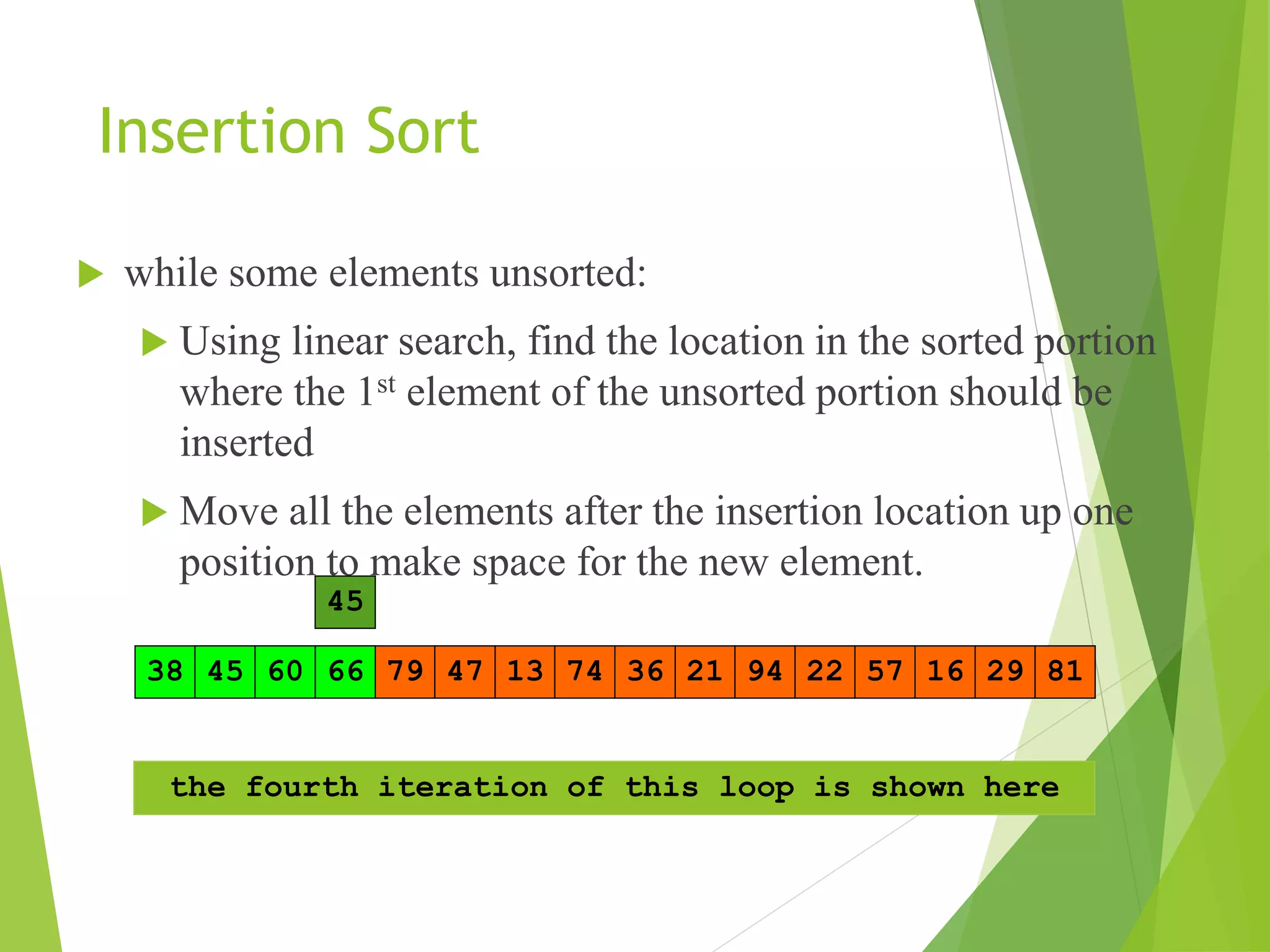
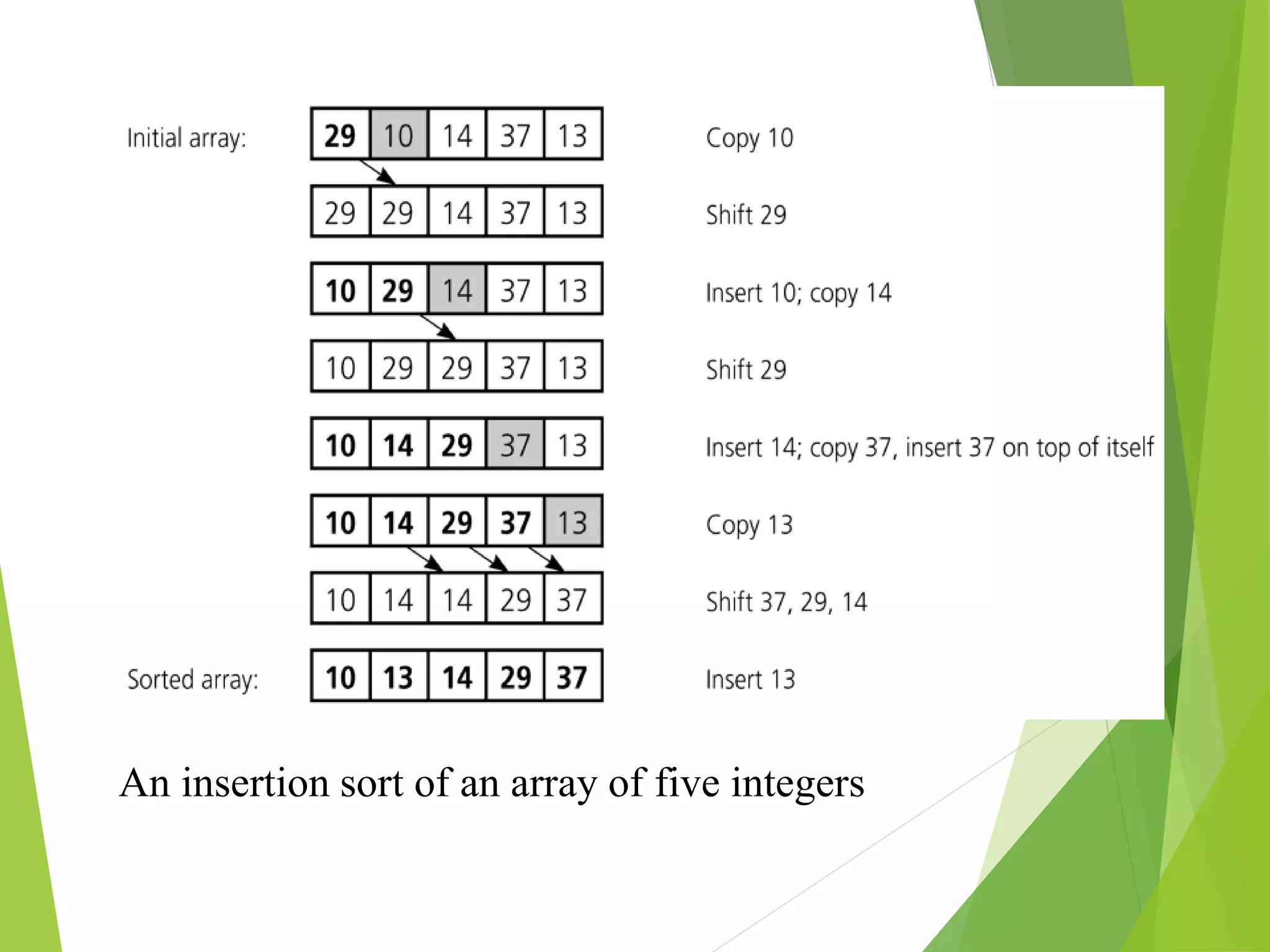
This document introduces algorithms and discusses their role in computing. It defines an algorithm as a well-specified computational procedure that takes inputs and produces outputs. Algorithms must be correct, producing the right output for each input, and efficient in terms of time and memory usage. The document provides examples of sorting algorithms like insertion sort and discusses analyzing the running time of algorithms.




![A Simple Algorithm
INPUT: a sequence of n numbers
T is an array of n elements
T[1], T[2], …, T[n]
OUTPUT: the smallest number among them
Performance of this algorithm is a function of n
5
min = T[1]
for i = 2 to n do
{
if T[i] < min
min = T[i]
}
Output min](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uniti-230818033649-9fad6675/75/UNIT-I-ppt-5-2048.jpg)